Can lubricant materials be used to model resin-based composites?
Lorenzo Breschi
Introduction
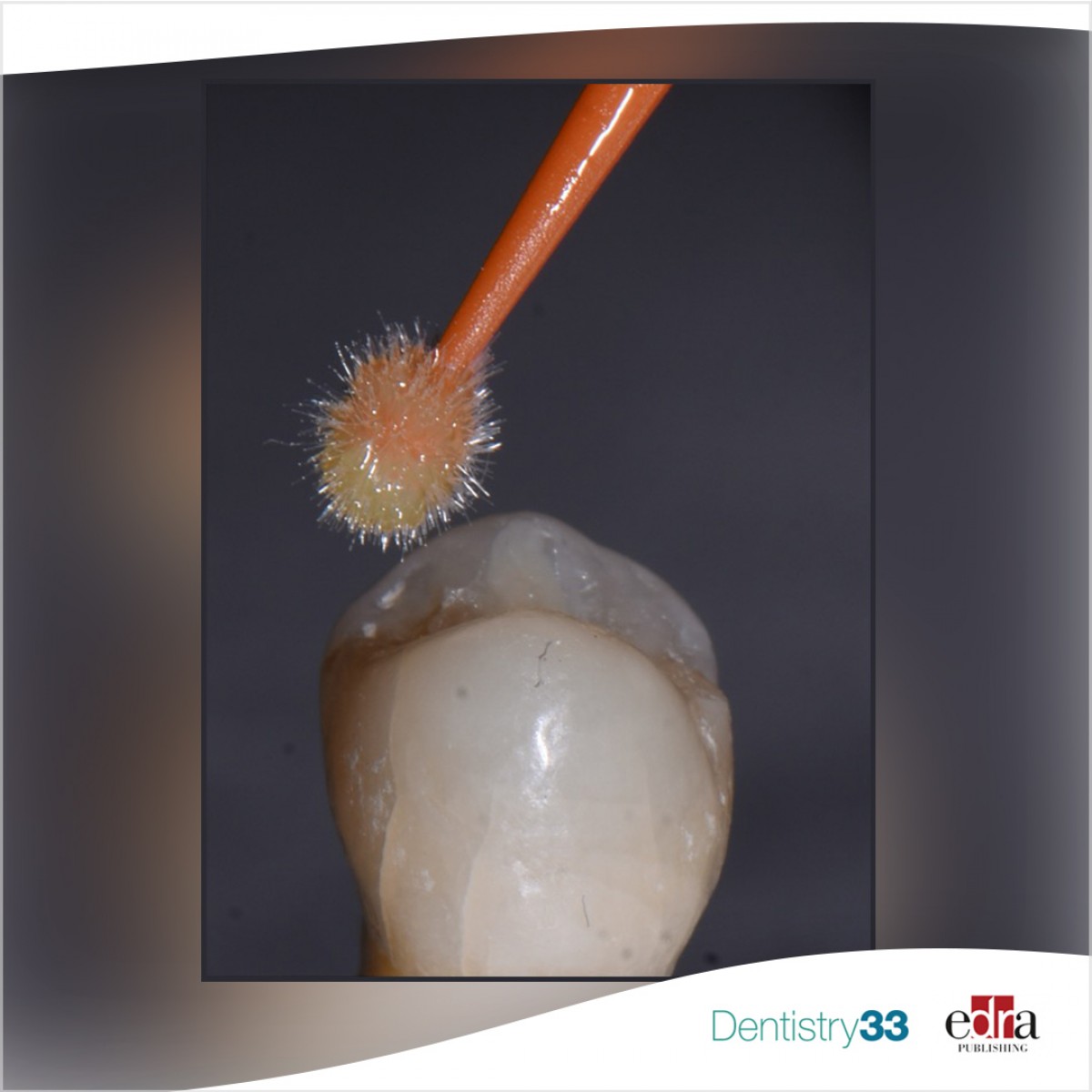
Modeling of composite resins is currently one of the bases of modern restorative dentistry. Several lubricant materials can be used to model resin-based composites (RBCs). Clinically, instruments or brushes are wet with bonding agents (BAs) or modeling liquids (MLs) for sculpturing purposes. Paolone et al. recently aimed to analyze existing scientific literature to explore advantages and limits of lubricant materials used during restorative procedures.
Materials and methods
Five databases were searched, including a review of 295 in vitro studies on the use of lubricant materials for modeling RBCs during restorative procedures. Only English language articles were included, with no limits on the publication date. The most recent research was published in March 2022.
The present study followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) extension for scoping reviews in terms of: (1) identification of the research question, (2) identification of relevant studies (keywords and databases), (3) determination of inclusion and exclusion criteria, (4) data extraction, and (5) summary of the results.
Results
In the 17 studies included in the review process, a total of 17 BAs and 7 MLs were investigated. Tensile (n = 5), flexural strength (n = 2), water sorption (n = 2), color stability (n = 8) and translucency (n = 3), micro-hardness (n = 4), roughness (n = 3), degree of conversion (n = 3), and monomer elution (n = 2) tests were carried out. In general, a maximum of 24 hours of artificial storage was performed (n = 13), while four papers tested the specimens immediately.
Conclusion
Clinicians should be aware that sculpturing RBCs with modeling resins might influence the composite surface properties in a way that is material dependent. The use of non-solvated adhesives (3-step etch-and-rinse, ER) or modeling resins enhances the cohesive bond strength between RBC layers.
Higher color stability was reported with non-solvated adhesives or modeling resins between RBC layers. Increased translucency values were observed when lubricants were used. However, after lubricant application, finishing and polishing procedures were not always able to provide similar surface properties to specimens treated with no lubricants.
The effect on the degree of conversion depended on the type of lubricant and RBC. MLs and self-etched adhesives presented higher monomer elution with respect to ER adhesives.
Paolone G, Mazzitelli C, Josic U, Scotti N, Gherlone E, Cantatore G, Breschi L. "Modeling Liquids and Resin-Based Dental Composite Materials-A Scoping Review." Materials (Basel) May 2022; 15; 3759. doi: 10.3390/ma15113759
 Related articles
Related articles
Restorative dentistry 10 February 2025
Dental students' experience and perceived confidence level in different restorative procedures
Graduating confident students who are able to flourish and develop in their future careers is an importance outcome of the dental education.
 Read more
Read more
News 28 November 2025
Flex Dental Solutions, a leading patient-engagement software and authorized integration vendor for Open Dental users, today announced a new strategic relationship with DentalHQ, a premier...
News 28 November 2025
The Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC) has accredited two additional U.S. Oral Surgery Management (USOSM) partner practices. They are North Sound Oral & Facial Surgery...
Pediatric dentistry 28 November 2025
Retrospective Review of Pediatric Oral Lesions from a Dental School Biopsy Service
This report presents a review of the results from 5457 biopsies of patients, 0-16 years of age, received over 15 years at the University of the Pacific School of Dentistry
Editorials 28 November 2025
RE-JOIN research project receives $1.4 million extension to advance joint pain research
A research team co-led by University of Michigan School of Dentistry faculty member Joshua Emrick has received substantial extended funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), paving the...
Products 28 November 2025
DEXIS has announced the results of new independent radiation testing for its handheld, portable X-ray system, NOMAD™ Pro 2.