The efficacy of miniscrew-supported distal-jet in clinical practice
Authors:Michele Cassetta, Rosanna Guarnieri, Ersilia Barbato, Federica Altieri
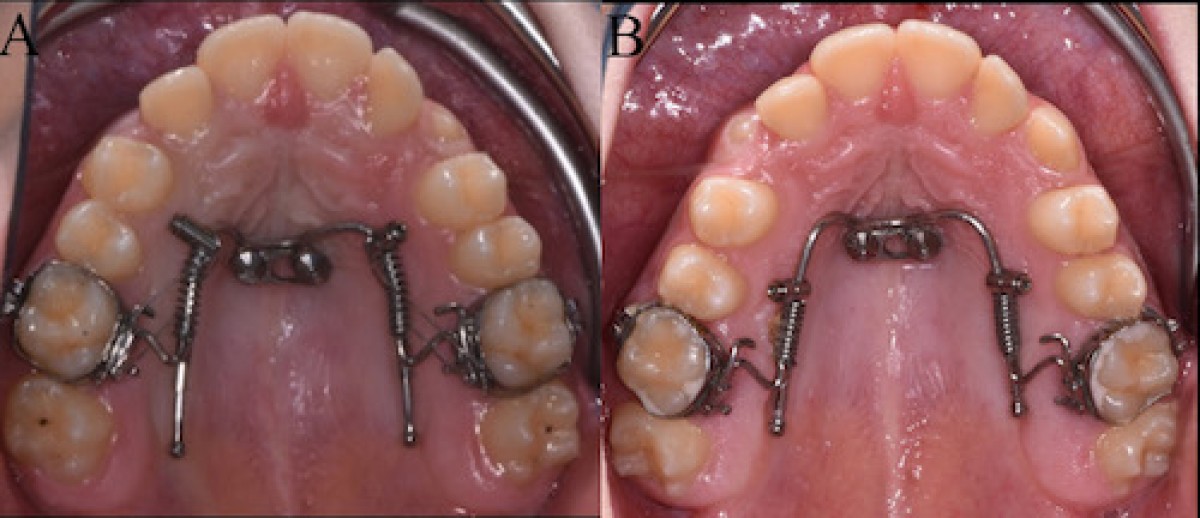
OBJECTIVE: The aim of the present pilot study was to evaluate the efficacy of the miniscrew-supported distal jet appliance versus traditional distal jet appliance in terms of amount of upper first molar distalization and the dentoalveolar side effects, obtained in six months.
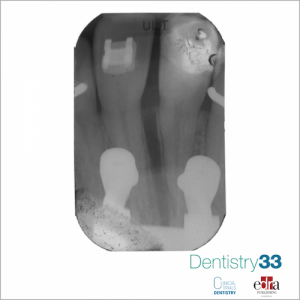
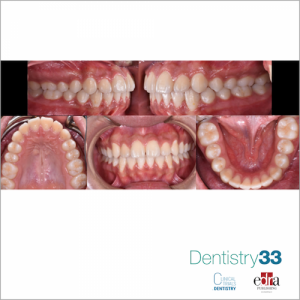
MATERIAL AND METHODS: 20 patients were randomly assigned to receive a treatment with miniscrew-supported distal jet appliance (Group A) or with traditional distal jet appliance (Group B). To ensure a minimally invasive miniscrew insertion a computer-guided surgical guide was designed and subsequently manufactured using a 3D printer. Digital models and lateral cephalograms were obtained and analyzed before orthodontic treatment and at 6-month follow-up. The amount of upper first molar distalization and the dentoalveolar side effects were assessed both on digital models and on lateral cephalograms. In order to reduce the bias in the selection of subjects, considering that the sample size was too small to represent the entire spectrum of subjects in the target population, the results were analyzed at 6 months from the start of therapy. A descriptive statistical analysis was carried out. Intergroup differences were determined using T- test. The significance was set at P ≤0.05. The intra-operator reliability was calculated and a 2 sample T-test was used with significance estabilished at P ≤0.05.
RESULTS: In Group A, a greater maxillary first molar distalization was recorded in 6 months of follow-up with a statistically significant difference between the groups (P=0.002). Considering the dento-alveolar side effects, in Group A, a spontaneous distalization of the first premolars and a retroclination of central incisors were observed. In Group B, on the other hand, the first premolars tipped mesially (mesial drift) and a proclination of the maxillary central incisors (incisal flaring) was observed, causing a loss of anterior anchorage. The transverse widths of the dental arch increased in both groups, and a greater tendency of maxillary first molar rotation was observed in the group with traditional distal-jet appliance.
CONCLUSIONS: The present pilot study compared two maxillary molar distalization systems: the traditional distal jet appliance versus the miniscrew-supported distal jet appliance. The skeletal anchorage device achieved a greater first molar distalization at 6-month follow-up and did not cause dento-alveolar side effects, such as the mesial drift of the premolars and the incisors. Randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm these preliminary results.
CLINICAL IMPLICATION: Maxillary molar distalization is the most frequently used non-extraction treatment in the correction of Class II malocclusion. The use of traditional intra-oral devices shows unreliable results. Nowadays the use of miniscrew-supported appliances helps prevent anchorage loss. The present pilot study has provided results that, in the short follow-up, demonstrate a greater amount of maxillary molar distalization without the anchorage loss observed in traditional distal-jet appliances. These results should encourage the clinical use of supported-miniscrew orthodontic appliances but randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm these preliminary results.
 Related articles
Related articles
Authors: Marco Brady Bucci, Andrea Pase, Dario Brady Bucci
OBJECTIVESIn orthodontics, the evaluation and scheduling of the anchorage represent the crucial phase of the treatment, capable of often influencing the therapeutic result. The purpose of this work...
Oral surgery 11 August 2021
Palatal miniscrew insertion using a CAD-CAM surgical guide: a case report
Authors: Michele Cassetta, Federica Altieri, Rosanna Guarnieri, Gabriella Padalino, Martina Mezio, Ersilia Barbato
OBJECTIVES: The aim of the present case report is to describe an orthodontic treatment to gain space in the maxillary arch by using a bone-anchored molar distalization appliance (distal-jet)....
 Read more
Read more
Editorials 10 October 2025
With proud smiles and crisp white coats, ninety-three learners from the DDS Class of 2029 and the International Dentist Pathway Class of 2028 marked the start of their dental careers at the UCSF...
Periodontology 10 October 2025
Continuous professional development (CPD) in Periodontology refers to the overall framework of opportunities that facilitate a life-long learning practice, driven by the learner-practitioner and...
TheraBreath, the #1 alcohol-free mouthwash brand in the U.S.*, has introduced a new line of dentist-formulated, clinically tested toothpastes designed to support professional oral care...
News 10 October 2025
New officers and trustees were installed at the Minnesota Dental Association’s Leadership Conference on September 19 in Minneapolis.
News 10 October 2025
Smartee Denti-Technology today announced that Professor Gang Shen, its Chief Scientist and Executive President of TaiKang ByBo Dental, has once again been named to the World’s Top 2% Scientists...