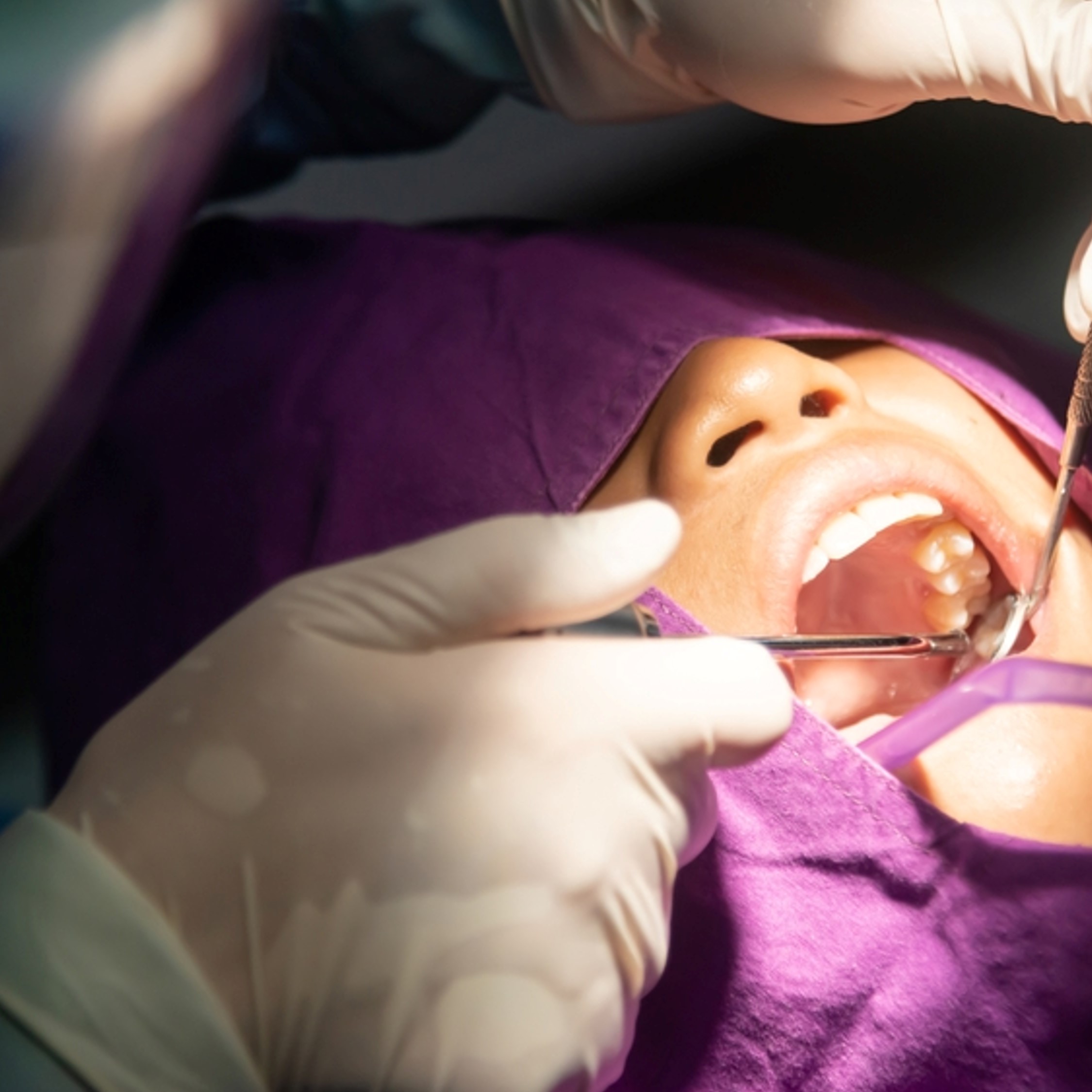
Risk factors for bleeding after oral surgery in patients who continued using oral anticoagulant therapy
Background
The authors assessed the incidence of postoperative bleeding in patients who were highly anticoagulated and in patients who underwent extensive oral surgical procedures and who continued using oral anticoagulant therapy.
Methods
The authors placed 125 patients receiving anticoagulant therapy into 1 of 3 groups. Group A had 54 patients who were highly anticoagulated (international normalized ratio [INR] ≥ 3.5) in whom up to 3 teeth were extracted. Group B had 60 patients with INR 2.0 to less than 3.5 in whom higher-risk dentoalveolar surgery (extraction of more than 3 teeth or other oral surgery procedure involving raising a mucoperiosteal flap, osteotomy, or biopsy) was performed. Group C had 11 patients whose INR values were 3.5 or higher and who required higher-risk dentoalveolar surgery. Eighty-five healthy participants who underwent surgical procedures similar to those performed in group A and group B were the control group.
Results
Two patients in group A (3.7%), 3 in group B (5.0%), and 2 in group C (18.2%) experienced postoperative bleeding. In the control group, a single bleeding event (1.2%) occurred. All cases of hemorrhage were mild and easily controlled using local hemostatic measures.
Conclusions
Dental extractions in patients who are highly anticoagulated (INR, 3.5-4.2), as well as more extensive oral surgical procedures in patients who are therapeutically anticoagulated, can be performed safely without interruption or modification of the therapy.
Practical Implications
Tooth extractions and even more extensive surgical procedures can be performed safely in patients who continue using anticoagulant therapy if proper local hemostatic measures are used and if no other coagulopathies are present.
 Related articles
Related articles
Guide treatment planning by analyzing the rates of dental implant failure to determine associated risk factors.
Endodontics 27 September 2023
What are the risk factors, signs and symptoms of vertical root fractures
A vertical root fracture (VRF) is defined as a longitudinal fracture along the axis of the root, which may appear as incomplete (involving only part of the root) or complete (extending from one side...
Pediatric dentistry 26 July 2023
Predicting dental caries in young children in primary health care settings
The objective of this study was to develop a parent-completed, easy-to-score, short, accurate caries risk tool for screening in primary health care settings to identify children at increased risk for...
Pediatric dentistry 16 May 2023
Microbial indicators of dental health, dysbiosis and early childhood caries
Dental caries lesions are a clinical manifestation of disease, preceded by microbial dysbiosis, which is poorly characterized and thought to be associated with saccharolytic taxa. Here, researchers...
The aim of this study was to evaluate the risk indicators associated with noncavitated and cavitated lesions in preschool children.
 Read more
Read more
With a new name, Tufts Special Care Dental Clinics continues a 50-year mission of treating people with intellectual and developmental disabilities
Ultradent Products, Inc., a leading developer and manufacturer of high-tech dental materials, is announcing the launch of VALO X Colors: new, vibrant finishes for the award-winning VALO X curing...
News 27 October 2025
OrthoFX, a leading innovator of shorter wear time aligner systems, announces AirFlex with new PrecisionFinish Aligners.
News 27 October 2025
Young Innovations Strengthens North American Leadership Team
Young Innovations, a leading global manufacturer and distributor of dental supplies and equipment, is pleased to announce two significant additions to its North American leadership team as part of...
Oral pathology 24 October 2025
Isolation and characterization of dental pulp stem cells from a supernumerary tooth
Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) were primarily derived from the pulp tissues of primary incisors and permanent third molar teeth, whereas no report to our knowledge has yet been documented on deriving...