Artifact-resistant superimposition of digital dental models and cone-beam computed tomography images
Purpose
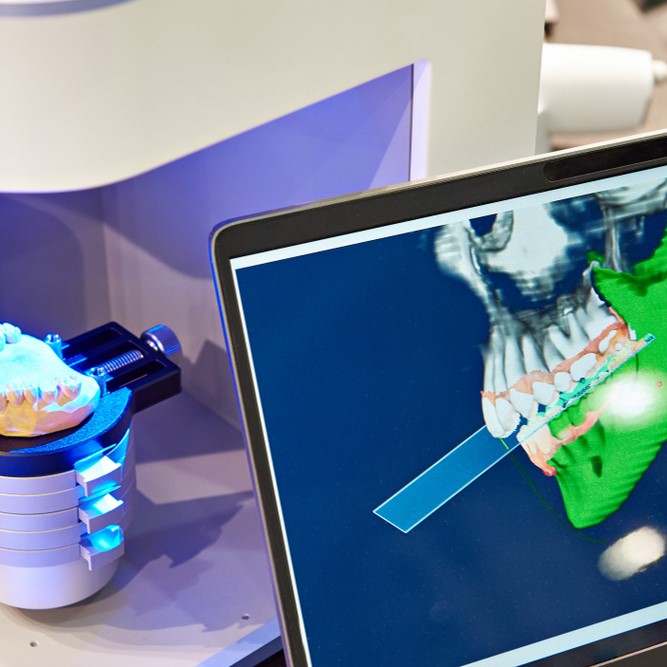
Combining the maxillofacial cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) model with its corresponding digital dental model enables an integrated 3-dimensional (3D) representation of skeletal structures, teeth, and occlusions. Undesired artifacts, however, introduce difficulties in the superimposition of both models. We have proposed an artifact-resistant surface-based registration method that is robust and clinically applicable and that does not require markers.
Materials and Methods
A CBCT bone model and a laser-scanned dental model obtained from the same patient were used in developing the method and examining the accuracy of the superimposition. Our method included 4 phases. The first phase was to segment the maxilla from the mandible in the CBCT model. The second phase was to conduct an initial registration to bring the digital dental model and the maxilla and mandible sufficiently close to each other. Third, we manually selected at least 3 corresponding regions on both models by smearing patches on the 3D surfaces. The last phase was to superimpose the digital dental model into the maxillofacial model. Each superimposition process was performed twice by 2 operators with the same object to investigate the intra- and interoperator differences. All collected objects were divided into 3 groups with various degrees of artifacts: artifact-free, critical artifacts, and severe artifacts. The mean errors and root-mean-square (RMS) errors were used to evaluate the accuracy of the superimposition results. Repeated measures analysis of variance and the Wilcoxon rank sum test were used to calculate the intraoperator reproducibility and interoperator reliability.
Results
Twenty-four maxilla and mandible objects for evaluation were obtained from 14 patients. The experimental results showed that the mean errors between the 2 original models in the residing fused model ranged from 0.10 to 0.43 mm and that the RMS errors ranged from 0.13 to 0.53 mm. These data were consistent with previously used methods and were clinically acceptable. All measurements of the proposed study exhibited desirable intraoperator reproducibility and interoperator reliability. Regarding the intra- and interoperator mean errors and RMS errors in the nonartifact or critical artifact group, no significant difference between the repeated trials or between operators (P < .05) was observed.
Conclusions
The results of the present study have shown that the proposed regional surface-based registration can robustly and accurately superimpose a digital dental model into its corresponding CBCT model.
Authors: Hsiu-Hsia Lin, Wen-Chung Chiang, Lun-Jou Lo, Sam Sheng-Pin Hsu, Chien-Hsuan Wang, Shu-Yen Wan
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/
 Related articles
Related articles
Orthodontics 08 October 2025
The field of orthodontics in its new era is venturing ahead to more up-to-date technological point of view.
Fracture of shaping instruments within root canals is a common undesirable incident in endodontics. These fractures can prevent proper preparation, disinfection and obturation of the canal. They can...
Digital Dentistry 09 June 2023
Association between intracanal medicament radiopacity, streak artifact production using CBCT
This study aimed to calculate the correlation between the radiopacity levels of various intracanal medicaments and radiolucent streak formation using cone-beam computed tomography.
This meta-analysis sought to identify the in vivo prevalence and influencing factors of middle mesial canal in mandibular first and second molars based on cone-beam computed tomography scans.
A study in the Angle Orthodontist evaluated the validity and reliability of marginal bone level measurements made on CBCT images produced using two reconstruction techniques, two viewing modes, and...
 Read more
Read more
Editorials 05 December 2025
Rural dental residency program receives a lifeline from donor organizations
When federal funds to HSDM’s rural residency program went unpaid, a coalition of regional partners stepped up to secure the program’s future.
Products 05 December 2025
VideaHealth, the leading dental AI platform, recently announced the appointment of Austen Asadorian as Chief Revenue Officer. With two decades of experience scaling high-performing organizations,...
News 05 December 2025
VELMENI, a global leader in artificial intelligence (AI) solutions for dental care, and Jazz Imaging, an innovative provider of dental imaging systems, recently announced a strategic partnership...
News 05 December 2025
BIOLASE, the global leader in dental lasers, announced its participation in the 2025 Greater New York Dental Meeting (GNYDM), taking place November 28–December 3 in New York City.
Biomimetic has emerged as a multi-disciplinary science in several biomedical subjects in recent decades, including biomaterials and dentistry.