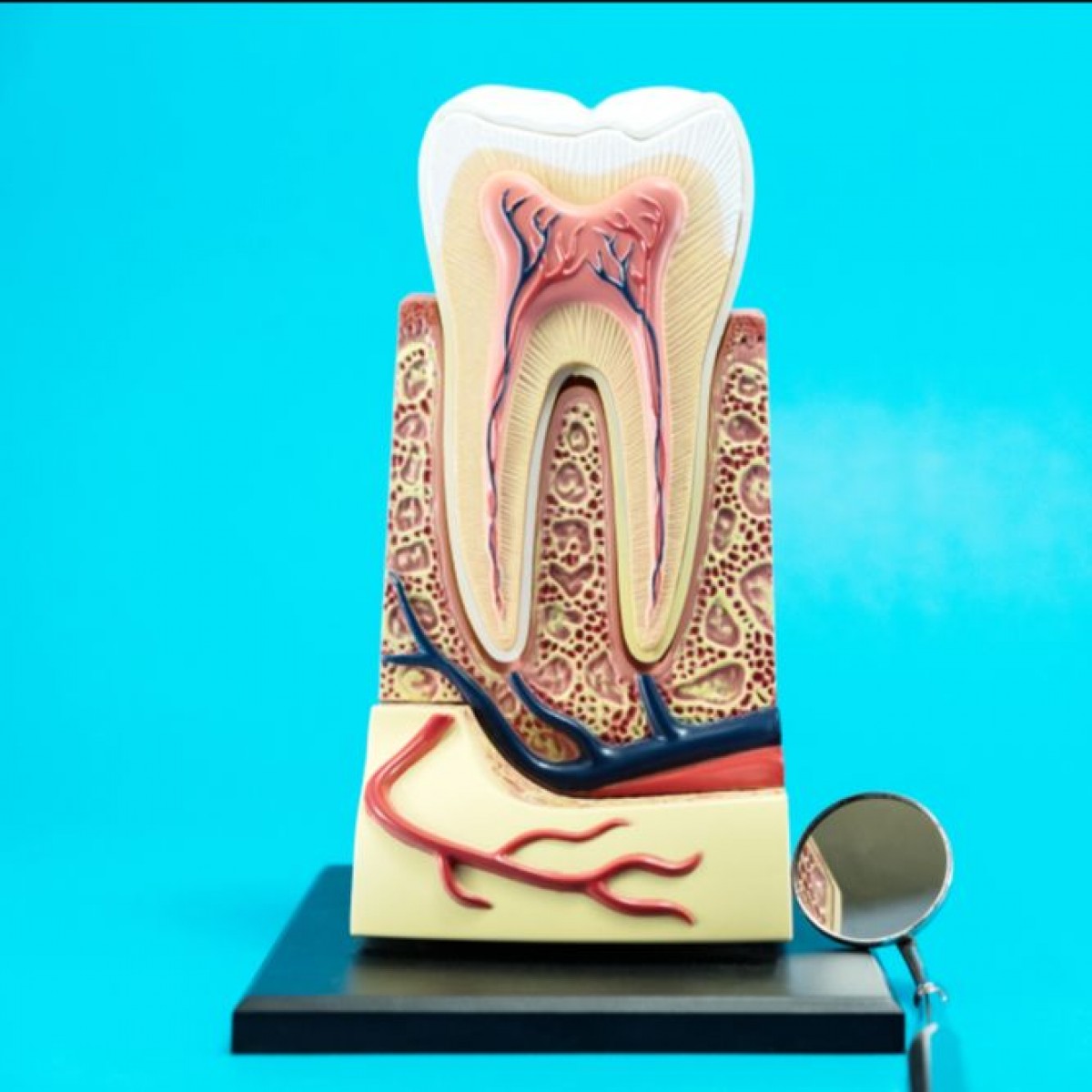
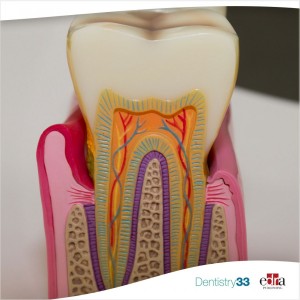
How dental pulp changes based on age
Lara Figini
Literature studies report that the blood vessels in different organs or even in different tissues are not all the same but are heterogeneous, classifiable into various subtypes (type H, type L and type E vessels, VEGFR3+CD34− VEGFR2+CD45 vessels − in the liver, and CD31hiEmcn+ESM-1+ vessels in the islets of the pancreas etc.).
These specific blood vessel subtypes usually regulate perivascular cell/tissue function through angiocrine effects.
Already in 1992, a study by Vongsavan reported that the dental pulp in cats is more vascularized than most other organs. Blood vessels are fundamental in the regeneration of the dental pulp, so much so that many recent studies have focused their attention on the reconstruction of the vascularization of the pulp through tissue engineering.
Recently, a study based on single cell sequencing demonstrated that dental pulp vascular endothelial cells could be classified into three subpopulations (Krivanek, 2020).
However, the distribution pattern of specific vascular subtypes of the dental pulp and its perivascular parts and the mapping of the microenvironment is still poorly studied.
In organs/tissues such as the kidney, spleen and muscles, blood vessels show a significant age-dependent decrease, while in tissues with a high turnover rate, such as the skin, there is no obvious change with age. time. However, age-related dental pulp vascular changes in mice and humans remain poorly understood.
In an in vitro study, published in the September 2023 Journal of Dentistry, the authors analyzed age-related dental pulp vascular changes present in mice and humans. The authors developed a new tissue removal method and mapped the vasculature, pericytes and perivascular matrix in the dental pulp via high-resolution 3D imaging.
Young and aged pulps were isolated from mouse teeth, and the vasculature was mapped through a high-resolution section imaging method and a modified tissue clearing method. Human dental pulps and their vasculature were also mapped for study. Young and aged human dental pulps were collected and compared to mouse pulps through RNA sequencing.
Results
Five vascular subtypes of blood vessels were found in the dental pulp of mice, which constituted the arteriole-capillary-venule network. The density of molar capillaries and venules was decreased in aged mice. Among the age-dependent changes in the perivascular pulp matrix, perivascular macrophages were significantly increased, lymphatic capillaries increased, while nerves and extracellular matrix remained unchanged. Furthermore, human vascular patterns formed a complex vascular network. Both human and mouse dental pulps showed an inflammatory state. The TNF pathway and the Rap1 pathway could become promising targets to fight inflammation and promote angiogenesis.
Conclusions
From the data of this study, which must be confirmed in other similar works, it can be concluded that there are five subtypes of blood vessels identified in the dental pulp of mice. In particular, the density of capillaries and venules in the pulps of aged mice is reduced. Furthermore, partial similarities in vascular patterns were observed between the dental pulps of humans and mice.
RNA sequencing analysis revealed that both mouse and human dental pulps show signs of inflammatory state.
 Related articles
Related articles
Oral pathology 24 October 2025
Isolation and characterization of dental pulp stem cells from a supernumerary tooth
Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) were primarily derived from the pulp tissues of primary incisors and permanent third molar teeth, whereas no report to our knowledge has yet been documented on deriving...
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified three 4,000-year-old British cases of Yersinia pestis, the bacteria causing the plague. This is the oldest evidence of the plague in Britain...
By Arianna Bianchi
Endodontic therapy is one of the most used techniques in dentistry, allowing the removal of contaminated or damaged pulp tissue and replacing it with a biocompatible synthetic material to prevent...
Endodontics 29 April 2023
Factors affecting decision-making of direct pulp capping procedures among dental practitioners
A web-based multicentered survey had three purposes: to investigate the factors that affect clinicians' decisions in DPC cases, to determine which method of caries removal is preferred, and to...
News 07 October 2025
New data from Delta Dental highlights how dental care utilization among insured Americans has rebounded following the COVID-19 pandemic but also reveals several lasting shifts in treatment patterns...
 Read more
Read more
Oral pathology 25 November 2025
Virtual microscopy (VM) is a technology for showing microscope slides using computers and could be considered a progression of classic methodology using optical microscopes.
For every assist this season, the insurance provider will donate $25 to TUSDM Cares for Veterans
Products 25 November 2025
J. MORITA USA, a world leader in handpiece technology, has announced the Rotary Master+ Electric Motor. Compatible with Morita TorqTech electric attachments and most competing electric handpieces on...
News 25 November 2025
Let’s be honest: nothing kills the vibe quite like bad breath. However, while 85% of people prefer for someone to tell them if their breath needs some freshening up, only 15% are willing to break...
News 25 November 2025
Vitana Pediatric & Orthodontic Partners (Vitana), a dentist-led dental partnership organization (DPO) focused exclusively on elite pediatric dental and orthodontic practices with operations in...