Bulimia nervosa and oral cavity: a review of the literature
OBJECTIVES
Bulimia nervosa is a multifactorial health disorder characterized by a disturbed self-perception of body weight and shape and therefore by cycles of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviours such as self-induced vomiting and consequent serious dental problems. Bulimia nervosa is often associated with serious physical and psychosocial morbidity. Persons with bulimia nervosa often tend to hide their disease and avoid professional help. Because body appearance is often normal, diagnosis is complicated because it is based on self-report according to the criteria defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
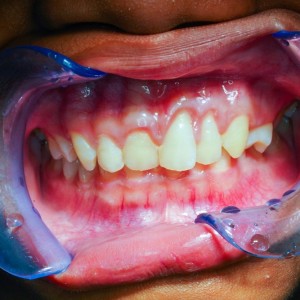
Intraoral manifestations of bulimia include tooth erosion and sensitivity, xerostomia, mucosal lesions, as well as increased rates of dental caries and periodontal disease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A review of articles published presenting cases and populations of patients affected by oral and dental lesions associated with bulimia nervosa were identified and included, as well as reviews regarding such topic. Data were collected on epidemiology, diagnosis, etiopathology, mucosal lesions, dental lesions, and dental management.
RESULTS
The diagnosis of the eating disorders is made on clinical grounds. A history of binge eating without major weight gain, evidence of induced vomiting or regular use of laxatives or diuretics, obsessive/ compulsive behavior, and antisocial activity or self-mutilation, may determine a diagnosis of bulimia nervosa.
Oral manifestations of bulimia are usually provoked by vomit, by nutritional deficiencies and consequent metabolic impairment, but may also be related to lack of importance given to personal hygiene⁄ care, underlying psychological disturbances, modified nutritional habits (tendency to eat particular foods) or assumption of certain drugs.
Patients with bulimia nervosa usually present several oral manifestations that are associated with this eating disorders, such as dental erosion, dental caries, glossodynia, and xerostomia.
Dental treatment often requires numerous restorations, extractions or both, as well as frequent preventive care. For these patients on of the dentist’s goals is to improve the patient’s oral hygiene. This will include tooth brushing instructions, use of
dental floss, and topical fluoride application.
Tooth sensitivity can be managed by using desensitizing toothpastes, fluoride applications, and other means. As for restorations, tooth structure affected by dental erosion can be restored with either direct or indirect restorations.
As for teeth with a moderate erosion/ destruction, since most of the enamel is eroded from the lingual surfaces of the teeth, a layer of resin-based composite is needed to cover these surfaces. Instead, patients with severe erosion have four main alternatives: maintain a wait and see approach until one of the following treatments is mandatory; make a maxillary polymer occlusal splint; place crowns on all affected teeth; extract the teeth and fabricate removable complete dentures.
DISCUSSION
The importance of dental practitioners in the early diagnosis of bulimia nervosa should be stressed.
CONCLUSIONS
An appropriate treatment of oral signs of such pathology should be performed, with particular attention to the management of dental erosion.
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
Patients affected by bulimia nervosa may present several oral disturbances.
Authors: Paolo Boffano, Francesco Cavarra, Gerardo Tricarico, Andrea Melle, Muhammad Ruslin, Vincenzo Rocchetti
Source: https://www.dentalcadmos.com/
 Related articles
Related articles
Restorative dentistry 20 June 2021
Full-mouth adhesive treatment in Bulimia-Related Dental Erosions: a clinical report
Authors: Francesca Muzzarelli, Lorella Marinucci, Stefano Cianetti, Guido Lombardo, Cinzia Barilotti, Stefano Pagano
Dental erosion, which is defined as the gradual but irreversible loss of hard tissue is a major dental issue as it may be linked to systemic diseases such as eating disorders or gastroesophageal...
Periodontology 25 September 2025
Throughout history, education has evolved, and new teaching/learning methods have been developed.
Oral pathology 10 March 2025
Clinico‐pathologic correlations of myofibroblastic tumors of the oral cavity: nodular fasciitis
Nodular fasciitis (NF), a soft tissue lesion mainly composed of myofibroblastic cells, is well documented in various body locations however, in the oral cavity it is rare.
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 17 August 2023
Oral cancer screening knowledge, practices at the University of Toronto
Opportunistic oral cancer screening during visits to the dentist is a non-invasive and accessible option for detection of pre-malignant lesions and early-stage malignancies.
Oral pathology 11 February 2023
By Valentina Viganò, University of Milan
Professor Lodi is one of most appreciated oral pathologists that we know, and he has always fought to make dentists aware of the attention to the early diagnosis of this neoplasm.
 Read more
Read more
Editorials 16 January 2026
Benjamin Brudner still remembers the moment his patient looked in the mirror and smiled—really smiled—for the first time in years.
Priva Rotary Instruments Diamond Burs from Premier Dental are high-performance electroplated diamonds featuring SmartEdge Technology designed to enhance a clinician’s rotary portfolio.
News 16 January 2026
PepperPointe Partnerships, one of the largest privately doctor-owned, doctor-led dental service organizations (DSO), announces the expansion of its senior leadership team with the creation of three...
News 16 January 2026
Spear Education, the leading provider of advanced dental education and practice management solutions, today announced a major update to Spear Online, its virtual learning platform for general...
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 15 January 2026
The effectiveness of mouthwash on orthodontic and prosthetic complications: a systematic review
The present study aimed to determine the effectiveness of mouthwashes on the complications of orthodontic treatments and dental prostheses, in addition to filling research gaps, to identify and...