Direct or indirect composite for restoring permanent first molars affected by molar incisor hypomineralization
Aim
This study was undertaken to compare direct composite resin restorations (DCRR) and indirect composite resin restorations (ICRR) for treating permanent first molars affected by MIH in terms of clinical performance.
Materials and methods
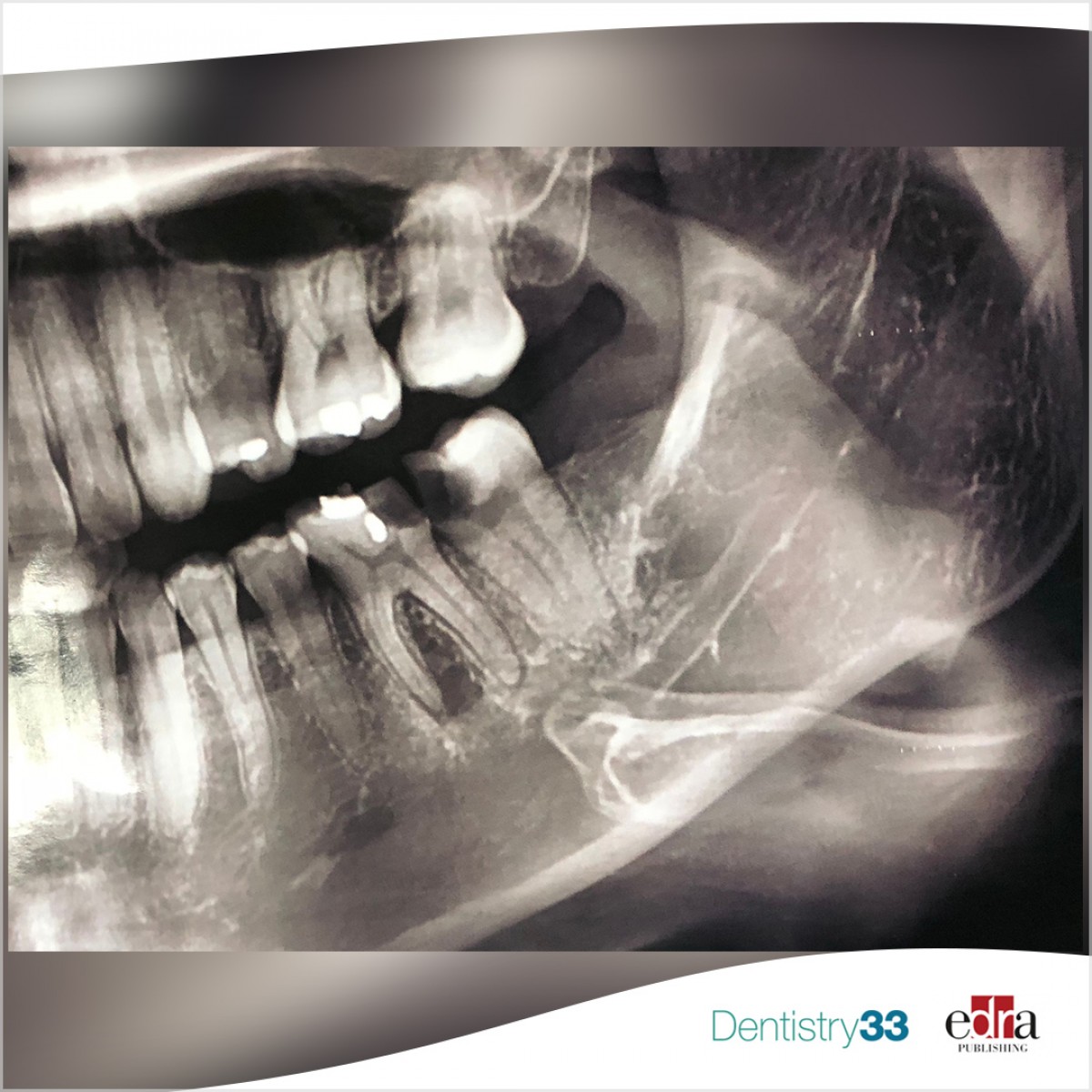
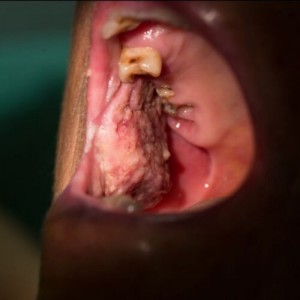
This was a controlled, randomized, clinical split-mouth study. The studied sample consisted of 40 asymptomatic first permanent hypomineralized mandibular molars in 20 children aged between 7–11 years, these cases were divided randomly into two groups: Group 1 (experimental): 20 first permanent mandibular molars were restored with ICRR, and Group 2 (control): 20 first permanent mandibular molars that were restored with DCRR.
The cavity was prepared using a diamond bur on a high-speed handpiece, and the prepared cavity was wiped with cotton moistened with sodium hypochlorite. The composite was applied directly with a total-etch bonding system. In the ICRR group, an impression for the prepared cavity was taken using a silicon-based material, and the restoration was adhesive with self-adhesive resin cement.
The child’s satisfaction with each of the two application techniques was assessed through the scale FACES. Restorations were evaluated during follow-up periods (3, 6, and 12 months) according to Modified USHPH criteria.
Results
The clinical success rate was 90% in the ICRR group versus 85% in the DCRR group after 12 months of follow-up without statistically significant differences (P = 0.218). Children were significantly more satisfied (P = 0.0351) with ICRR than DCRR.
Conclusions
Both DCRR and ICRR can be considered effective restorations with acceptable clinical performance in the restoration of hypomineralized first permanent molars with an advantage of ICRR in terms of child acceptance of the restoration application technique.
Hakmi, A., Dashash, M. "Direct or indirect composite for restoring permanent first molars affected by Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation (MIH): a randomized clinical controlled trial." BDJ Open 9, 37 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41405-023-00165-5.
 Related articles
Related articles
Editorials 12 September 2025
1 in 3 Florida third graders have untreated cavities – how parents can protect their children’s teeth
Company will showcase the toothbrush solution at the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry conference in Denver.
Products 15 April 2025
Families in Oceanside and the greater San Diego region now have greater access to essential pediatric dental care with the recent opening of a new Children’s Choice Dental Care office.
Patients’ and parents’ perception of malocclusion are important in determining orthodontic treatment demand, motivation, and cooperation.
News 07 February 2025
Benevis Highlights Emergent Oral Health Coverage Needs for Children’s Dental Health Month
Benevis has issued a call to action to expand Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) eligibility and ensure vulnerable U.S. children continue to receive coverage for dental health...
 Read more
Read more
Implantology 17 October 2025
To investigate whether cross-section imaging influences the planning and therapy of standard implant cases in the posterior mandible.
Editorials 17 October 2025
In her new role she is providing direction and supporting initiatives that elevating UFCD's translational research agenda.
Products 17 October 2025
Presto Dental, a new brand affiliated with the Abra Health Group, proudly announces the grand opening of its flagship Connecticut location in Bridgeport. This state-of-the-art.
News 17 October 2025
The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons (AAOMS) celebrated the achievements of more than 30 individuals at the association’s 107th Annual Meeting, Scientific Sessions and...
Phenom, an applied AI company that helps organizations hire faster, develop better, and retain longer, announced The Aspen Group (TAG) earned the Brandon.