What are the risk factors, signs and symptoms of vertical root fractures
Lara Figini
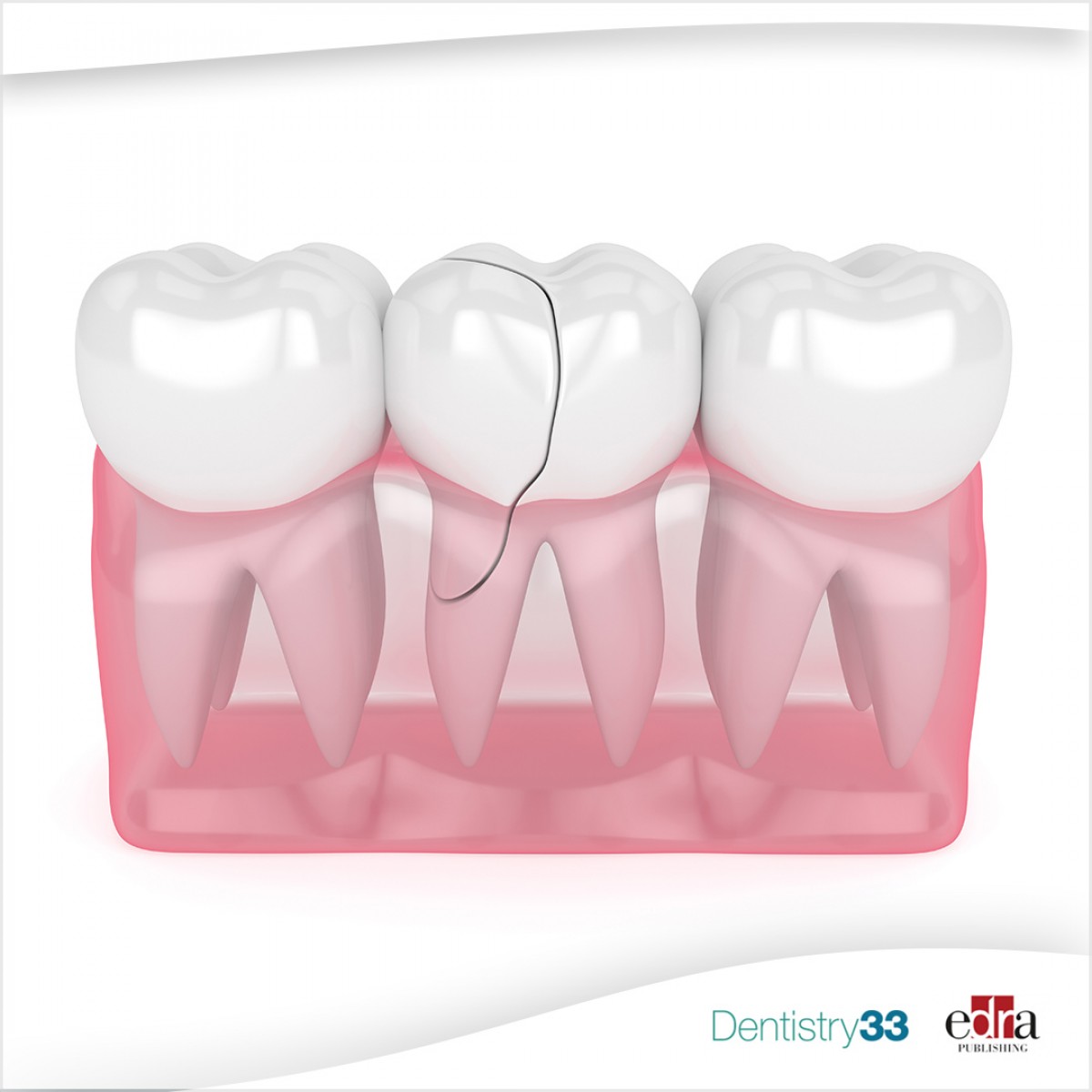
A vertical root fracture (VRF) is defined as a longitudinal fracture along the axis of the root, which may appear as incomplete (involving only part of the root) or complete (extending from one side to the opposite side of the root) .
In advanced stages a VRF may develop as a visible separation of the 2 parts of the root. Without a doubt, VRF is one of the most frustrating events that can occur in dentistry as it usually involves the extraction of the root or affected tooth.
Several studies have reported that VRF is a multifactorial phenomenon and it could be helpful to identify and understand risk factors early (such as loss of coronal tooth substance, pre-existing cracks, changes in the biomechanical properties of dentin and age-related microstructural changes). , root anatomy, tooth position and parafunctions) as well as concomitant risk factors (excessive removal of dentin during root canal preparation and inappropriate insertion of posts, exposure to overly aggressive endodontic disinfectants) associated with the etiology of such fractures.
VRF usually occurs in endodontically treated (ETT) teeth; it has occasionally been observed in vital teeth.
Materials and methods
In a recent systematic review, published in the Journal of Endodontics, the authors identified specific clinical signs or symptoms and potential risk factors associated with the presence of a vertical root fracture (VRF) in endodontically treated teeth (ETT).
Electronic databases (Medline via PubMed, Embase via Ovid, Scopus, and Web of Science) were used by 2 reviewers in October 2022 to track clinical trials in which potential risk factors associated with a VRF were evaluated.
Risk of bias was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale. Odds ratio (OR) meta-analyses were performed separately for different signs or symptoms and risk factors.
Results
Fourteen studies were included in the final meta-analyses, reporting data on 2877 teeth (489 with VRF and 2388 without VRF). The presence of fistulous tracts (OR = 4.87; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.58-15.0), the greater depth of periodontal probing (OR = 13.24; 95% CI, 5.44 -32.22), swelling/abscess (OR = 2.86; 95% CI, 1.74-4.70) and pain on percussion (OR = 1.76; 95% CI, 1.18-2 ,61) were significantly associated with the presence of VRF. None of the risk factors evaluated (gender, tooth type, tooth position, presence of posts, indirect restorations and apical extension of the root canal filling) were significantly associated with the presence of a VRF.
Conclusions
From the data of this review, which must be confirmed in other similar studies and reviews, it can be concluded that there are mainly four clinical manifestations identified as the most significant signs or symptoms of a vertical root fracture (VRF) in endodontically treated teeth (ETT ): fistulous tract, greater probing depth, swelling/abscess and pain on percussion.
None of the risk factors evaluated were significantly associated with vertical root fracture (VRF).
Risk factors for and clinical presentations indicative of vertical root fracture in endodontically treated teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
 Related articles
Related articles
Oral surgery 27 October 2025
The authors assessed the incidence of postoperative bleeding in patients who were highly anticoagulated and in patients who underwent extensive oral surgical procedures and who continued using oral...
Guide treatment planning by analyzing the rates of dental implant failure to determine associated risk factors.
Pediatric dentistry 26 July 2023
Predicting dental caries in young children in primary health care settings
The objective of this study was to develop a parent-completed, easy-to-score, short, accurate caries risk tool for screening in primary health care settings to identify children at increased risk for...
Pediatric dentistry 16 May 2023
Microbial indicators of dental health, dysbiosis and early childhood caries
Dental caries lesions are a clinical manifestation of disease, preceded by microbial dysbiosis, which is poorly characterized and thought to be associated with saccharolytic taxa. Here, researchers...
The aim of this study was to evaluate the risk indicators associated with noncavitated and cavitated lesions in preschool children.
 Read more
Read more
Digital Dentistry 05 December 2025
Artifact-resistant superimposition of digital dental models and cone-beam computed tomography images
Combining the maxillofacial cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) model with its corresponding digital dental model enables an integrated 3-dimensional (3D) representation of skeletal structures,...
Editorials 05 December 2025
Rural dental residency program receives a lifeline from donor organizations
When federal funds to HSDM’s rural residency program went unpaid, a coalition of regional partners stepped up to secure the program’s future.
Products 05 December 2025
VideaHealth, the leading dental AI platform, recently announced the appointment of Austen Asadorian as Chief Revenue Officer. With two decades of experience scaling high-performing organizations,...
News 05 December 2025
VELMENI, a global leader in artificial intelligence (AI) solutions for dental care, and Jazz Imaging, an innovative provider of dental imaging systems, recently announced a strategic partnership...
News 05 December 2025
BIOLASE, the global leader in dental lasers, announced its participation in the 2025 Greater New York Dental Meeting (GNYDM), taking place November 28–December 3 in New York City.