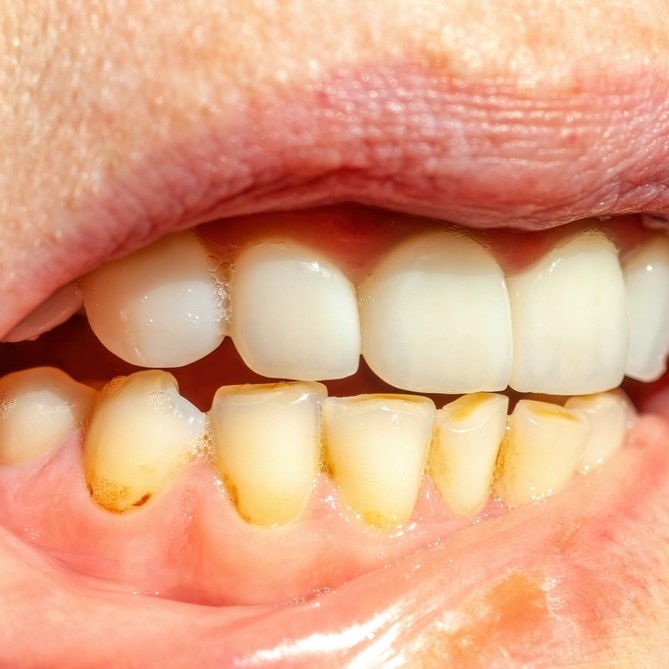
Garlic (Allium sativum L.) Bioactives and Its Role in Alleviating Oral Pathologies
Garlic (Allium sativa L.) is a bulbous flowering plant belongs to the family of Amaryllidaceae and is a predominant horticultural crop originating from central Asia.
Garlic and its products are chiefly used for culinary and therapeutic purposes in many countries. Bulbs of raw garlic have been investigated for their role in oral health, which are ascribed to a myriad of biologically active compounds such as alliin, allicin, methiin, S-allylcysteine (SAC), diallyl sulfide (DAS), S-ally-mercapto cysteine (SAMC), diallyl disulphide (DADS), diallyl trisulfide (DATS) and methyl allyl disulphide.
A systematic review was conducted following the PRISMA statement. Scopus, PubMed, Clinicaltrials.gov, and Science direct databases were searched between 12 April 2021 to 4 September 2021. A total of 148 studies were included and the qualitative synthesis phytochemical profile of GE, biological activities, therapeutic applications of garlic extract (GE) in oral health care system, and its mechanism of action in curing various oral pathologies have been discussed. Furthermore, the safety of incorporation of GE as food supplements is also critically discussed.
To conclude, GE could conceivably make a treatment recourse for patients suffering from diverse oral diseases.
Natural products and traditional medicines are of substantial importance. Modern medicine may not be the sole antidote for the ailments prevailing today. Therefore, people positively perceive ‘back to nature’ approaches like phytotherapy as plant products are rich in pharmaceuticals. Allium sativum, which is well-known as garlic, belongs to the family Amaryllidaceae. It has been known to humankind for many ages for its bioceutical properties. Garlic is indigenous to central Asia and has long been an important crop in the Mediterranean region and as seasoning in continents like Africa and Europe. India ranks second in garlic production, where the first is China.
Allium sativum is conventionally employed to cure infections, common cold, diabetes, and heart diseases. Ancient Egyptians used garlic for both culinary and curative purposes. In Egypt, garlic was fed to the working class involved in heavy labour during the construction of the pyramids and in Greece, during the earliest Olympics, it was provided as “performance enhancers” in competitive athletics, meanwhile, among the Romans, garlic was known to purify the arteries. In India, the excellent surviving medical book, Charaka- Samhita, suggested the consumption of garlic to treat heart disease and arthritis 1900 years ago.
Fresh raw garlic bulbs comprise of ∼66% water, ∼27% carbohydrate, ∼2.5% protein, ∼1.3% amino acids, ∼1.6% fiber, fatty acids, phenols, trace minerals and more than 34 (∼2.4%) sulfur-containing compounds. The phytochemicals majorly belong to polyphenols, amino acids, benzenoids, sulfur-containing compounds, fatty acyls, glycerophospholipids, heteroaromatic compounds, indoles, phenol lipids, pyrrolizines, quinolines, steroid derivatives, tetrahydrofurans and other compounds. The beneficial effect of GE on health could be ascribed to the phytochemicals generated during the extraction process, like alliin, methiin and SAC. When garlic is ground, the structure of the sulphur components are altered into various organosulfur compounds. The primary sulfur-containing constituents in whole, intact garlic are the SAC, SAMC, N-alfa-fructosyl arginine, glutamyl 7 cysteines and S allyl cysteine sulfoxides, including alliin. Enzymes in garlic like allinase will convert alliin into allicin, which has antimicrobial action against oral pathogens and confines promise to cure periodontal diseases, dental caries and oral cancers. Volatile compounds in finely ground garlic and essential oil include DAS, DADS, DATS, methyl allyl disulfide, methyl allyl trisulfide, 2-vinyl-1, 3-dithiin, 3-vinyl-1, 2-dithiin and ajoene.
Clinically, garlic has been established for reducing blood pressure, cholesterol, and amounts of glucose, as well as for the prohibition of arteriosclerosis and cancer. Lack of regular oral sanitation results in accretion of dental plaque and calculus, which are the critical etiology reasons for gingivitis and periodontitis. Caries is one of the most common oral infectious diseases widespread globally in every segment of population and the development is influenced by dietary components which interfere with etiological agents Streptococcus sobrinus and Streptococcus mutans. In recent years, active research to find generally recognized as safe compounds is ongoing with goal to prevent and to reduce caries and number of foods e.g., in vivo studies of garlic extract has shown potential anticaries activities against pathogen mutans group Streptococci. Globally, second most common diseases are periodontitis, prevalent at 30 to 50% of United States population. Novel ideas are emerging with new investigations, one of them is aged garlic extract (AG) which has been used for medicinal purposes since 3000 B.C. Recently, a clinical trial reported that 18 months use of AG reduced the periodontitis level as compared to the placebo group. Garlic is well acknowledged for its dominant anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal and antimutagenic properties. These play a significant role in alleviating various oral diseases like pulpitis and periodontitis gingivitis, stomatitis, herpes labialis, oral candidiasis, dental plaque and oral cancers. It is a challenge for researchers worldwide to make proficient use of garlic and relish its maximum health benefits as it is the most inexpensive way to prevent or alleviate the effects of oral diseases.
Authors: Minnu Sasi, Sandeep Kumar, Manoj Kumar, Sandhya Thapa, Uma Prajapati, Yamini Tak, Sushil Changan, Vivek Saurabh, Shweta Kumari, Ashok Kumar, Muzaffar Hasan, Deepak Chandran, Radha, Sneh Punia Bangar, Sangram Dhumal, Marisennayya Senapathy, Anitha Thiyagarajan, Ahmad Alhariri, Abhijit Dey, Surinder Singh, Ravi Pandiselvam, Mohamed Mekhemar
Source: https://www.mdpi.com/
 Related articles
Related articles
Products 05 February 2026
Harcum College is stepping up to promote oral health and wellness in the community with its upcoming Sealant Day, a day dedicated to providing free preventive dental care.
Products 14 October 2025
How oral health professionals can better support patients’ oral and systemic health with more microbiome-friendly oral care
Digital Dentistry 16 May 2025
Digital Dentistry & Material Science: Sculpting the Future of Oral Care- A Narrative Review
This review examines the dynamic intersection of digital dentistry and material science, exploring current trends and advancements shaping modern dental practice.
Elevate Oral Care’s Povi•One and FluoriMax Varnish Convenience Kit is an easy-to-use prevention product that delivers the convenience of a market-leading varnish, and a potent bacteria-killing...
News 14 February 2025
Greenland Advanced Oral Care is proud to announce the addition of Dr. Eryn Huber to its expert dental team.
 Read more
Read more
Oral surgery 06 February 2026
Oral epithelial dysplasia and the development of invasive squamous cell carcinoma
Oral epithelial dysplasia, the histopathologic marker of a premalignant disorder of the mouth mucosa, may present clinically as leukoplakia, erythroplakia, or leukoerythroplakia.
Editorials 06 February 2026
Dr. James E. Newman of the Department of Restorative Dentistry has been named as the 2026 recipient of the School of Dentistry’s Martin Luther King, Jr. Community Service Award.
PDS Health, a leading integrated healthcare support organization, reported meaningful progress in 2025 as it expanded access to integrated dental-medical care, strengthened early detection, and...
News 06 February 2026
3Shape today announced the appointment of Rasmus Hannemann as Senior Vice President, Portfolio & Product Strategy, effective 9 March. Rasmus will join the senior leadership team and will report...
News 06 February 2026
Dental Intelligence, a leading provider of practice performance solutions for the dental industry, recently announced that the company’s Board of Directors has appointed Scott Johnson as Chief...