Remineralizing effect of contemporary ion-releasing materials in mineral-depleted dentin
By Lorenzo Breschi and Carlo D’Alessandro
Introduction
The preservation of dental hard tissues represents the main principles of the minimal invasive dentistry. Nowadays, in case of intervention, several bioactive materials — such as glass-ionomer cements, GICs, calcium silicate cements, MTA, resin-modified calcium silicate cements, RMTA — are available to replace tooth substance loss after selective caries removal. Besides, bio-interactive materials also optimize tissue mineral recovery through remineralization properties when used in restorative dentistry.
Despite the increasing interest for these materials, data comparing their remineralizing abilities under conditions similar to the clinical ones, are still insufficient and inconsistent.
In this regard, Maciel Pires et al. have conducted an in vitro study to evaluate the ability of current ion-releasing materials to remineralize bacteria-driven artificial caries lesions.
Materials and methods
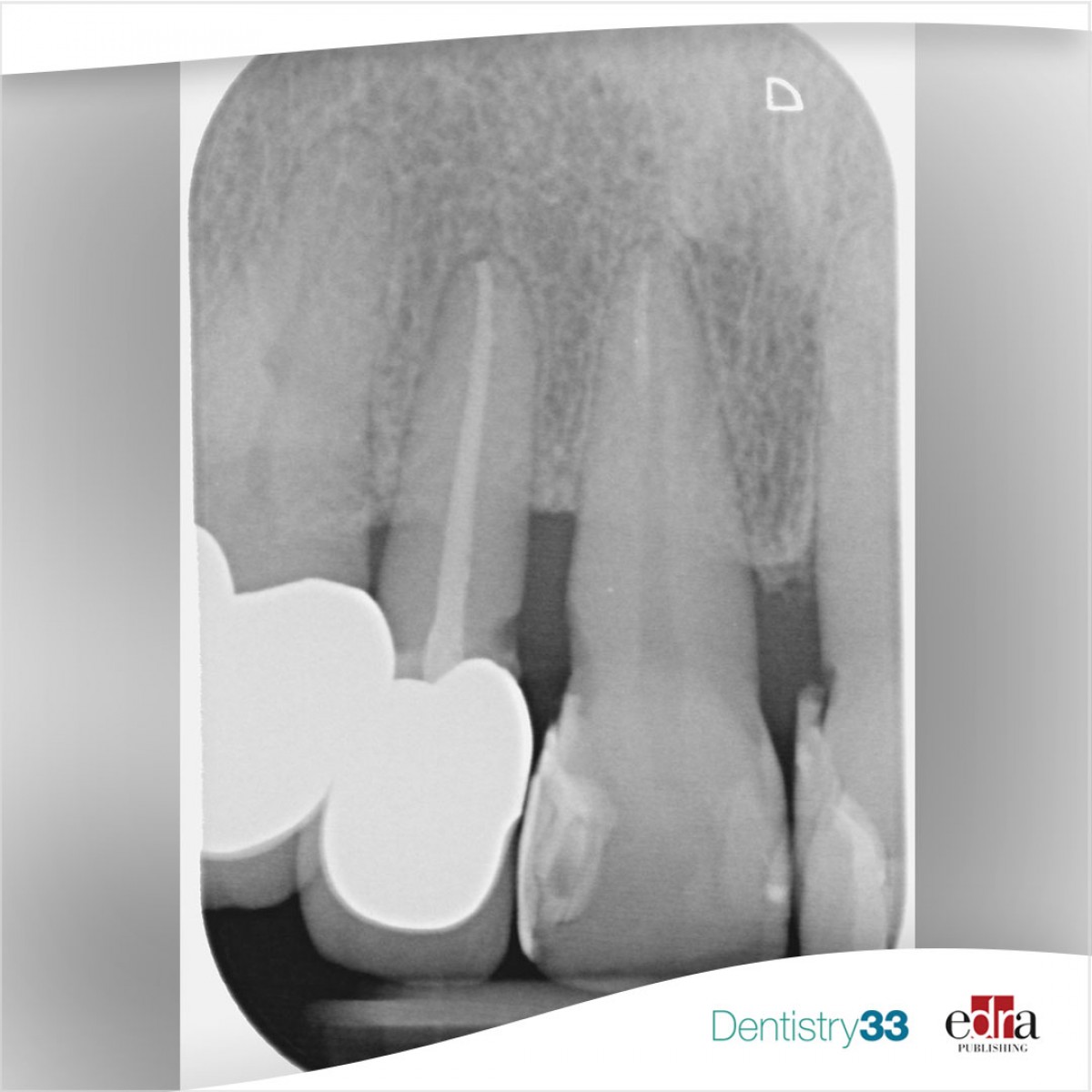
Researchers obtained standardized class I cavities (4 mm length × 3 mm width) in 60 extracted sound human molars. Specimens underwent a microbiological cariogenic protocol (28 days) in order to generate artificial caries lesions and, subsequently, were randomly divided into four restorative groups (n=15): adhesive + composite (control), GIC, MTA and RMTA.
After 24 hours, microhardness analysis (ΔKHN) was performed on 40 specimens (n=10) at baseline and after 30, 45 and 60 days of artificial storage. Micro-CT scans were acquired (3/group, t=0 days, 30 days and 90 days). Confocal microscopy was employed for interfacial ultra-morphology analysis (2/group, t=0 days and 60 days).
Three additional specimens per group were prepared and processed for scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and FTIR to analyze the ability of the tested materials to induce apatite formation on totally demineralized dentin discs (60 days in artificial saliva). All data were statistically analyzed with a significance level of 5% (p<0.05).
Results
Control specimens showed the lowest ΔKHN values and the presence of gaps at the interface when assessed through micro-CT even after artificial storage. However, all the tested ion-releasing materials induced an overall increase of the ΔKHN after storage (p<0.05). MTA best reduced the demineralized artificial carious lesions gap at the interface. Moreover, MTA and RMTA showed apatite deposition on totally demineralized dentin surfaces though SEM and FTIR analyses.
Conclusions
All the tested ion-releasing materials can induce remineralization expressing mineral precipitation in artificial carious dentin. Furthermore, MTA showed enhanced ability of precipitation of hydroxyapatite and hardness recovery of in mineral-depleted dentin over time. RMTA and GIC may be more appropriate for preserving the demineralized collagen fibrils in the caries-affected tissues.
Maciel Pires P, Ionescu AC, Pérez-Gracia MT, Vezzoli E, Soares IPM, Brambilla E, de Almeida Neves A, Sauro S. “Assessment of the remineralisation induced by contemporary ion-releasing materials in mineral-depleted dentine.” Clin Oral Investig. 2022 Oct; 26(10):6195-6207. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04569-9. Epub 2022 Jun 7. PMID: 35670863.
 Tag
Tag
 Related articles
Related articles
By Arianna Bianchi
Endodontic therapy is one of the most used techniques in dentistry, allowing the removal of contaminated or damaged pulp tissue and replacing it with a biocompatible synthetic material to prevent...
Digital Dentistry 09 February 2023
Since the mid-1770s the history of dentistry has involved the introduction of new high-tech materials and manufacturing processes, materials often borrowed from fields unrelated to dentistry.
Market 03 March 2022
The global market for dental biomaterials is projected to grow by a CAGR of 8.41% during the forecast period of 2020 to 2025, according to a report by Technavio, a market analysis company. Across the...
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 07 September 2023
Root caries: effect of fluoride toothpastes and bioactive F-glass
Root caries is one of the main causes of tooth loss in the aging population. Toothpastes containing fluoride are considered inexpensive anti-caries agents due to...
Restorative dentistry 09 August 2023
By Arianna Bianchi
Modern dentistry is increasingly focused on developing a more effective means of restoring enamel.
 Read more
Read more
Oral pathology 25 November 2025
Virtual microscopy (VM) is a technology for showing microscope slides using computers and could be considered a progression of classic methodology using optical microscopes.
For every assist this season, the insurance provider will donate $25 to TUSDM Cares for Veterans
Products 25 November 2025
J. MORITA USA, a world leader in handpiece technology, has announced the Rotary Master+ Electric Motor. Compatible with Morita TorqTech electric attachments and most competing electric handpieces on...
News 25 November 2025
Let’s be honest: nothing kills the vibe quite like bad breath. However, while 85% of people prefer for someone to tell them if their breath needs some freshening up, only 15% are willing to break...
News 25 November 2025
Vitana Pediatric & Orthodontic Partners (Vitana), a dentist-led dental partnership organization (DPO) focused exclusively on elite pediatric dental and orthodontic practices with operations in...