Orthodontic treatment and periodontally compromised patients: effects of the treatment
Davide Elsido
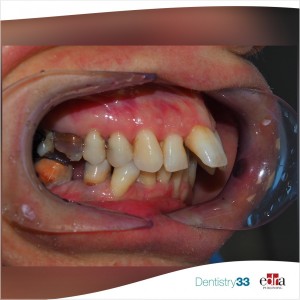
An increasing number of adult patients are now seeking orthodontic treatment due to an increased focus of society on esthetics and health consciousness. With the incidence of periodontal problems shown to increase with age, ortho-perio interactions play an important role in management of these patients. Orthodontic problems in the majority of these adult patients are a consequence of their underlying periodontal issues leading to reduced periodontal support and resulting in pathological migration, proclination of maxillary anterior teeth, interdental spacing, rotation and overeruption, resulting in compromised function and esthetics. Unfortunately there is no evidence-based solution to these problems and, with an increasing number of adults with malocclusion and compromised periodontium seeking orthodontic treatment, it is important to clarify the various issues involved in managing periodontally compromised dentitions.
As orthodontic tooth movement is basically a bone remodeling phenomenon, the effect of orthodontic treatment on osseous topography in patients whose bone levels are already compromised is crucial.
This was a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Thirty-six periodontally compromised adult patients (mean age: 29.67 ± 4.8 years) were randomly allocated to either test (perio-ortho) or control group (perio). After periodontal stabilization in both groups, orthodontic treatment was started in the test group, whereas the control group remained on periodontal maintenance only. Evaluation and comparison of clinical parameters (plaque index [PI]; gingival index [GI]; bleeding on probing [BOP]; probing depth [PD]; clinical attachment level [CAL]) of both groups was assessed at three time intervals: T0 (base line), T1 (at start of orthodontic treatment), and T2 (1 year after start of orthodontic treatment). Radiological parameters (alveolar bone levels [ABL]) were recorded using CBCT at T1 and T2.
The results of the study showed favorable results of a combined periodontic-orthodontic treatment in periodontally compromised patients. There was a statistically significant improvement in all the periodontal parameters in the control and test groups with a highly significant CAL gain of 0.74 mm (CI: 0.64-0.83) and 0.98 mm (CI: 0.94-1.01), respectively, from T0-T2. Use of CBCT enabled evaluation of ABL changes on all four surfaces of upper and lower anterior teeth and showed statistically significant improvement in ABL from T1 to T2 in both groups.
Within the limitations of the study, it can be concluded that orthodontic treatment does not have a deleterious effect on periodontal health after periodontal stabilization in periodontally compromised patients.
 Related articles
Related articles
Orthodontics 05 September 2022
Effect of orthodontic treatment on periodontal health of periodontally compromised patients
An increasing number of adult patients are now seeking orthodontic treatment due to an increased focus of society on esthetics and health consciousness. With the incidence of periodontal problems...
 Read more
Read more
Restorative dentistry 13 February 2026
Integrating Laser Technology with CAD/CAM for Advanced Smile Design in Dentistry
This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of integrating laser treatment with CAD/CAM systems in restoring dental function and aesthetics in a 35-year-old male patient suffering from bruxism.
Editorials 13 February 2026
The SRG is UFCD’s student‑run chapter of the American Association for Dental, Oral and Craniofacial Research, or AADOCR.
Products 13 February 2026
Parkview Dental, a leading Dental Support Organization committed to providing comprehensive management services to dental practices, announced the appointment of Lisa Burris as its new Director of...
News 13 February 2026
DentaQuest, part of Sun Life U.S., recently announced the appointment of Dr. Ronke Ogunbameru as dental director for Texas, where the organization covers more than 1.4 million Medicaid and CHIP...
News 13 February 2026
Unlock CE Credits by Reading One Move Makes All the Difference
Dental professionals can now earn 4 hours of continuing education credit by reading One Move Makes All the Difference by Martin R. Mendelson, DDS, FIADFE, CPC. Dr. Mendelson and Metamorphosis...


.jpg)