Screening and monitoring of periodontitis by analyzing the levels of myeloid proteins in saliva
Lara Figini
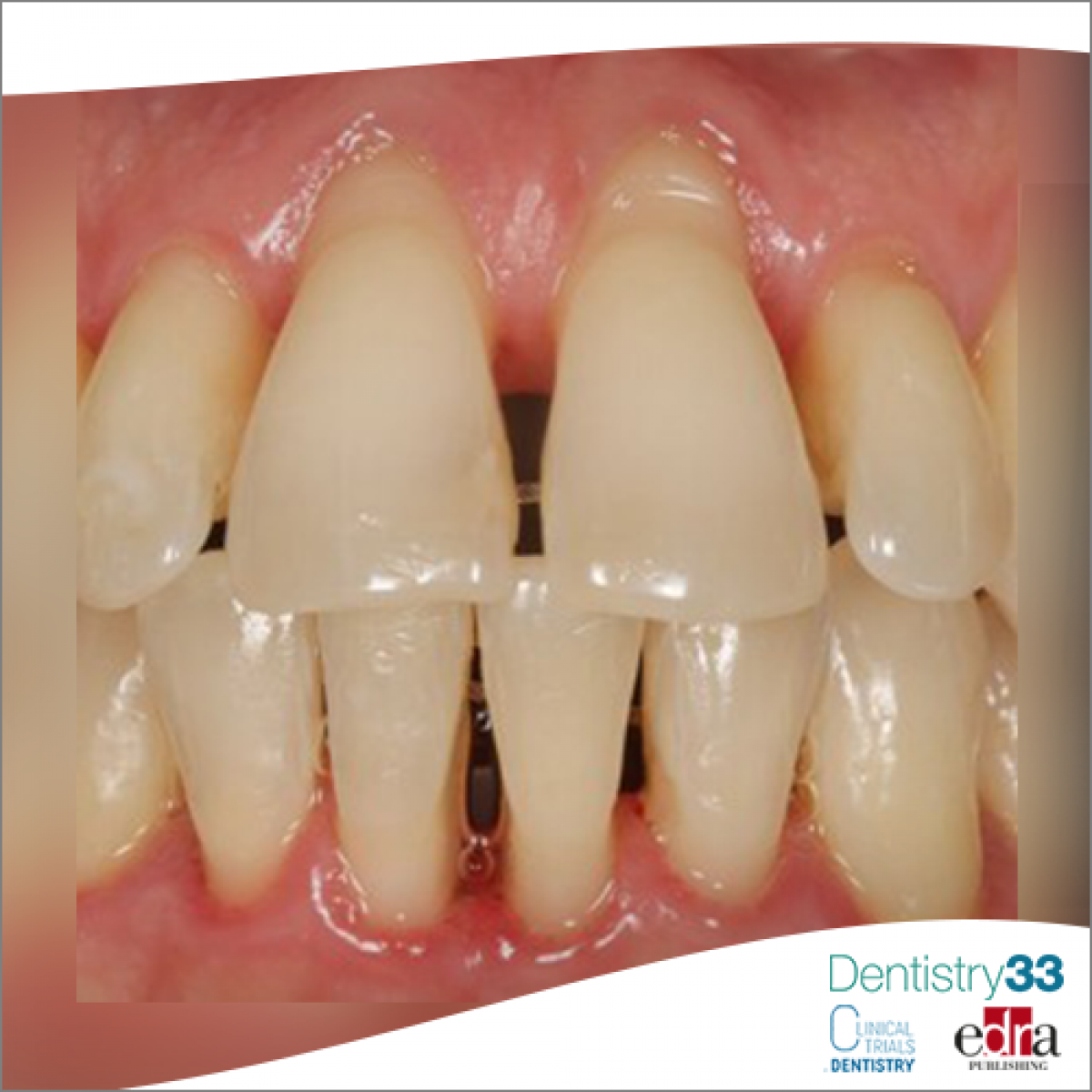
Periodontitis is a very widespread chronic disease, characterized by microbiota-induced inflammation of the supporting tissues of the tooth and can also lead, if neglected, to tooth loss as well as contributing to the systemic inflammatory load. In cases of periodontitis, immune cells infiltrate the periodontal tissues producing high concentrations of cytokines and proteolytic enzymes, such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which mediate tissue damage leading to loss of function and clinical disease. Among the immune cells, myeloid cells, which produce enzymes that undermine the integrity of the oral mucosa and mediate alveolar bone resorption, play a significant role in the pathogenesis of periodontitis. Therefore, myeloid cell-reflecting molecules are potential biomarkers for screening for periodontitis and for assessing response to therapy.
Materials and Methods
In a clinical study, published on Journal of Clinical Periodontology, November 2021, the authors evaluated the salivary levels of myeloid markers related to periodontal disease and their potential screening capacity, as well as the effects of periodontal treatment on these markers in patients with periodontitis. Participants with healthy periodontium (n = 60) and with gingivitis (n = 63) and periodontitis (n = 72) were recruited. Patients with periodontitis received non-surgical treatment and were re-examined after 3 and 6 months. Unstimulated saliva was collected at baseline time 0 and at 1, 3 and 6 months after periodontal therapies. Levels of factor-1 (CSF-1), interleukin-34 (IL-34), S100A8 / A9, S100A12, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), IL-1β, and matrix metalloproteinase- 8 (MMP-8) were analyzed by immunoassays.
Results
CSF-1, S100A8 / A9, S100A12, IL-1β, MMP-8 and HGF were significantly more elevated in the saliva of patients with periodontitis and gingivitis compared to that of healthy subjects. IL-34 was significantly lower in periodontitis than in both healthy individuals and in patients with gingivitis. IL-34 significantly increased 3 months after treatment, while IL-1β and MMP-8 decreased 1 month after therapy. Patients were then divided into subjects with high-level and low-level S100A8 / A9 periodontitis, and subjects with high levels had more bleeding, deeper pockets, and higher S100A12.
Conclusions
From the data of this study, which must be confirmed in other similar studies, it can be concluded that the salivary levels of myeloid markers are altered in periodontitis and are partially modulated by periodontal treatment. Measurement of S100A8 / A9 in saliva can identify distinct groups of patients with periodontitis (high-level and low-level).
Clinical implications
Myeloid cells are essential for the inflammatory process in periodontitis. Therefore, measuring the molecules that reflect their functions in saliva has the potential to improve it screening and monitoring of periodontal inflammation. Measuring myeloid markers in saliva can be helpful in evaluating periodontal disease. Assessment of S100A8 / A9 in saliva can inform the identification of distinct groups of patients with periodontitis, potentially helping patient monitoring and treatment.
For additional information: Levels of myeloid-related proteins in saliva for screening and monitoring of periodontal disease
 Related articles
Related articles
Editorials 25 April 2025
New Drug Therapy with Natural Compound Shows Promise Against Periodontal Diseases
A translational study from the lab of Dr. Esra Sahingur shows “senotherapy” drug combination was effective in lab-dish and animal models.
Periodontology 14 March 2025
Implementation of the new classification of periodontal diseases requires careful navigation of the new case definitions and organization of the diagnostic process along rationale and easily...
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 12 December 2024
Contemporary practices for mechanical oral hygiene to prevent periodontal disease
It is well established that dental plaque on teeth leads to gingivitis and periodontitis, and that several mechanical and chemical methods of plaque control can prevent gingivitis.
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 19 November 2024
Oral hygiene in the prevention of caries and periodontal disease
While some periodontal disease may be as old as mankind itself, caries as a public health problem appeared with the development of flour and sugar mills, and the universal access to fermentable...
Editorials 08 August 2024
Researchers find mutated gene contributes to development of periodontal disease
Adams School of Dentistry researcher Kimon Divaris, DMD, PhD, MS, along with collaborators from the University of Pennsylvania, have found that patients diagnosed with clonal hematopoiesis of...
 Read more
Read more
Bulimia nervosa is a multifactorial health disorder characterized by a disturbed self-perception of body weight and shape and therefore by cycles of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviours...
Editorials 16 January 2026
Benjamin Brudner still remembers the moment his patient looked in the mirror and smiled—really smiled—for the first time in years.
Priva Rotary Instruments Diamond Burs from Premier Dental are high-performance electroplated diamonds featuring SmartEdge Technology designed to enhance a clinician’s rotary portfolio.
News 16 January 2026
PepperPointe Partnerships, one of the largest privately doctor-owned, doctor-led dental service organizations (DSO), announces the expansion of its senior leadership team with the creation of three...
News 16 January 2026
Spear Education, the leading provider of advanced dental education and practice management solutions, today announced a major update to Spear Online, its virtual learning platform for general...