Minimally invasive class II restoration of an upper premolar: a clinical case
Author: A. Colella
Thanks to the introduction of new technologies and more performing materials, in recent years Restorative Dentistry has focused on a less invasive clinical approach. In the age of adhesion, preparing a class II cavity allows to preserve a greater share of healthy tissue than in the past, however the preparation of the cervical step and proximal margins can be a delicate procedure due the risk of damaging the adjacent tooth. Given these premises, protecting the healthy tooth becomes imperative.
In this step-by-step procedure of a class II restoration of an upper premolar the use of special plastic wedges with a steel insert reduces the number of steps and the time required to carry out the procedure, making it safe and predictable.
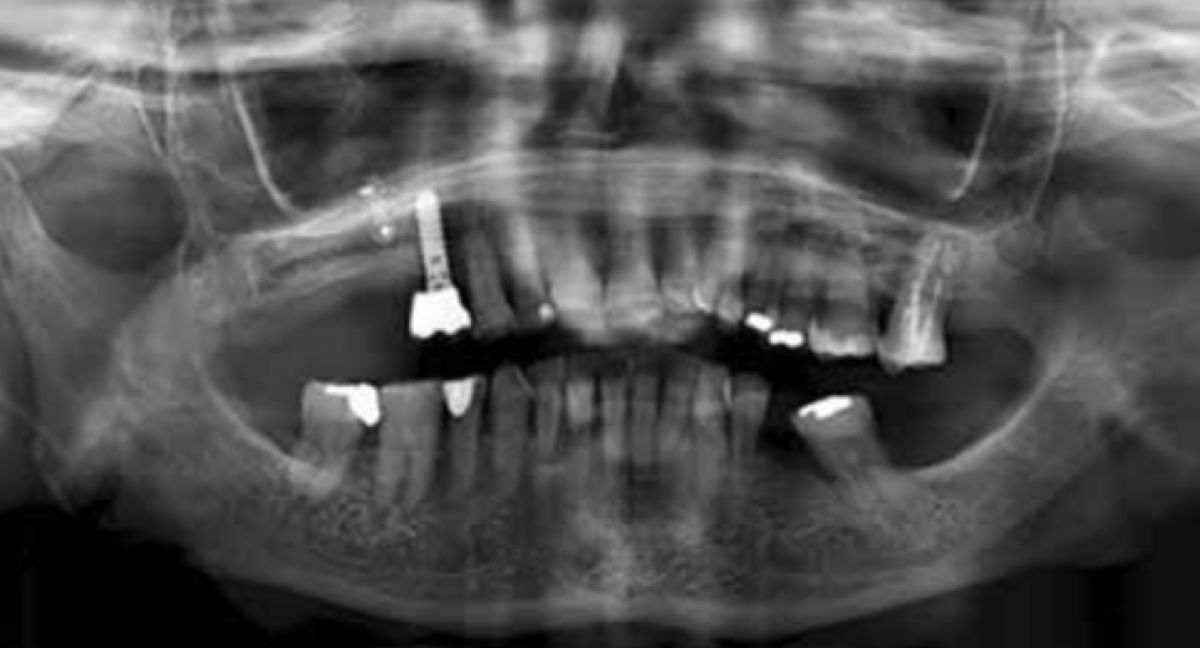
A female patient aged 16, in a good state of systemic health, comes to my attention complaining about food impact and difficulty in using dental floss in the upper left sextant. On physical examination, a significant accumulation of plaque is seen at the interproximal level. The radiographic examination performed by bitewing revealed a carious lesion of type D3 of tooth 2.5 according to the classification of Marthaler and Lutz. (Fig 1)
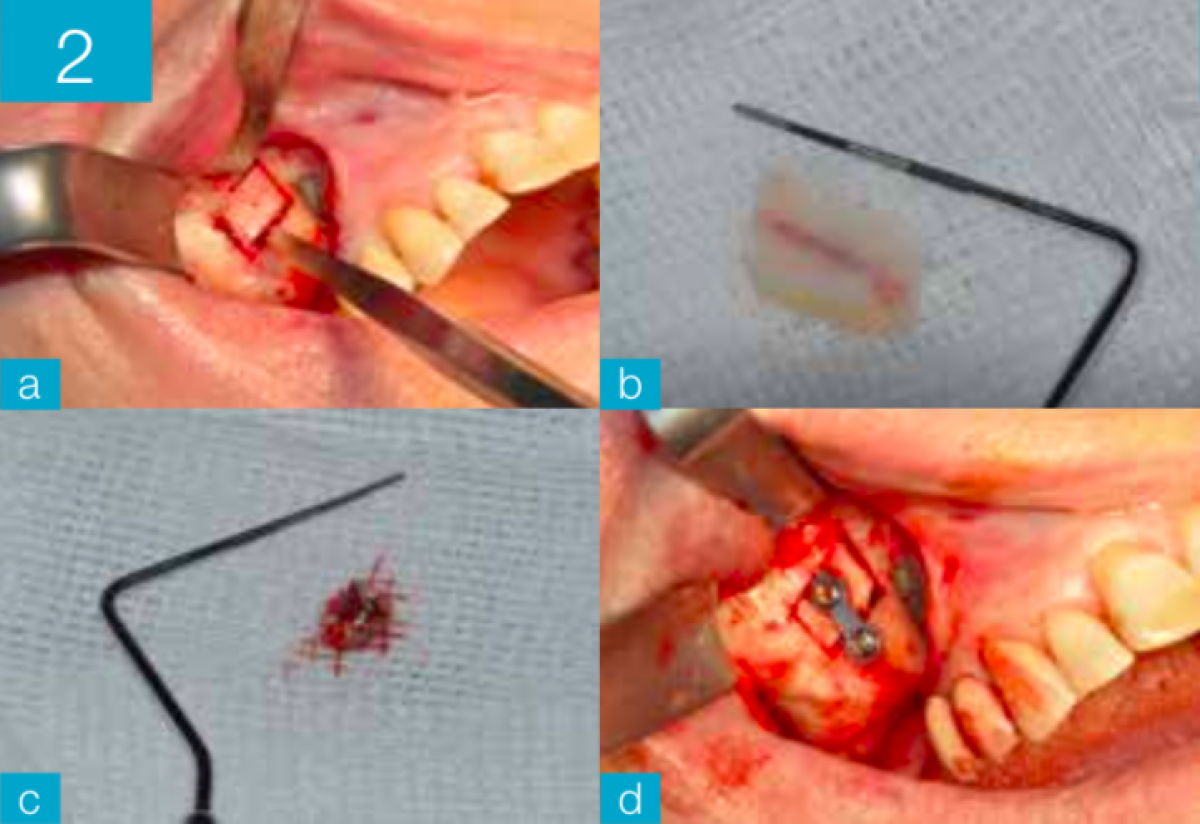
After isolating the entire quadrant with rubber dam, a FenderWedge (Directa) was positioned between the elements 2.4 and 2.5, ie a plastic wedge equipped with a steel insert which, in addition to protecting the dam and gently separating the teeth, prevents damage to tooth 2.4 during cavity preparation of tooth 2.5. The FenderWedge was inserted with the help of a dental tweezer and selected from 4 different sizes to ensure the correct separation between two contiguous elements, up to the marginal ridge. The latter is not demolished initially but access to the lesion is obtained by opening the cavity towards the center of the tooth. (Figure 2)
Once the caries was removed, the finishing stage of the cervical step and the buccal and palatal margins of the tooth in question was performed. The resulting cavity is sufficient to properly carry out a restoration with easily refinable and polished edges. At this point the FenderWedge was removed, the adhesive procedures were completed, taking care to protect the adjacent teeth and a second wedge was inserted. The FenderMate (Directa) is equipped with a sectional matrix which in this case perfectly adapts to the cavity design without having to apply an additional separator ring as in traditional sectional matrix systems. (Figure 3,4)
Thanks to the intimate contact between the wedge and the cervical step, it was possible to convert a class II into a simpler class I without incurring in cervical overhangs which make the subsequent finishing and polishing phases longer and more complex, due to the difficulty to remove polymerised composite in a critical area without affecting the contact area just restored. The reconstructed interproximal wall therefore has a close contact and a natural anatomy that make the subsequent steps simpler and more predictable. (Figure 5)
An “all-in-one” adhesive (Universal Adhesive, Parkell) and a thin layer of flowable composite (LC Fill, Parkell) were applied to the bottom of the cavity to avoid the risk of detachment of the newly reconstructed wall during the removal of the FenderMate. The absence of the separator ring allows a wide freedom of movement making it very easy to exploit the residual information of the tooth to obtain, already in the first instance, a more accurate contact surface. (Figure 6)
The latter is however appropriately finished with an abrasive disk and with an Arkansas bur before completing the occlusal surface. (Figure 7)
The residual surface to be restored is very small, therefore the occlusal anatomy can be sculpted with a single increment of composite, modelled with a subtractive technique. Before removing the dam, the finishing stages are performed, in this case limited to the use of a thin finishing strip at the cervical step, the reciprocating handpiece with extra-fine files to polish the tooth-restoration interface, and to final polishing. (Figure 8)
Once the rubber dam has been removed, it is possible to check the occlusion with articulation papers, which demonstrate, in this case, the absence of premature contact. (Figure 9)
With a considerable saving of healthy teeth and chair time, to the benefit of both the patient and the operator, this sectional matrix system allows - in fewer steps - results comparable to those obtained with "traditional" systems. The advantage of immediately obtaining an intimate adaptation of the matrix to the prepared cavity prevents the unpleasant inconvenience, which often occurs with traditional systems when the matrix does not close perfectly, of having to manage the bleeding caused by the displacement of the wedge. When this occurs, the adhesive bond is inevitably invalidated and it is necessary to once again carry out the procedures necessary to restore it.
 Tag
Tag
 Related articles
Related articles
Biomimetic has emerged as a multi-disciplinary science in several biomedical subjects in recent decades, including biomaterials and dentistry.
Digital Dentistry 19 November 2025
Increasing awareness of tooth fracture, both complete and incomplete, as a significant disease entity has led to improved diagnostic techniques.
Restorative dentistry 03 November 2025
The worldwide interest of both dentists and patients in esthetic dentistry has affected decision-making in dental practice.
Restorative dentistry 12 September 2025
Traumatic tooth injuries involve function and aesthetics and cause damage that range from minimal enamel loss to complex fractures involving the pulp tissue and even loss of the tooth crown.
The purpose of restorative dentistry is to restore and maintain health and functional comfort of the natural dentition combined with satisfactory aesthetic appearance.
 Read more
Read more
Bulimia nervosa is a multifactorial health disorder characterized by a disturbed self-perception of body weight and shape and therefore by cycles of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviours...
Editorials 16 January 2026
Benjamin Brudner still remembers the moment his patient looked in the mirror and smiled—really smiled—for the first time in years.
Priva Rotary Instruments Diamond Burs from Premier Dental are high-performance electroplated diamonds featuring SmartEdge Technology designed to enhance a clinician’s rotary portfolio.
News 16 January 2026
PepperPointe Partnerships, one of the largest privately doctor-owned, doctor-led dental service organizations (DSO), announces the expansion of its senior leadership team with the creation of three...
News 16 January 2026
Spear Education, the leading provider of advanced dental education and practice management solutions, today announced a major update to Spear Online, its virtual learning platform for general...