Dental caries in primary molars: how to simplify the restoration
Alessandra Abbà
Preservation of primary teeth is essential for oral health and for the maintenance of functions of chewing and speech. Nonetheless dental caries among children continues to be one of the major public health disease. To face this problem a variety of resin materials with different physical properties have been studied for use in primary dentition with the aim of time saving and simplification of the technique. One of this is the so-called “self-adhering composite resin” in a flowable composition. It can eliminate the need for a separate adhesive application reducing treatment time.
The purpose of this single blind randomized clinical study was to evaluate the 1year clinical performance of a self-adhering flowable composite and a commercially available self-etch adhesive / composite system in occlusal restorations of primary molars.
Materials and methods
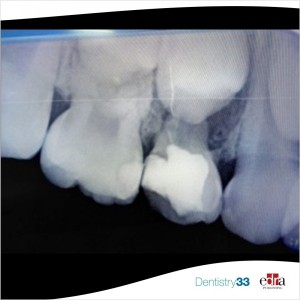
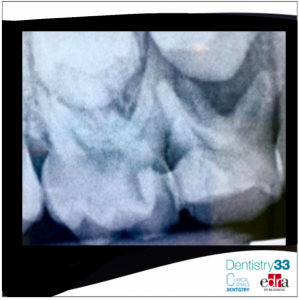
From March 2012 to September 2013, thirty-one children (10 male, 21 female between 4 and 9 years) were screened and enrolled for this study. The major inclusion criteria was having at least two occlusal primary caries lesions on primary molars in a split-mouth design with no involvement of the pulp. After the clinical and radiographic examination patients were treated with local anesthesia and rubber dam isolation and a randomly assigned restoration method by a pediatric dentist with a split-mouth design. Each child was treated by the same operator. All 31 patient received two different types of restorative treatment. A total of 62 occlusal cavities were restored with either a self-adhering flowable composite or a commercially available self-etch adhesive/composite system according to manufacturers' instructions. The restorations were clinically evaluated after 1 month, and after 3, 6 months and 1 year post-operatively using modified United States Public Health Service (USPHS) criteria for retention (R), color match (CM), marginal discoloration (MD), secondary caries (SC), wear (W), marginal adaptation (MA) and postoperative sensitivity (PS).
Results
31 patients attended the 1st, 3rd and 6th months recall and 29 patients attended 1 year recall. Lack of retention was not observed in any of the restorations. None of the restorations had marginal discoloration and anatomic form loss on the 1 year follow-up. Restorations did not exhibit post-operative sensitivity at any evaluation period. There were no significant differences between the groups for retention, color match, marginal discoloration, secondary caries, wear, marginal adaptation, postoperative sensitivity after 1 month, 3 months, 6 months and 1 year.
Conclusions
This study aimed to evaluate the clinical performance of a new self-adhering flowable composite for 1 year. Based on the findings of the present study, self-adhering flowable composite exhibited acceptable clinical results. This material, incorporating bonding agent, allows to save time and minimizes handling errors. Nonetheless there are limited studies about self-adhering flowable composite resin.
According to the results of the study, self-adhering flowable composite resin can be used successfully in occlusal cavities of primary teeth.
For additional information: Clinical evaluation of a self-adhering flowable composite as occlusal restorative material in primary molars: one-year results
 Related articles
Related articles
Pediatric dentistry 12 May 2025
A Diagnostic Insight of Dental Pulp Testing Methods in Pediatric Dentistry
The accurate diagnosis of pulpal pathology in pediatric dentistry is essential for the success of vital pulp therapy. Pulp testing is often a challenging task due to understanding and cooperation...
Pediatric dentistry 05 November 2022
The use of electronic apex locators during the endodontic treatment of primary teeth
The main goal of endodontic therapy in primary dentition is to preserve the teeth in a symptom-free state until they are naturally replaced by their...
Pediatric dentistry 16 May 2022
Primary Molars Restorations: Flowable Bulk-fill Materials VS Nano Ceramic Composites
One of the most common materials for the restoration of primary teeth are glass ionomer cements (GIC), because of their time-saving feature. Nonetheless their...
Pediatric dentistry 04 May 2022
The evaluation of MTA and Biodentine as a pulpotomy materials for carious exposure in primary teeth
The aim of the present study was to compare the long term clinical and radiographic success rates of Biodentine and MTA pulpotomies, performed on primary teeth...
Pediatric dentistry 12 January 2021
The Hall Technique: a misunderstood method against cariuous primary molars
The high frequency of carious lesions in primary teeth is one of the major public health problems during childhood. However, inadequate treatment of these cases are often found. Traditional treatment...
 Read more
Read more
Implantology 03 February 2026
Bone Structure, Metabolism, and Physiology Its Impact on Dental Implantology
When placing implants in the mandible or maxilla, it is important for clinicians to understand the process of bone remodeling, the different types of bone, and how these factors can affect the...
Editorials 03 February 2026
Dr. Alireza Sadr of the Department of Restorative Dentistry has been appointed as the first-ever UW School of Dentistry Director of Digital Dentistry and Innovation, effective Jan. 1, 2026.
Products 03 February 2026
Families can now use SmileScan™, a free, AI-powered oral health scan offered by Dentistry.One, to identify potential areas of concern and receive an overall oral health score.
Investment supports professional growth for future oral health leaders and expands community outreach for underserved Oklahomans
News 03 February 2026
Henry Schein, Inc. (Nasdaq: HSIC), the world’s largest provider of health care solutions to office-based dental and medical practitioners, announced recently that it will release its fourth quarter...