Prosthetic failures in single implant-retained crown: a literature review
Edoardo Mancuso
Implant placement has become a well-established and highly successful therapy in the rehabilitation of partially and fully edentulous patients. In this context, missing teeth can either be replaced by fixed or by removable implant-supported prostheses. However, high survival rates and low complication rates of the prostheses are an important prerequisite for the general success of treatment, as failures of the prosthesis may result in failures of the entire implant rehabilitation.
A literature review, written by Professor Sailer and her group was recently published on periodontology 2000 with the aim to address and discuss the most frequent prosthetic complications for implant prostheses, including risk factors for the complications, associations with early and late implant survival, and the prevention and management of complications. The articles analyze numerous systematic reviews written in recent years considering the survival and complication rates of implant-retained prostheses.
The article first investigates the single implant-retained crown different material options. Metal-ceramic crowns have been the gold standard for decades, and today, all-ceramic implant crowns (lithium disilicate or zirconia ceramics) are successfully used as alternatives. For these types of prosthesis, is reported that the overall 10-year survival rate is at 95.2%, independently of which crown material is used. The article adds that the overall 10-year survival rate of the crowns is slightly lower at 89.4%. The crown survival rate might be influenced by the materials used for their fabrication. Is then reported that the 5-year survival rate of veneered alumina crowns is 96.8%, for veneered zirconia crowns it is 91.6%, while for monolithic lithium disilicate it is 91%. Hybrid resin-matrix ceramic crowns only survived in 67%8 of cases.
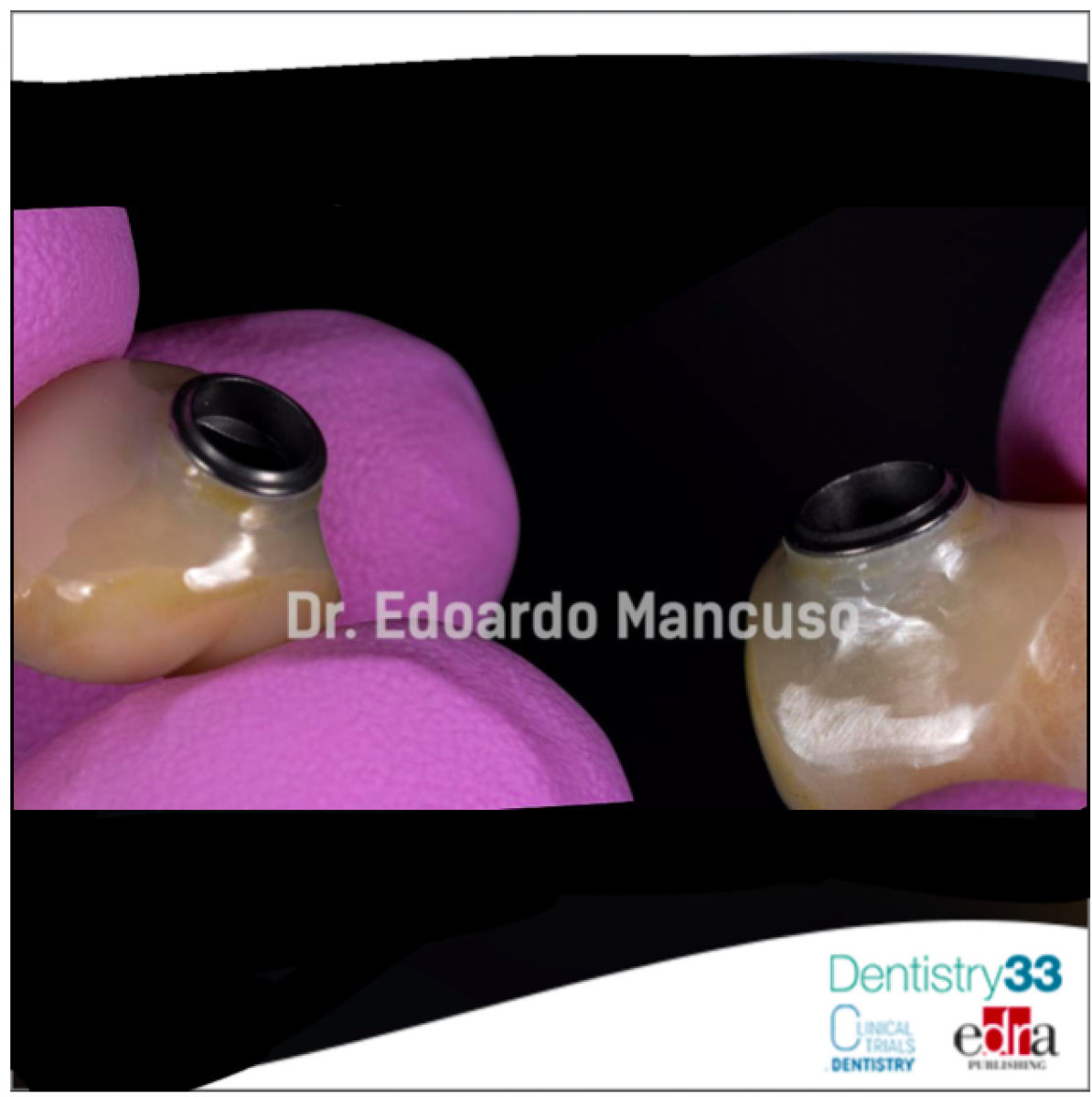
Another complication analyzed in the review is screw loosening of the implants that still remains the most frequent technical problem with single implant-retained crowns, with a cumulative 5-year complication rate of 8.8%. As it is explained in the research, although numerous developments of new screw designs and materials have led to a reduction of this problem over time, the stability of the screw joint is greatly influenced by the prosthetic implant axis. It is shown that more screw loosening occurred with angulation-correcting implants than with straight implants. Hence, it is suggested a deep and appropriate three-dimensional position planning of the implant to decrease the risk of complications.
Chipping of the veneering ceramic is reported to be the third most frequent complication with fixed implant prostheses. Veneering ceramics are applied to different metallic or ceramic framework materials, establishing a bond between the veneering ceramic and the framework material important for clinical performance. The review analyzes several factors influencing the risk of chipping of the veneering ceramic. The first factor enunciated is the framework material that could play an important role in preventing high chipping rates. It has been shown that veneered alumina or lithium disilicate crowns experienced chipping in 1.8% and 3.5% of cases after 5 years of function, respectively, whereas veneered zirconia crowns exhibited very high chipping rates of 11.8% over the same time frame. Moreover, also the occlusion/function are taken into consideration to the long-term integrity of the veneering ceramic, as the forces applied to implant restorations are significantly higher than those applied to tooth-borne restorations. The paper explains how the occlusal load on implant-retained crowns is almost nine times higher than when supported by natural teeth. Given the above, it is clear how the chipping of the veneering ceramic may not be avoided as a complication at veneered restorations. Therefore, Prof. Sailer indicates as the current concepts involve avoiding veneering materials by fabricating restorations out of monolithic ceramics.
The article concludes by evaluating Esthetic problems, a reason for the failure of implant treatment in specific clinical situations. A discoloration of the peri-implant mucosa, for example, caused by implant parts or components, can be a major problem with implants in the esthetic zone. Therefore, recent studies are cited in the article, where the main focus is on the effect of different restorative materials on the color of the peri-implant soft tissues.
It has been shown that metallic abutments and metal-ceramic implant crowns caused a grayish discoloration of the mucosa. It is then clarified that the amount of discoloration and its effect on esthetic outcomes may be associated with the thickness of the mucosa. From the literature scrutinized, a grayish shine-through of the metallic implant components might be manifested in cases with thin soft tissues of < 2 mm. The color of tissues with thicknesses of > 2 mm was not influenced by the abutment or restorative materials. Hence, in esthetically important clinical situations, could be recommended to use whiteish ceramic zirconia abutments and ceramic implant restorations, or to increase the thickness of the peri-implant mucosa to values > 2 mm with soft tissue grafts.
The review concludes by confirming that technical complications cannot be avoided in implant-retained prostheses and that technical complication can lead to the failure of implant treatment. However is suggested, in order to reduce the risk of failure, to perform a comprehensive pretreatment diagnostic work-up, including defining the prosthetic goal with the aid of a wax-up or set-up and to define the associated ideal prosthetic-oriented three-dimensional implant position.
Is also to always keep in mind that selection of the ideal type of prosthesis, including the respective implant components and materials, is crucial for the clinical long-term success of the reconstruction.
For additional informations: Prosthetic failures in dental implant therapy
 Related articles
Related articles
Prosthodontics 11 September 2025
New paradigms in prosthodontic treatment planning: a literature review
New treatment modalities have expanded the choices available to prosthodontists and their patients.
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 03 September 2025
Oral hygiene care for residents with dementia: a literature review
This paper presents a literature review of oral hygiene care for adults with dementia in residential aged care facilities
Restorative dentistry 24 January 2025
The aim of this review was to update the literature with regard to the digital methods available by CEREC Chairside system to register and design the occlusion, to report their efficacy and technical...
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 26 August 2024
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is the most common nosocomial infection reported among mechanically ventilated patients.
Oral surgery 23 July 2024
Primary intraoral melanoma is a rare neoplasm with a poor prognosis, accounting for 1% to 8% of all melanoma in Europe and the United States.
 Read more
Read more
Restorative dentistry 13 February 2026
Integrating Laser Technology with CAD/CAM for Advanced Smile Design in Dentistry
This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of integrating laser treatment with CAD/CAM systems in restoring dental function and aesthetics in a 35-year-old male patient suffering from bruxism.
Editorials 13 February 2026
The SRG is UFCD’s student‑run chapter of the American Association for Dental, Oral and Craniofacial Research, or AADOCR.
Products 13 February 2026
Parkview Dental, a leading Dental Support Organization committed to providing comprehensive management services to dental practices, announced the appointment of Lisa Burris as its new Director of...
News 13 February 2026
DentaQuest, part of Sun Life U.S., recently announced the appointment of Dr. Ronke Ogunbameru as dental director for Texas, where the organization covers more than 1.4 million Medicaid and CHIP...
News 13 February 2026
Unlock CE Credits by Reading One Move Makes All the Difference
Dental professionals can now earn 4 hours of continuing education credit by reading One Move Makes All the Difference by Martin R. Mendelson, DDS, FIADFE, CPC. Dr. Mendelson and Metamorphosis...