Dental root caries: risk predictors
Simona Chirico
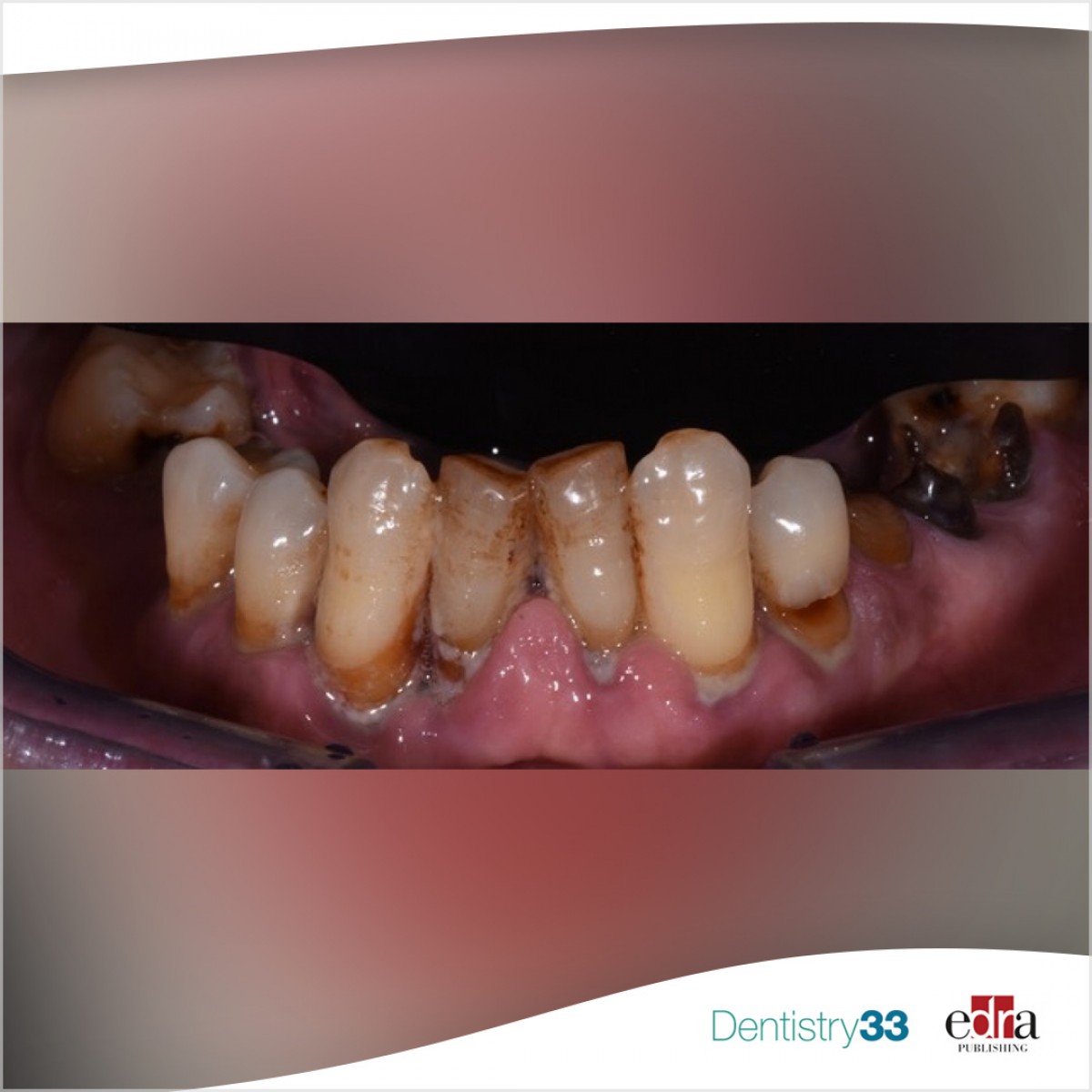
Root caries results from the dissolution of minerals in dentine by the acids produced by bacteria, since dentine have a much lower mineral content when compared to enamel, the risk factors associated with the development of root caries and coronal caries may be different. It is estimated that one-third of the geriatric population is subjected to root caries. Since people are retaining more teeth the management of this dental disease in older adults will become an important dental public health issue because of the high need for prevention and treatment.
The aim of this systematic review was to identify the risk predictors of new root caries and to describe their relationship with the incidence and increment of new root caries.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The electronical research was done in different databases using different key words such as “root caries”, “root decay”, “risk factor”, “risk predictor”, “adult” and “elder” . The inclusion criteria were:
1) papers on longitudinal observational studies;
2) reporting on at least one risk predictor of root caries;
3) the publication date was between 1 January 1990 and 31 January 2019.
RESULTS
The review includes 19 papers, 4 were classified as high quality, 13 as moderate quality and 2 as low . Risk predictors of root caries:
Socio-demographic factors:
Ten studies had assessed the correlation between DF-root and socio-demographic factors. Among the 5 studies that investigated the association between gender and root caries, only 1 study found a higher male predilection. Regarding ethnicity and race, 1 study reported that Asians had the highest risk for developing new root caries compared with Caucasians, African-Americans and the Hispanics while another study did not. Among the 5 studies that included education level, only 1 reported a negative correlation with the incidence of DF-root .
General health factors
Six studies assessed the correlation between DF-root and general health factors. Among the 3 studies assessing medication factors, 2 pointed out that taking medicine increased the incidence of DF-root. General health behavior A positive correlation between the use of tobacco and new DF-root was reported in 5 of the 7 studies. Fluoride exposure Only 1 study assessed the correlation between use of fluoride and root caries. The authors reported that people who avoided fluoride product had the highest risk of developing new DF-root.
Oral clinical parameters
Three studies found that having more root surfaces with recession or more gingival recession was associated with a higher incidence of DF-root. As the amount of gingival recession increases with age among older adults, this can partly explain why age was consistently reported to be a predictor of root caries. Regarding oral hygiene or plaque on root surfaces, 4 of the 5 studies found a positive correlation
Salivary parameters
Two of 4 studies found a higher risk of developing new DF-root among people who had a lower salivary flow.
CONCLUSIONS
According to this review is possible to say that people who are older, in lower socio-economic status or tobacco users, and those with more caries experience, gingival recession and poorer oral hygiene are at higher risk of developing new root caries.
For additional informations:
Risk predictors of dental root caries: a systematic review.
 Related articles
Related articles
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 19 November 2024
Oral hygiene in the prevention of caries and periodontal disease
While some periodontal disease may be as old as mankind itself, caries as a public health problem appeared with the development of flour and sugar mills, and the universal access to fermentable...
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 26 August 2024
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is the most common nosocomial infection reported among mechanically ventilated patients.
Adams School of Dentistry’s Amy Lawson, DDS ’27, and Ricardo Padilla, DDS, were recently invited to represent ASOD at the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center’s “Exploring Cancer Spring...
Prevention is to be considered the most significant tool for involving the assisted person in being the responsible protagonist of his or her lifelong health project.
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 24 January 2024
Clinical prevention approaches in the management of implant patients
The failure of implant therapy is characterized by the presence of visual signs of inflammation and bleeding on probing, mucositis (PIM) and in cases of peri-implantitis (PI), loss of supporting...
 Read more
Read more
Much like EMTs rushing to the scene after an accident, stem cells hurry to the site of a skull fracture to start mending the damage. A new finding has uncovered the signaling mechanism that triggers...
Products 05 November 2025
SimplyTest has launched a groundbreaking saliva-based test to detect high-risk strains of oral human papillomavirus (HPV), a major cause of oropharyngeal cancers.
News 05 November 2025
Perimetrics, Inc., a dental technology company pioneering quantitative diagnostics, announced today that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted clearance for the InnerView...
News 05 November 2025
On October 15, open enrollment for Medicare began nationwide. Hundreds of thousands of seniors in New Jersey will once again face the challenge of finding the right Medicare coverage, including the...
Digital Dentistry 04 November 2025
Digitalisation is an expanding field in dentistry and implementation of digital teaching methods in dental education is an essential part of modern education.