Rapid prototyping An innovative technique in dentistry
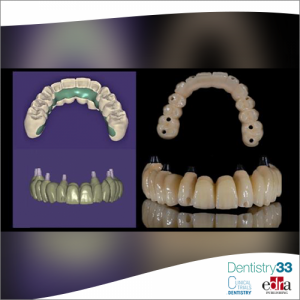
Emergence of advanced digital technology has opened up new perspectives for design and production in the field of dentistry. Rapid prototyping (RP) is a technique to quickly and automatically construct a three-dimensional (3D) model of a part or product using 3D printers or stereolithography machines. RP has various dental applications, such as fabrication of implant surgical guides, zirconia prosthesis and molds for metal castings, maxillofacial prosthesis and frameworks for fixed and removable partial dentures, wax patterns for the dental prosthesis and complete denture. Rapid prototyping presents fascinating opportunities, but the process is difficult as it demands a high level of artistic skill, which means that the dental technicians should be able to work with the models obtained after impression to form a mirror image and achieve good esthetics. This review aims to focus on various RP methods and its application in dentistry.
Introduction
The first method for rapid prototyping was introduced in the 1980s in the field of engineering for the fabrication of a solid model based on a computed file. The innovation of digital technology have revolutionized dentistry, and this digitized medical treatment has now become an integral part of dentistry. Rapid prototyping (RP) techniques, the so-called “generative manufacturing techniques have overcome the drawbacks of subtractive digital techniques.”
After its introduction in the field of ion optics, it became popular in the biomedical field, Weiss stated that this technology is helpful in producing the complex shapes such as cavities present in human anatomy. Small details such as slices, empty spaces, and internal complex geometries (neurovascular canals or sinus) can be easily reproduced by these technologies and also in a short time. Furthermore, according to Wohlers and Wohlers several advances have been made in dental medical area using RP, mainly in surgical planning which improves procedures carried out by the surgeon owing to better visualization and comprehension of the anatomy in complex pathologies of bone or vascular structures.
In dentistry, a trend of saving time applied from conventional dental impression technique transformed into a digital-based RP printed dental plastic model has been widely observed. Traditional impression-based dental model done in the most traditional dental laboratory for dental clinics is a time taking a procedure, digitalization system had created a great impetus on the current time consumed. Thus, a digitalization-based technology in dentistry will be further advanced in a fashion being necessarily state of – the art technique in the modern world.
Four purposes for the three-dimensional (3D) model used for surgical planning:
- Selection of the appropriate intervention observation, surgical embolization, surgery, or radiosurgery)
- Evaluation of the operative risk in surgical cases
- Visualization of the relations between the pathology and the normal state as well as selection of noninvasive surgery and postoperative period, and
- Localization of intraoperative lesions with video images.
Furthermore, RP has proposed various applications in dental fields, such as fabrication of implant surgical guides, zirconia prosthesis and molds for metal castings, and maxillofacial prosthesis and frameworks for fixed and removable partial dentures, wax patterns for the dental prosthesis and complete denture. Prosthesis should be customized precisely when attempting to restore a face with prosthesis; the prosthesis should restore the anatomy as closely as possible. Fabrication of prosthesis by these technologies have reduced reliance on human variables and thus have overcome the limitations of conventional method which requires considerable human intervention and manipulation of materials that may exhibit inherent processing shrinkage/expansion.
Authors: Quadri, Shakeba; Kapoor, Bhumika; Singh, Gaurav; Tewari, Rajendra Kumar
Source: https://journals.lww.com/
 Related articles
Related articles
Dentists have used rapid prototyping (RP) techniques in the fields of oral maxillofacial surgery simulation and implantology
Implantology 08 December 2021
An Innovative Technique for Complete Digital Workflow in Full Arch Implant Rehabilitations
Authors: F. Zingari F. Gallo S. Ghezzi E. Carozzi
The digitalization of the dental field has been recently introduced and has resulted in a significant simplification of clinical procedures. Accuracy of intraoral scanner was improved over the years,...
Restorative dentistry 12 September 2025
Traumatic tooth injuries involve function and aesthetics and cause damage that range from minimal enamel loss to complex fractures involving the pulp tissue and even loss of the tooth crown.
The purpose of restorative dentistry is to restore and maintain health and functional comfort of the natural dentition combined with satisfactory aesthetic appearance.
Oral surgery 15 July 2025
The influence of patients' decisions on treatment planning in restorative dentistry
As part of treatment planning, options are presented to patients by dentists. An informal discussion takes place involving a cost-benefit analysis and a treatment plan is agreed.
 Read more
Read more
Editorials 10 October 2025
With proud smiles and crisp white coats, ninety-three learners from the DDS Class of 2029 and the International Dentist Pathway Class of 2028 marked the start of their dental careers at the UCSF...
Periodontology 10 October 2025
Continuous professional development (CPD) in Periodontology refers to the overall framework of opportunities that facilitate a life-long learning practice, driven by the learner-practitioner and...
TheraBreath, the #1 alcohol-free mouthwash brand in the U.S.*, has introduced a new line of dentist-formulated, clinically tested toothpastes designed to support professional oral care...
News 10 October 2025
New officers and trustees were installed at the Minnesota Dental Association’s Leadership Conference on September 19 in Minneapolis.
News 10 October 2025
Smartee Denti-Technology today announced that Professor Gang Shen, its Chief Scientist and Executive President of TaiKang ByBo Dental, has once again been named to the World’s Top 2% Scientists...