Evaluation of the risk of perforation of the mandibular incisor canal after implantology
Lara Figini
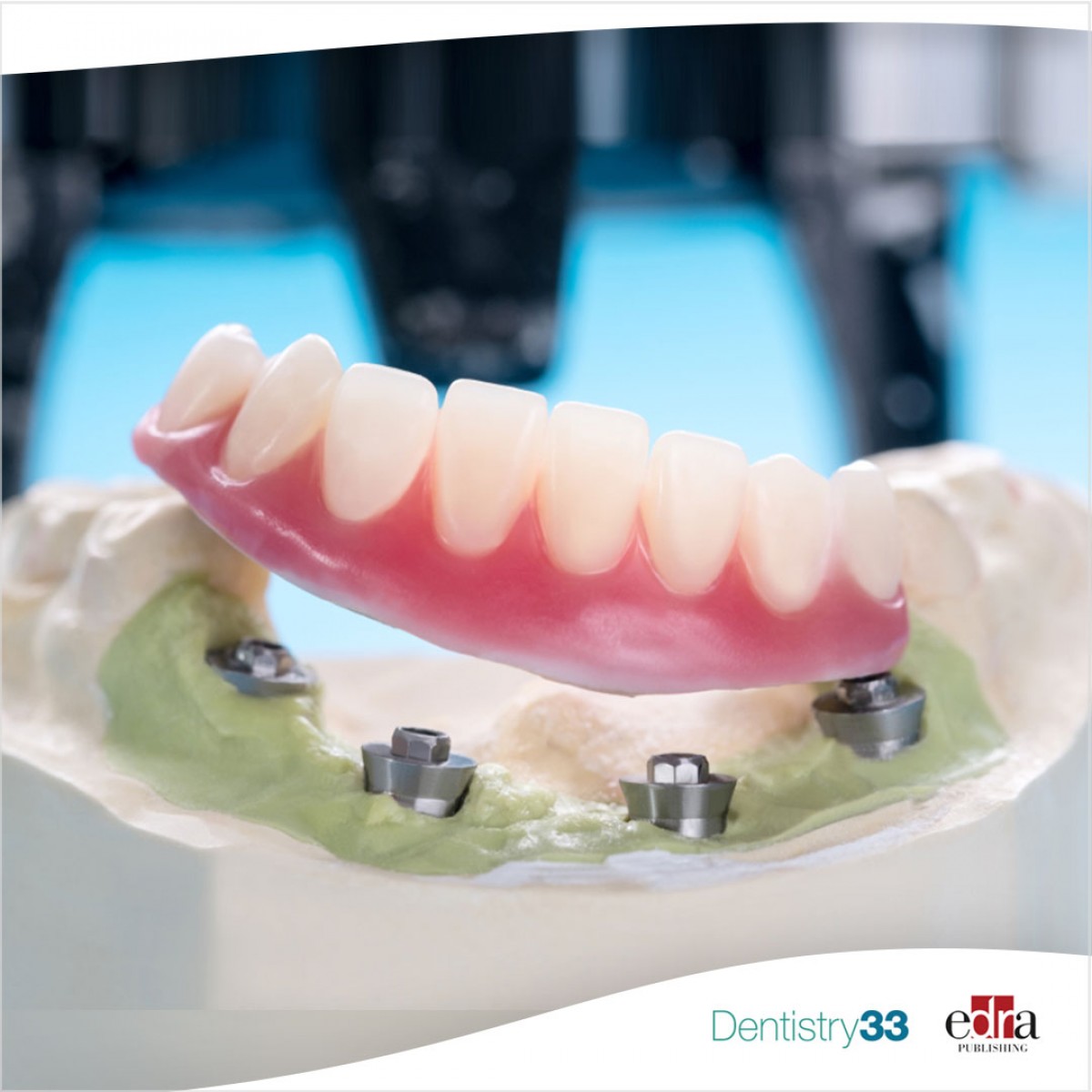
Overdentures supported by two implants, which are generally placed in the canine region, have been widely used in recent years in patients with severe atrophy of the jaw. With this method, high patient satisfaction and a high implant success rate can be achieved at a low cost.
When performing surgical procedures in the mandibular region, the inter-foraminal region is considered a safe area. But recent studies have reported various risks, ranging from minor complications to life-threatening conditions following procedures conducted in this region.
For example, the presence of the mandibular incisor canal (MIC) in the anterior mandibular region requires particular attention in implant surgery, during autogenous bone harvesting, genioplasty and fracture surgery.
However, in cases where the presence of the MIC is not paid attention to, various post-operative complications may occur such as bleeding, edema, sensory disturbances, failure of implant osseointegration and pulp sensitivity.
Due to the rapid spread of implantology, the number of procedures performed in the anterior mandible region is increasing, which in turn increases the importance of detecting vasculature, MIC and lingual concavities in this region.
Materials and methods
In a study published in May 2023 in Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology Oral Radiology, the authors evaluated the risk of perforation of the mandibular incisor canal (MIC) using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) images caused by the placement of implants in the edentulous anterior mandibular region.
Some 1,200 dental implants were placed with virtually 150 suitable CBCT scans. CBCT images of patients between 2012 and 2022 were taken from the CBCT Archive at the Faculty of Dentistry of Katip Celebi University in Izmir (Turkey).
Maxillofacial radiology department images of 150 patients meeting the inclusion criteria were scanned and the data obtained were included in the study. Four implants with the following dimensions were selected: 4x8, 4x10, 4x12, and 4x14 mm.
The position of the implants was determined by an experienced surgeon (IT) by measuring on the orthopantomography (OPG) reconstructed from CBCT images, approximately at least 2 mm from the mandibular base.
The implants identified in the OPG were placed at least 1 mm away from the buccal and lingual cortices in cross section and half bucco-lingually of the crest in axial section. MIC perforation was determined when the implant perforated the canal.
The relationship of different implant sizes with the incidence of MIC mandibular incisor canal perforation and the relationship between ridge height and perforation was evaluated.
Results
A total of 1200 virtual implant applications were performed in 150 patients. MIC was identified in 87% of cases. Perforation with 12- and 14-mm implants was significantly higher than with 8- and 10-mm implants (p < 0.05).
Perforation was found to be statistically significantly greater in alveolar ridge heights ≤20 mm than that obtained with ridge heights >20 mm (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
From the data of this study, it can be concluded that high perforation rates occur in 12- and 14-mm implants and with ridge heights ≤20 mm during implant surgery in the anterior mandibular region edentulous.
For more information: "Risk Assessment of Mandibular Incisive Canal Perforation During Dental Implant Surgery in the Anterior Edentulous Mandible: A Virtual Implant Placement Study Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography."
 Related articles
Related articles
Editorials 07 August 2025
Researchers are developing ‘smart’ implants that would provide a more natural feel while chewing or talking
Implantology 25 July 2025
Background: Cytokine–microbiology–virology monitoring after implant placement may help to develop profiles of variables that can help to explain interaction between the immune system and alveolar...
Patients with a history of head and neck cancer resection require extensive prosthodontic rehabilitation following cancer treatment.
Prosthodontics 30 June 2025
Prosthodontic rehabilitation in the maxillary area using zirconia dental implants: a case report.
Purpose: Zirconia (ZrO2) is a ceramic material with adequate mechanical properties for manufacturing of medical devices. Zirconia stabilized with Y2O3 has the best properties for these applications.
Periodontology 27 June 2025
Bone augmentation procedures to enable dental implant placement are frequently performed in practice.
 Read more
Read more
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 03 October 2025
Dental treatment planning and management for the mouth cancer patient
The need to deliver cancer treatment promptly often requires modification of ideal dental treatment plans.
Editorials 03 October 2025
To help stock the Filling Station, a food pantry open to anyone in our ASOD family who is experiencing food insecurity or needs help making ends meet, Adams School of Dentistry is holding a food...
Products 03 October 2025
From Scan to Smile: Aidite’s EZPRINT-P1 and Rapid 3 Deliver a Complete Digital Workflow
Digital dentistry thrives on precision, efficiency, and integration. Aidite has long been a leader in advancing these principles. With the introduction of the EZPRINT-P1 3D Printer, the company now...
Products 03 October 2025
Dentalhitec Americas recently announced the official U.S. launch of QuickSleeper5, following FDA clearance. Even prior to its American debut, demand from dentists for the QuickSleeper5.
News 03 October 2025
Excel Endodontics, a new specialty dental practice founded by endodontist Dr. Rachel Halpern, is proud to announce its official opening in Marlboro, New Jersey, along with the launch of its new...