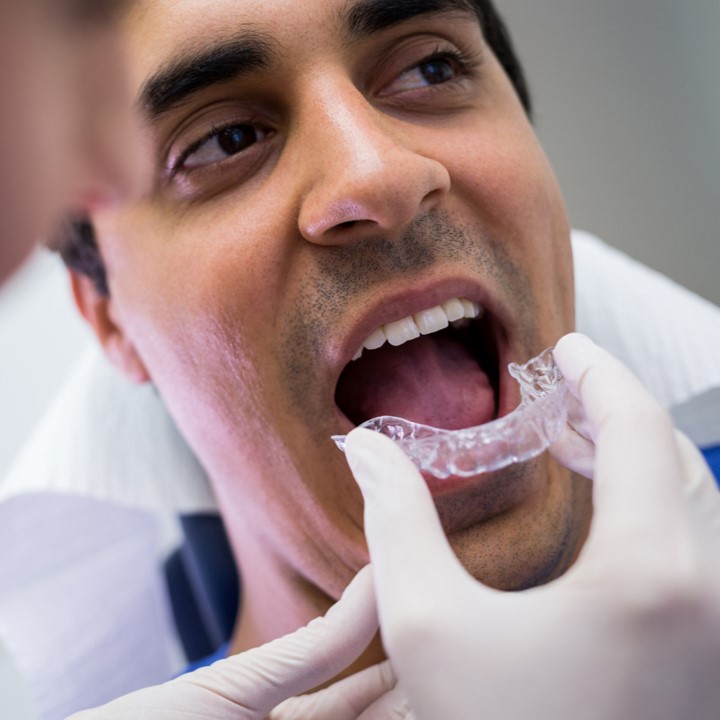
Partial Dentures: Evaluating Contemporary Materials, Functional Outcomes, and Patient Adaptation
Partial dentures continue to play a key role in the provision of prosthodontic services to restore the functionality and the appearance of partially edentulous patients.
Developments in materials, digital fabrication, and biomechanical design over the last several decades have transformed the approach that clinicians use in the process of planning treatment.
Knowledge of these developments together with the clinical and patient-centered variables that affect the outcomes is needed to offer a predictable and long-term recovery of oral functionality.
Introduction
Partial edentulism is not a simple case that can be solved by replacement of missing teeth. The loss of posterior or anterior units may result in the loss of occlusal stability and progressive bone resorption, as well as in the speech and mastication.
Besides these physiological outcomes, psychosocial ones, including a lack of self-confidence and quality of life, also testify to the necessity of proper restorative practices.
These issues have been traditionally resolved through the use of dentures, whereas modern-day dentistry provides a series of materials and fabrication methods that need to be evaluated.
Clinical Implications of Partial Edentulism
The loss of teeth causes a cascade of biomechanical alterations. Surrounding teeth are likely to slide or turn into the edentulous ridge, which changes the contact points and occlusal forces. In the long run, loss of vertical dimensions may be experienced in the temporomandibular joint and support of the face.
Masticatory efficiency is impaired and this could affect the food consumption and nutrient intake. Social interaction can also be affected by speech changes, especially in the loss of anterior teeth.
To overcome these multifactorial implications, there is a need to address it through prosthetic solutions that do not destroy the existing dentition, but instead stabilize the occlusion.
Advances in Partial Denture Materials and Fabrication
The cobalt-chromium traditional frameworks and acrylic bases were known due to their rigidity and strength. Modern flexible polymers e.g. polyamide based products have, however, provided broader clinical choices. They provide better comfort, appearance and lower visibility of the clasps.
Fit and occlusion precision can now be increased due to the use of digital technologies, such as intraoral scanning and CAD/CAM fabrication. Such developments also increase distribution of stress in abutment teeth and soft tissue and reduce localized traumas and increase the life of the prosthesis.
Treatment Planning Considerations
The therapy requires thorough examination of the remaining teeth, periodontal conditions, occlusions, and the anatomy of a patient.
The position of the clasp, the preparation of the rest seat, and the occlusal should be made to the needs of the patient in order to reduce unnecessary stress. Multidisciplinary approach is more effective in the cases of complexities, especially when it comes to the case of compromised abutment teeth or a combination of periodontal-prosthodontic issues.
The design should also be informed by patient expectations, lifestyle issues, and future restorative plans (i.e. eventual placement of implants).
Functional Performance and Patient Adaptation
Patients respond differently to the use of dentures, but in most cases, adaptation takes place after a few weeks. There are early mastication or phonetics challenges which reduce with time as the oral muscles have adapted.
It has been found that masticatory efficiency increases greatly when using dentures which are fitted properly, and this restores an acceptable percentage of natural chewing performance. The clarity of speech, particularly in the cases of the anterior replacement, generally improves as patients practice and become more confident.
The training of insertion, removal, and proper use is key to successful adaptation.
Maintenance and Long-Term Prognosis
The sustainability of functions depends on proper hygiene habits and frequent expert inspection. The patients should also clean their prostheses each day with non-abrasive brush and prescribed cleaning agents without exposing them to too much heat or other harsh substances that can deform materials.
Fit, tissue health, and wear on abutment teeth must be evaluated clinically, and relining or replacement done as needed. Ordinary problems, including clasp fatigue, slight tissue irritation, or breaking of acrylic elements can generally be addressed through timely action.
Misconceptions and Clinical Challenges
Dentures are not always seen as comfortable and are often thought to be better with older patients. However, in the real sense, with appropriate designs and manufacturing, they provide discrete and useful solutions to adults of all ages.
There are still clinical issues, especially when maximum retention and aesthetics are required in conditions of little abutment support or high aesthetic requirements.
These issues explain the need to plan carefully and educate patients instead of possible shortcomings of the prostheses.
Future Directions in Prosthodontics
New polymer composites that have stronger and more transparent properties keep on enhancing the aesthetic results. Combination of additive manufacturing methods and digital workflow is suggested to lead to shorter production time, as well as more accurate fit.
New possibilities of stability and distribution of the load are available in hybrid methods including implant-assisted dentures.
The above developments indicate a future where dentures will be able to become even more lifelike than natural dentition and at the same time be accessible to a wide range of patients.
Conclusion
Dentures are still an element of the restorative capacity of the oral functions, appearance, and patient self-esteem.
Modern materials and fabrication techniques have gone a long way to enhance their functionality and outlook, yet effective results remain to be achieved through effective diagnosis, careful design and subsequent maintenance.
With the current development of restorative dentistry, partial dentures will still be an essential and versatile method of treating partial edentulism and maintaining long-term oral health.
 Related articles
Related articles
By Lorenzo Breschi and Annamaria Forte
AI models have been applied to mapping the finishing line of tooth preparations or assisting in tooth anatomy selection for the automated design of dental restorations by using CAD methods.
Prosthodontics 04 May 2021
Posterior Fixed Partial Dentures: how Polymeric Restorative Materials influence stress distribution
Interim dental restorations are used during prosthetic rehabilitation in order to provide function, phonetics and aesthetics to the patient during a short period of the treatment while the final...
 Read more
Read more
Periodontology 14 November 2025
This study was carried out to assess the oral hygiene awareness and practices amongst patients visiting the Department of Periodontology at Gian Sagar Dental College and Hospital, Ramnagar (Patiala).
Editorials 14 November 2025
Penn Dental Medicine shared its expertise in caring for persons with disabilities with dental care providers from throughout Jamaica at a 1 ½ -day hands-on continuing education program, held October...
News 14 November 2025
Dr. Thomas M. Paumier, a dentist in Canton, Ohio, is the new President-Elect of the American Dental Association (ADA). Dr. Paumier was elected at the ADA House of Delegates meeting in Washington,...
News 14 November 2025
Premier Dental Implants & Prosthodontics is proud to announce the opening of its newly renovated dental office and the launch of its new website
News 14 November 2025
Henry Schein One and AWS Collaborate to Transform Global Dentistry with Generative AI
Industry leaders join forces to bring advanced AI capabilities to dental technology platforms — redefining patient care, clinical efficiency, and practice performance worldwide