Functional-aesthetic guided implant placement with double template in association with one-stage computer-guided bone regeneration procedure for aesthetic purposes: 18-month outcomes in a prospective case series
Authors: Silvio Mario Meloni, Marco Tallarico, Milena Pisano
Purpose. To evaluate the outcomes of a new computer-guided surgical approach for prosthetically - and aesthetically - driven implant insertion in horizontally atrophic ridges using a double template concept and one-stage guided bone regeneration (GBR) procedure at 1 year and half after loading.
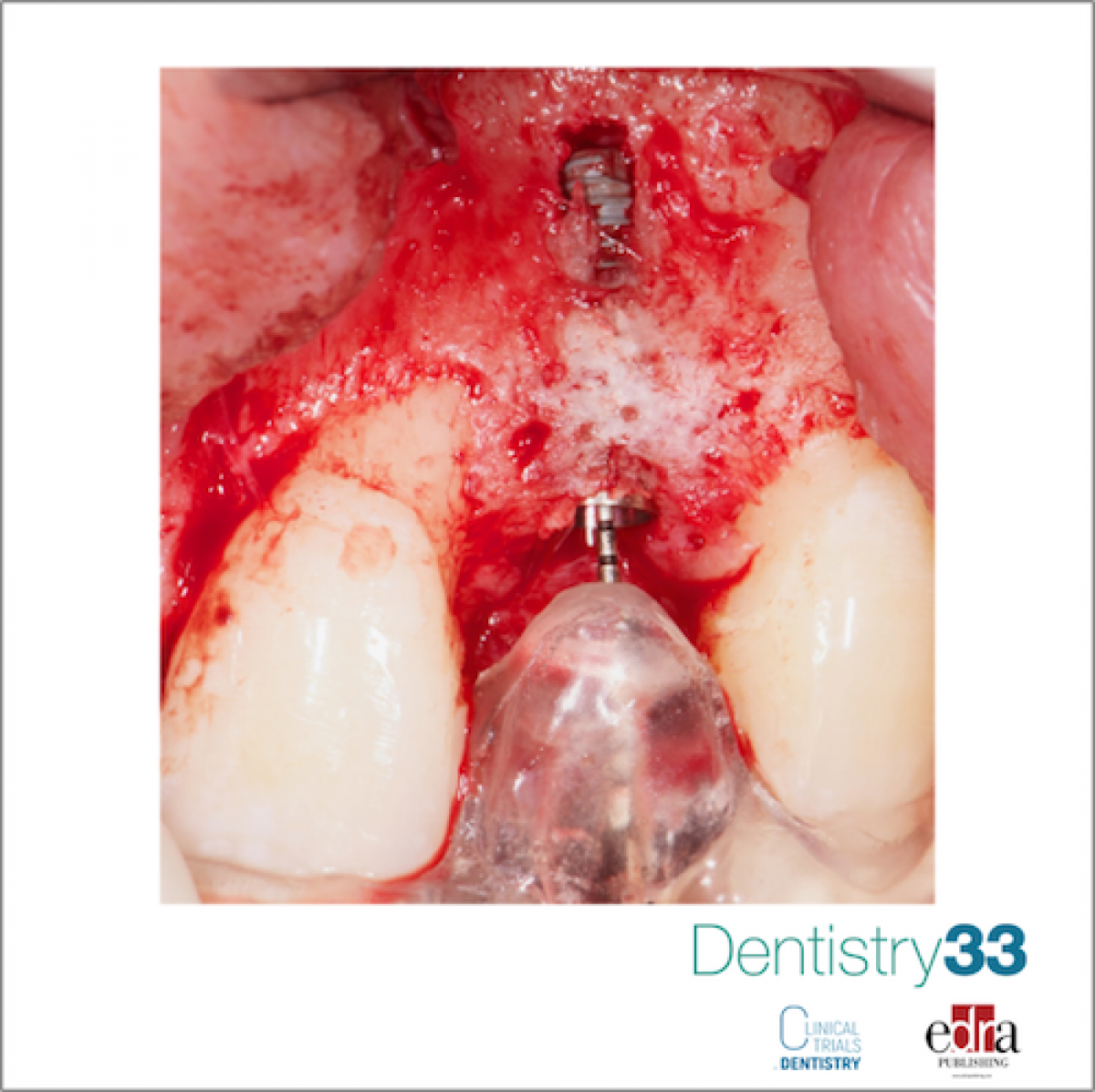
Materials and methods. This study was designed as a prospective case series. Patients in need of rehabilitation with an implant-supported restoration between the upper premolars, Cawood-Howell Class III defects and residual horizontal bone width of less than 6 mm and more than 4 mm were treated with computer-guided implant placement using two templates and simultaneous GBR, and, in cases of bone fenestration with autologous bone, anorganic bovine bone arranged in layers, or in cases of thin buccal bone, using a mix of 20% autologous bone and 80% anorganic bovine bone protected with a resorbable collagen membrane. After 6 months of healing, implants were fitted with temporary screw-retained acrylic resin crowns, and 6 months later permanent screw-retained zirconia-ceramic crowns. Outcome measures were: implant and prosthesis failures, complications, marginal bone level (MBL) changes, periodontal parameters, and pink aesthetic score (PES).
Results. Twenty-one consecutive patients (mean age 39.2 years) received one computer-guided GBR procedure each, with contemporary placement of 25 conical-connection implants. No implants or prostheses failed, and only two minor complications were observed. Mean marginal bone loss fom implant placement up to 18 months after loading was 0.71±0.23 mm (95% CI 0.59 to 0.83 mm); mean BoP was 1.12±0.88 (95% CI 0.77 to 1.47) percent of sites, mean PPD was 2.54±0.49 mm (95% CI 2.35 to 2.73 mm), and mean PES was 11.2±1.2 (95% CI 10.3 to 12.1).
Conclusions. Acknowledging the limitations of this study, the high survival rate and PES seem to validate the use of a double-template approach in association with one-stage GBR and implant placement in atrophic aesthetic areas. Randomised controlled trials are needed to properly evaluate the utility of this technique versus simple free-hand implant placement with no augmentation procedures.
 Tag
Tag
 Read more
Read more
Much like EMTs rushing to the scene after an accident, stem cells hurry to the site of a skull fracture to start mending the damage. A new finding has uncovered the signaling mechanism that triggers...
Products 05 November 2025
SimplyTest has launched a groundbreaking saliva-based test to detect high-risk strains of oral human papillomavirus (HPV), a major cause of oropharyngeal cancers.
News 05 November 2025
Perimetrics, Inc., a dental technology company pioneering quantitative diagnostics, announced today that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted clearance for the InnerView...
News 05 November 2025
On October 15, open enrollment for Medicare began nationwide. Hundreds of thousands of seniors in New Jersey will once again face the challenge of finding the right Medicare coverage, including the...
Digital Dentistry 04 November 2025
Digitalisation is an expanding field in dentistry and implementation of digital teaching methods in dental education is an essential part of modern education.