Hybrid Straightwire technique: a clinical case
Daniel Celli
Although there are various edgewise devices on the market, straightwire (SW) is definitely the most widespread due to its simplicity.
Within the various SW techniques, which differ from each other by design, prescription and slot size, self-ligating systems have gained popularity because they should bring benefits in terms of strength and friction.
The latter should be more efficient in some specific phases of orthodontic treatment: that of leveling and alignment and especially in that of closing spaces; the limitation of these self-ligating systems is represented by not achieving optimal three-dimensional control of the tooth, especially in the incisal region. To overcome this drawback, some authors have proposed a hybrid system or a two-dimensional system, which incorporates optimal sliding mechanics in the posterior region, while maintaining excellent three-dimensional control in the anterior region.
Based on these concepts, we have designed and developed a two-dimensional hybrid system to improve the efficiency of the straightwire technique; mainly the system consists of:
- conventional brackets with a 0.020x0.030 "slot on the incisors, self-ligating passive brackets on the premolars (f1000) and tubes with a 0.022x0.030" slot in the molar region.
- self-ligating brackets (f1000) or conventional brackets are used on canines depending on the need for treatment (plus or minus friction).
- bows that adapt to the different treatment phases, increasing their diameter and stiffness progressively, starting from 0.014 '' Nielts superelastic, going through the 0.016x0.025 '' and 0.019x0.025 '' NiTi thermal, up to 0.019 x0.025 '' in steel for the work phase with tiebacks.
- Use of various types of ligatures which progressively increase their strength (unconventional low friction ligatures, elastomeric ligatures in the shape of '0' or '8', and metallic ones).
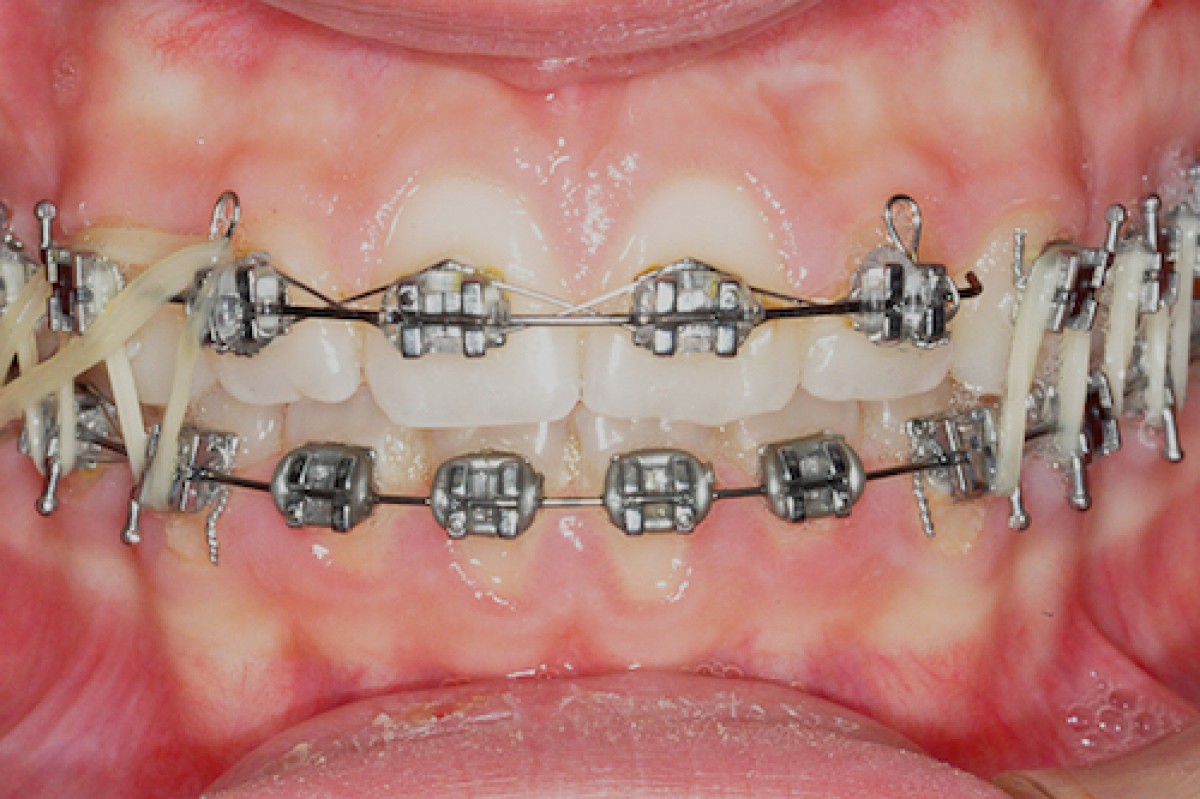
Thanks to the use of smaller slots in the incisal region (0.020x0.030 ''), less dispersion of third-order information is achieved and a reduction in the torque values of the upper incisors, when compared with the MBT prescription (torque upper central incisor: 14º; upper lateral incisor torque: 7º) (Fig.1)
As for the in-out dimension, we recommend using conventional and self-ligating brackets with correct in-out values. The choice of using a 0.020 '' instead of a 0.018 '' slot in the front region results from the decision to use a 0.019x0.025 '' steel for the closure of the spaces (work phase). Even if the difference is minimal, a steel wire 0.019x0.025 '' has less tendency to deformation and to the notch than a 0.018x0.022 ''; moreover, the stiffness of 0.019 * 0.025 '' in steel helps in sliding mechanics.It should also be remembered that most orthodontists use 0.019x0.025 '' in steel as an arch for closing spaces and end their cases with the same arch in 0.022 '' slots.
Therefore, the availability of a 0.020 '' slot allows the clinician, who routinely uses 0.019x0.025 '' arches, to achieve better control of the torque in the incisal region (fig. 2)
A clinical case of the method is shown below:
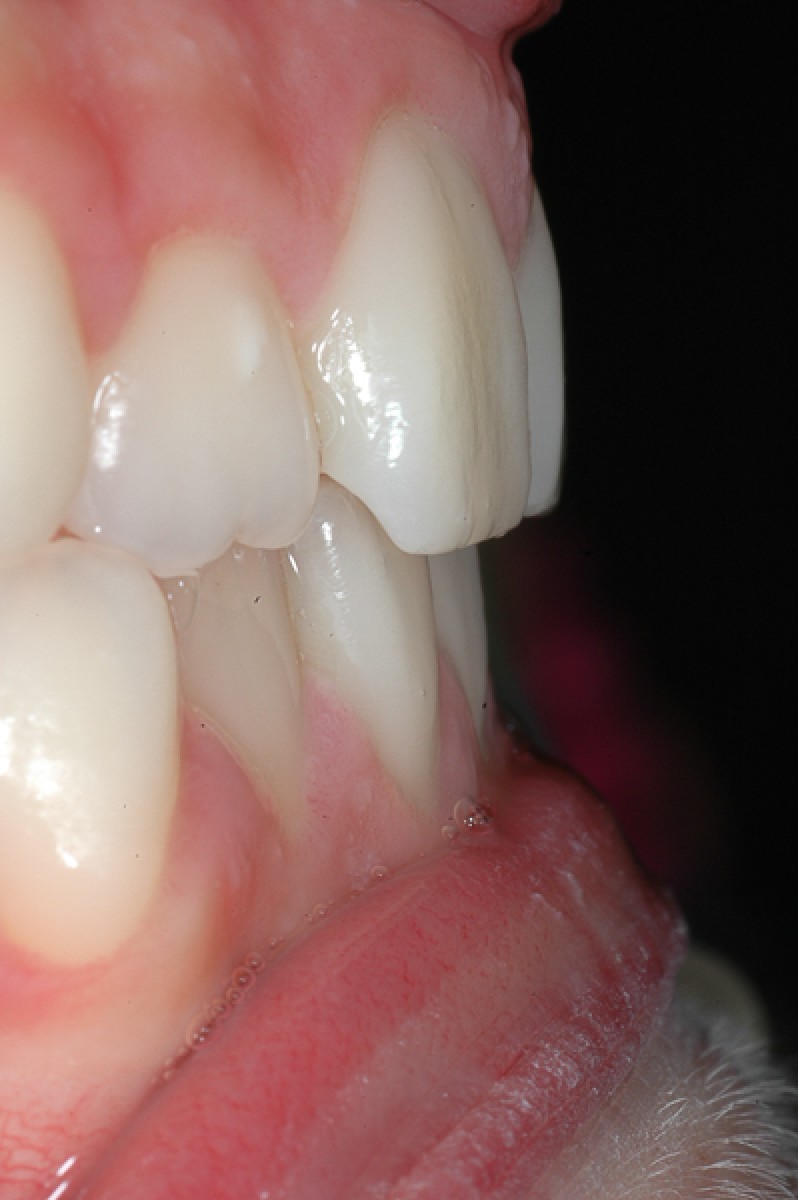
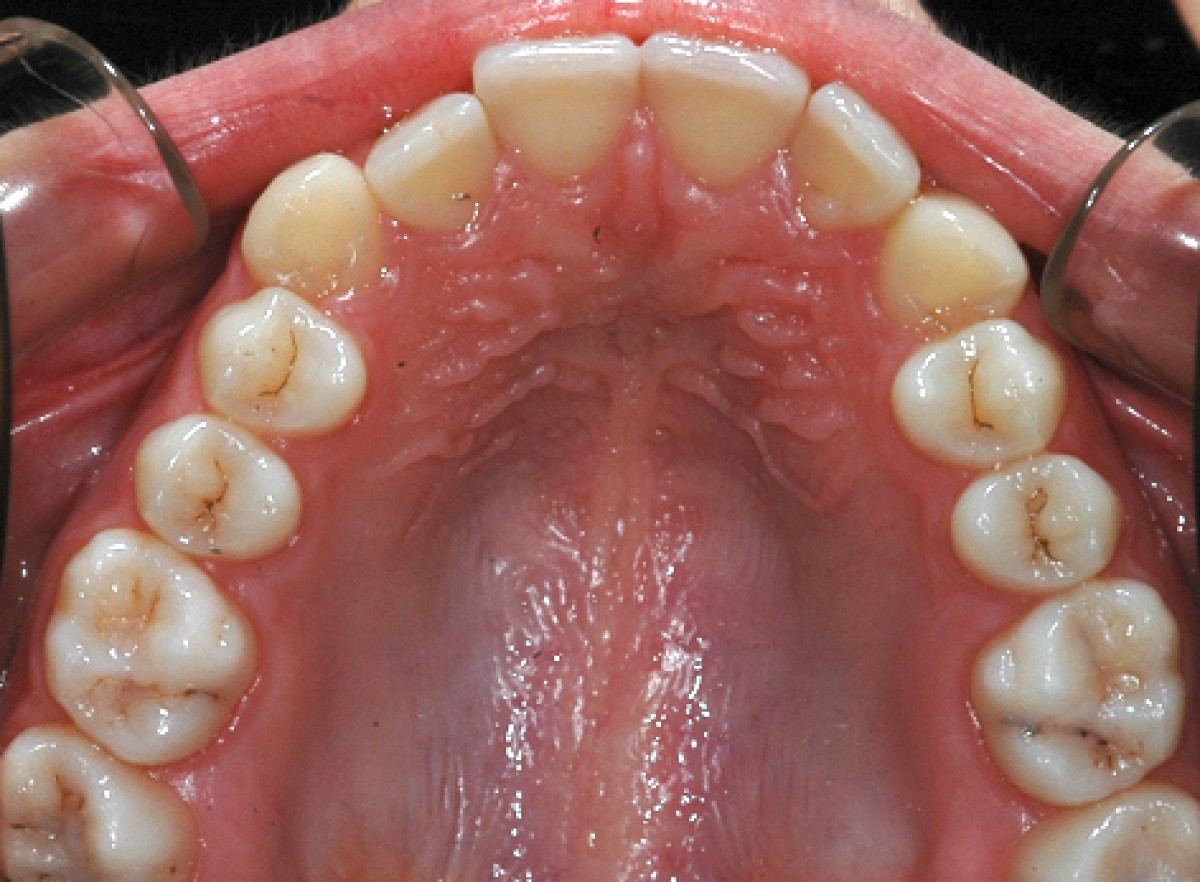
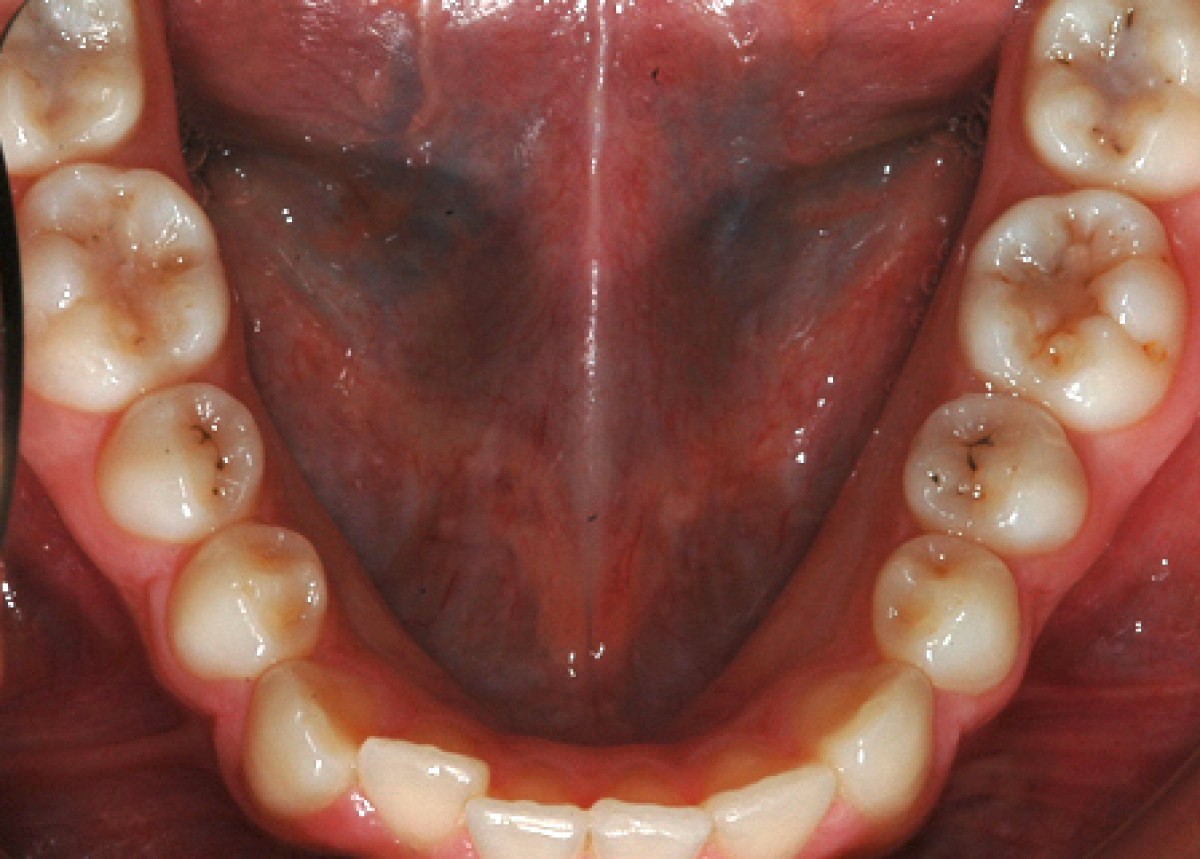
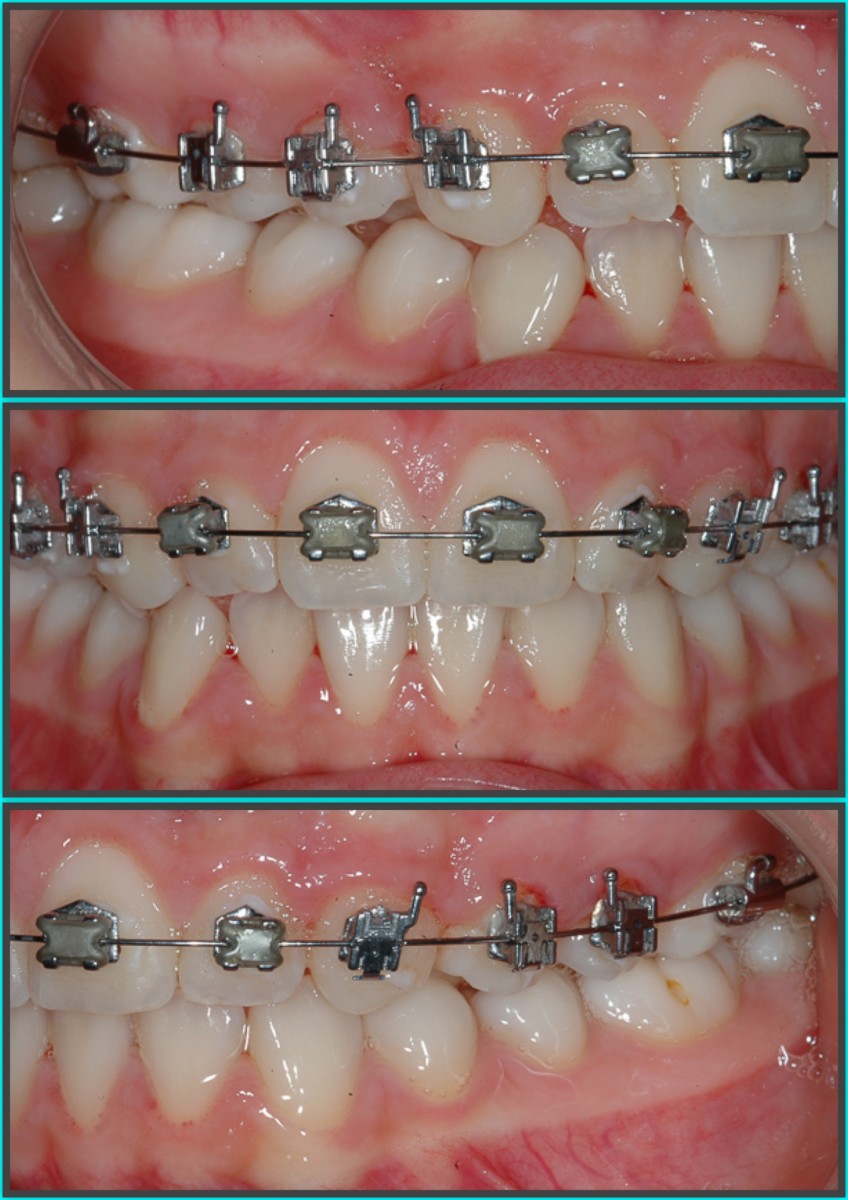
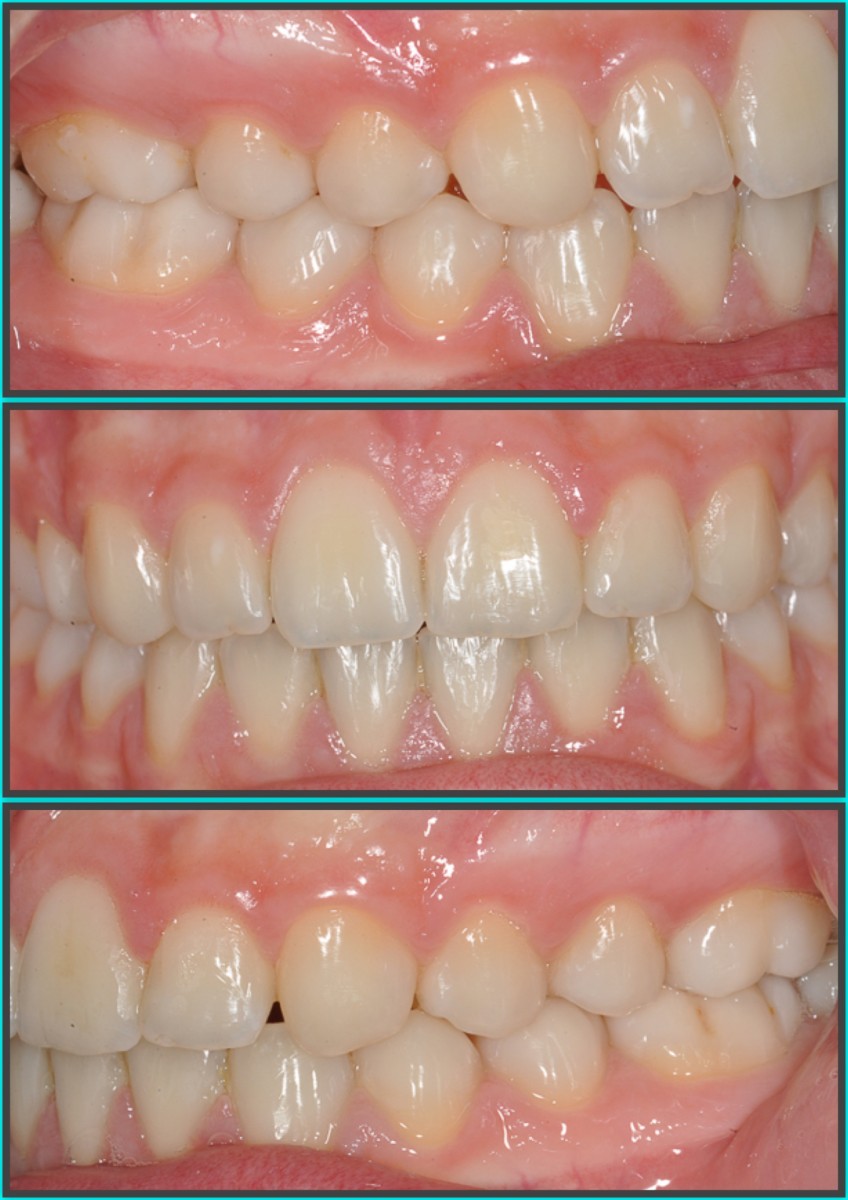
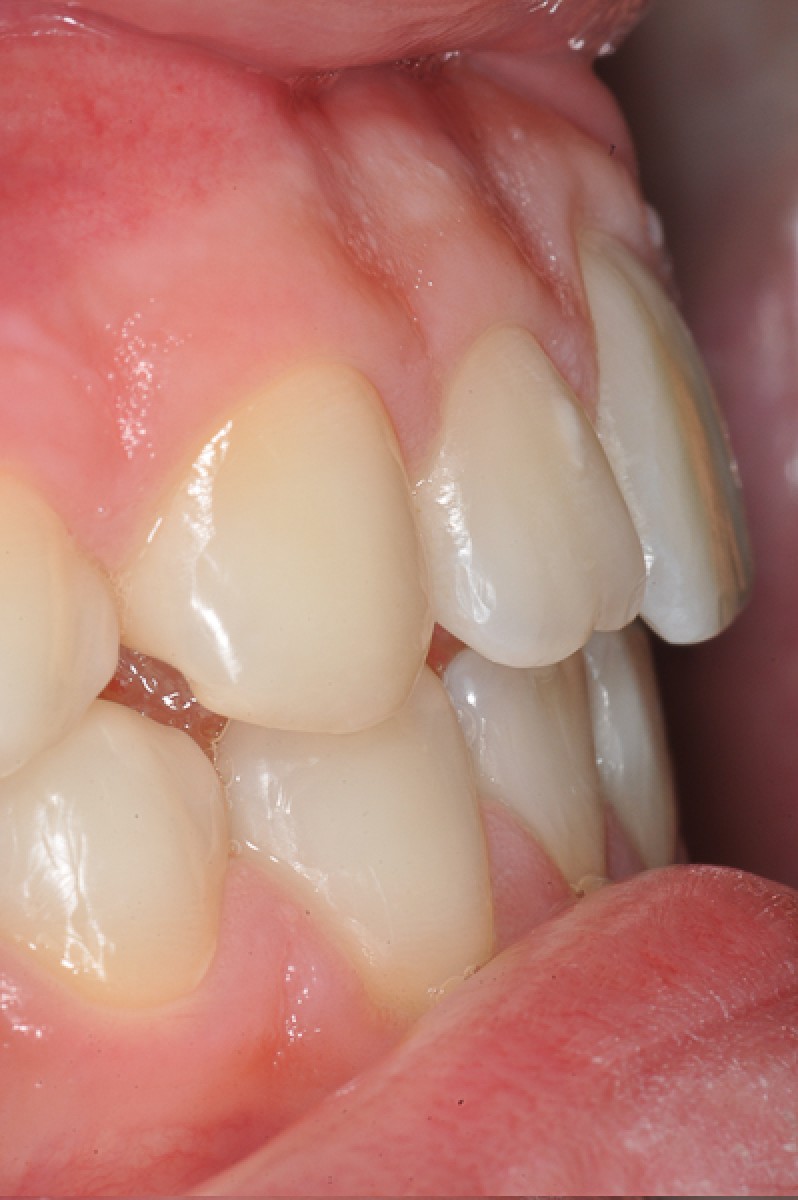
A 14-year-old female patient presents a class I malocclusion in permanent dentition.Good and aesthetic profile. In the intra-oral clinical examination, first class molars and canines are revealed, average crowding in both arches, normal overbite and overjet.
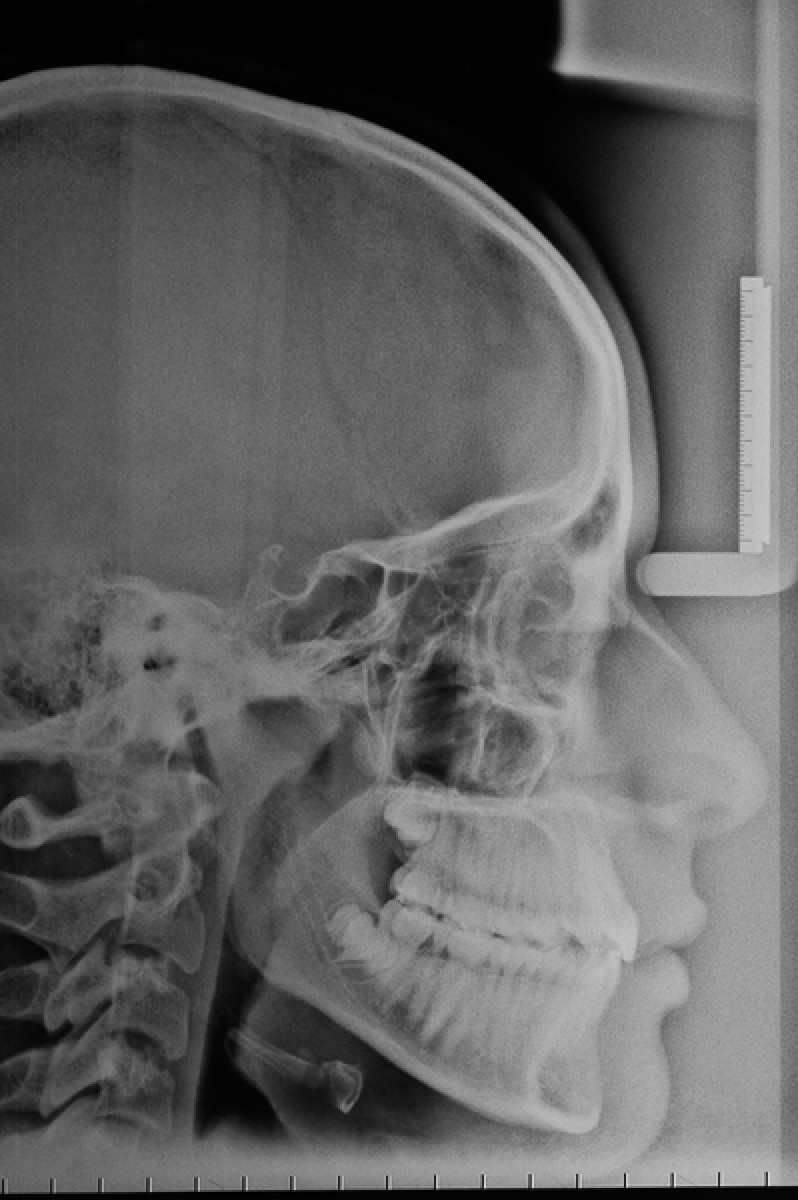
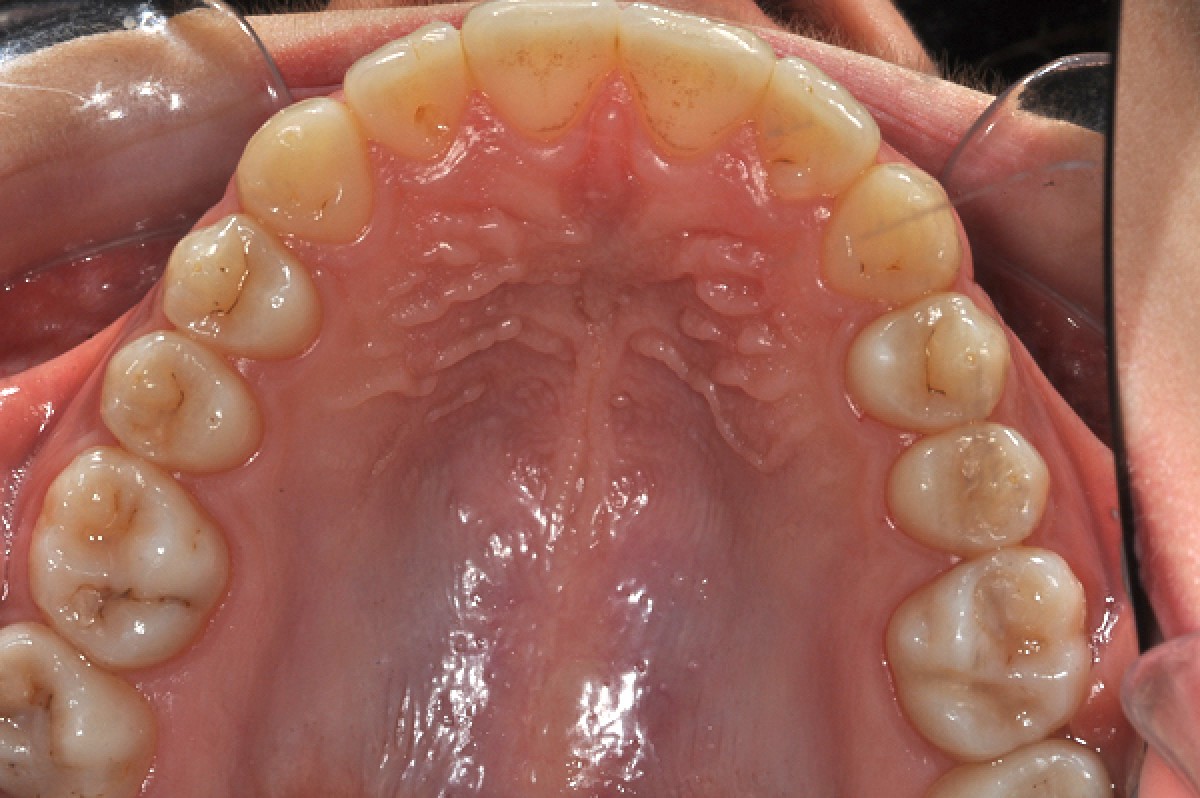
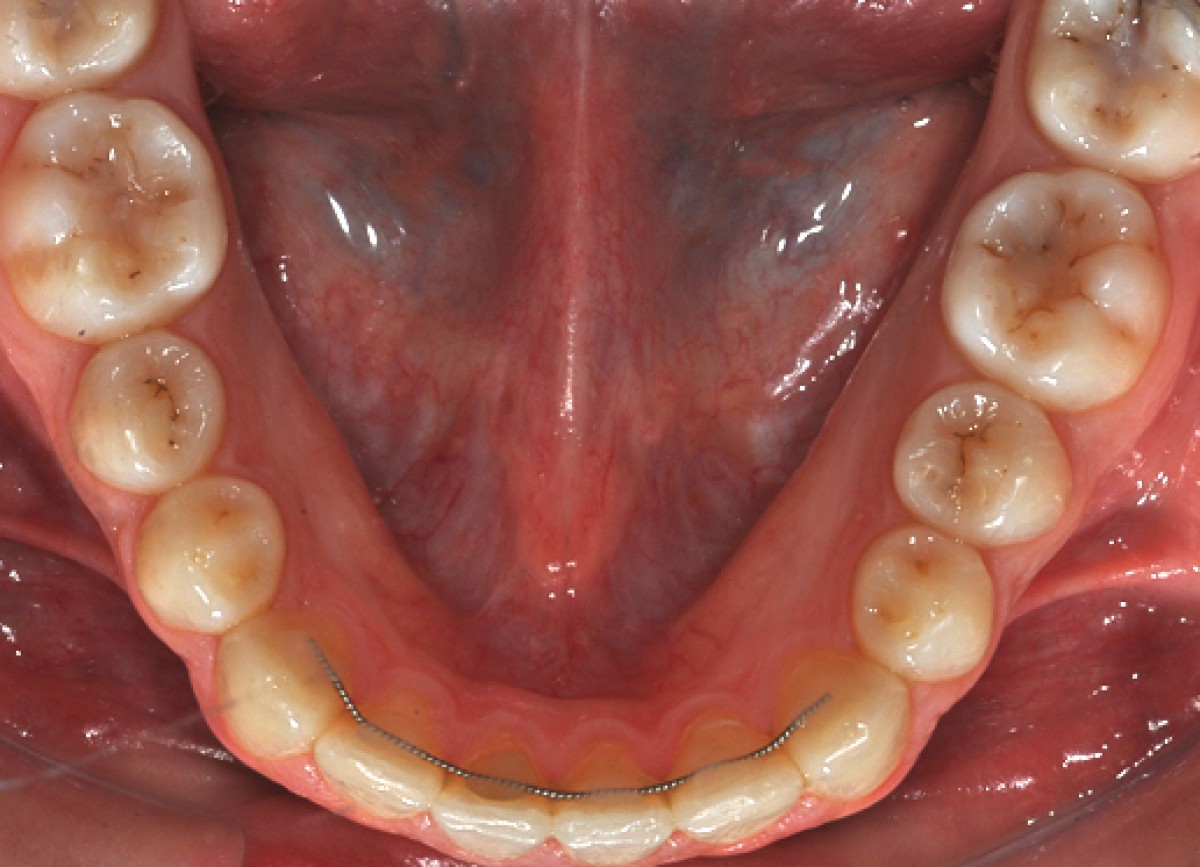
The periodontal tissue appears healthy. The right canine guide is missing. The lateral radiograph of the skull shows a normal mandibular plane angle and a class III tendency. The upper and lower incisors appear well positioned relative to the relative planes (+ 1 / ANS-PNS = 116º, -1 / GoGn = 88º) (Figures 3-7).
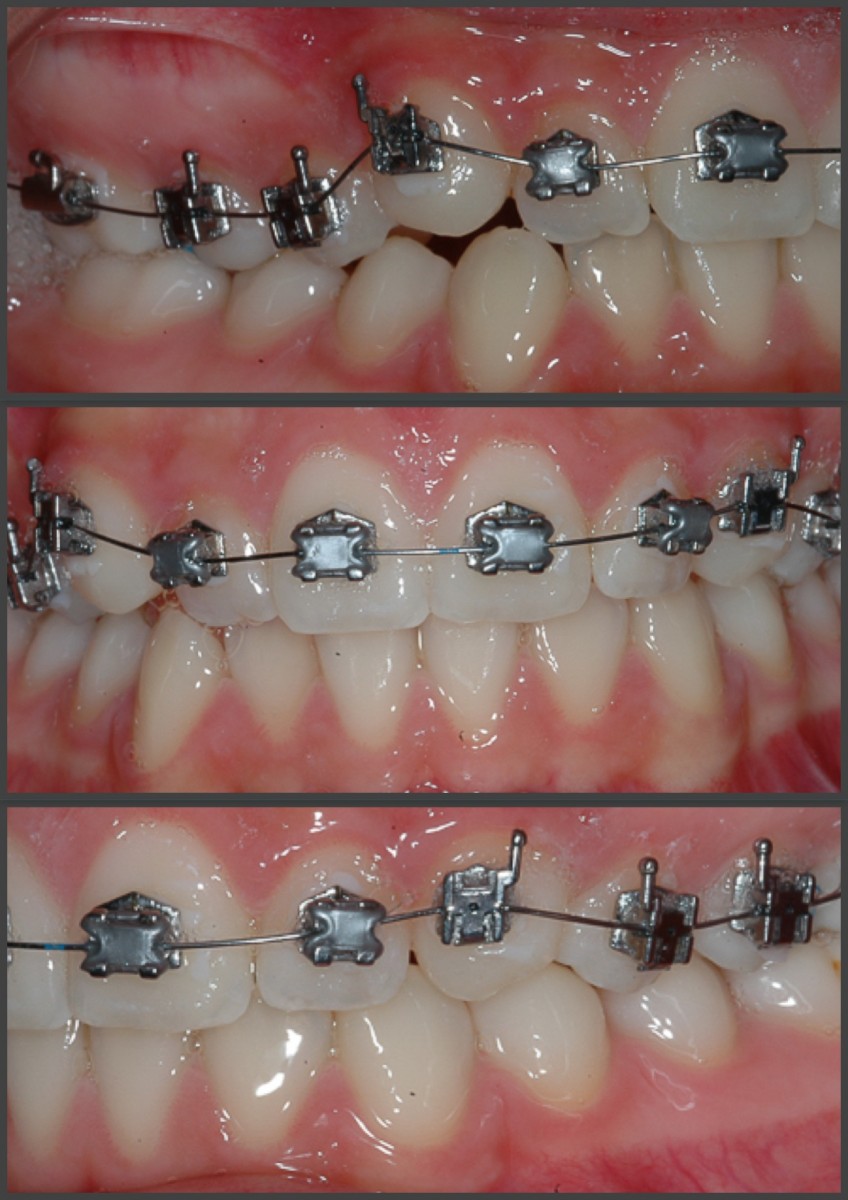
The treatment is summarized as follows:
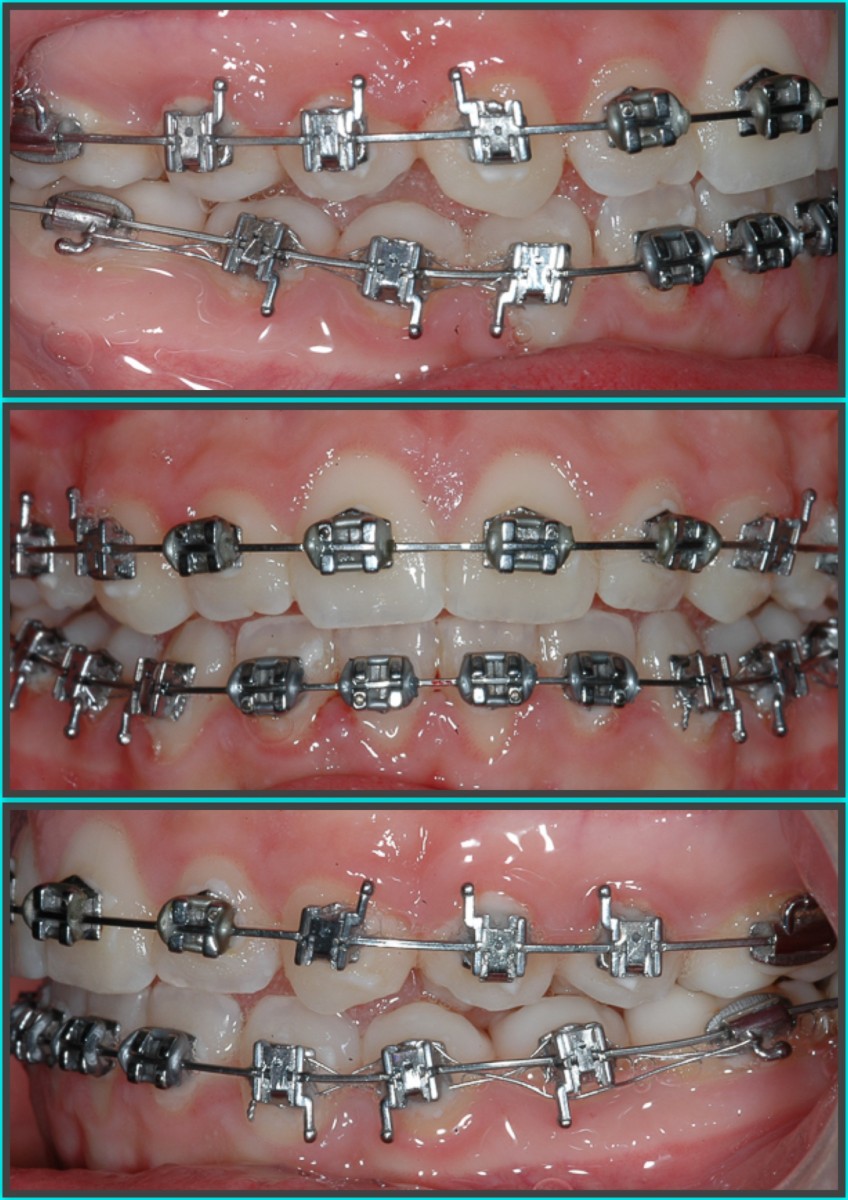
0.012 '' NiTi (1 month) in the upper arch;
0.014 '' NiTi (3 months) in the lower arch;
0.016 '' NiTi (2 months) in the upper arch;
0.016x0.025 '' NiTi thermal (2 months);
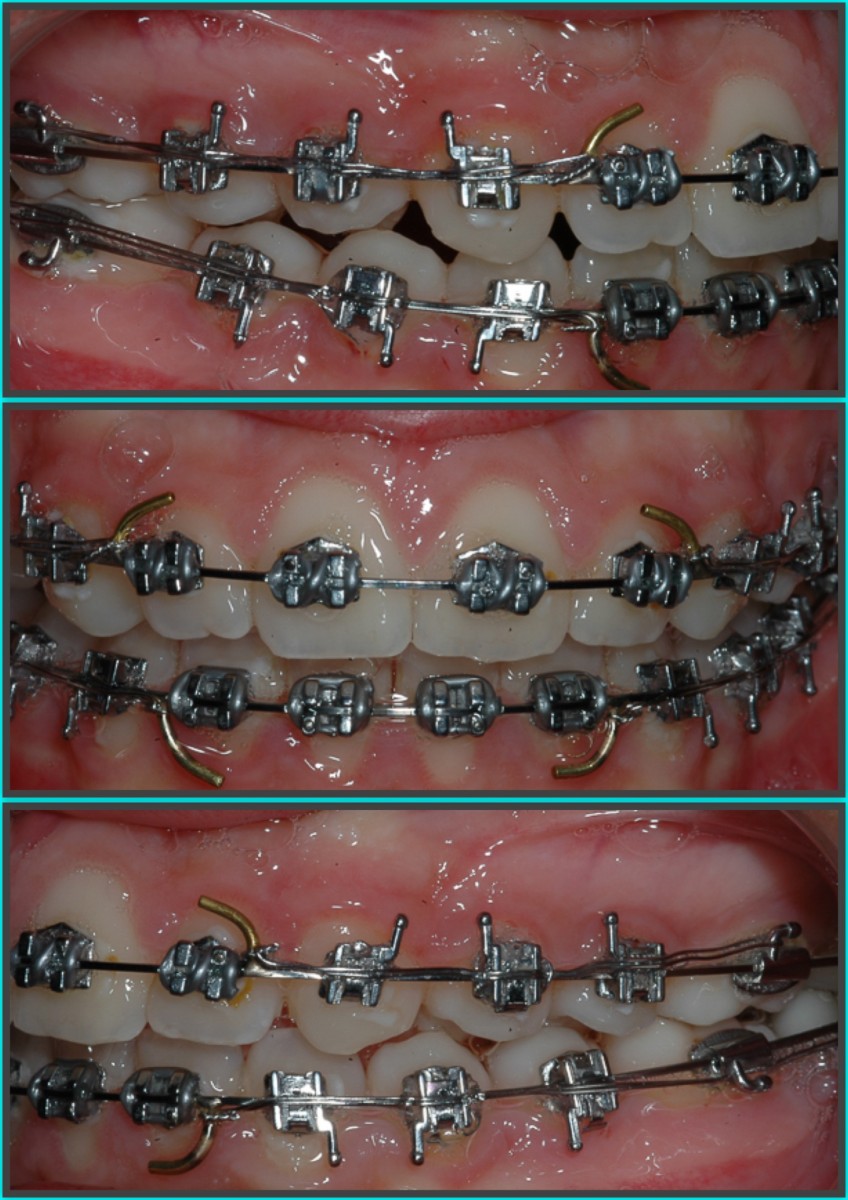
0.019x0.025 '' NiTi thermal (2 months);
0.020 '' Australian (1 month);
0.019x0.025 '' steel with tiebacks (6 months);
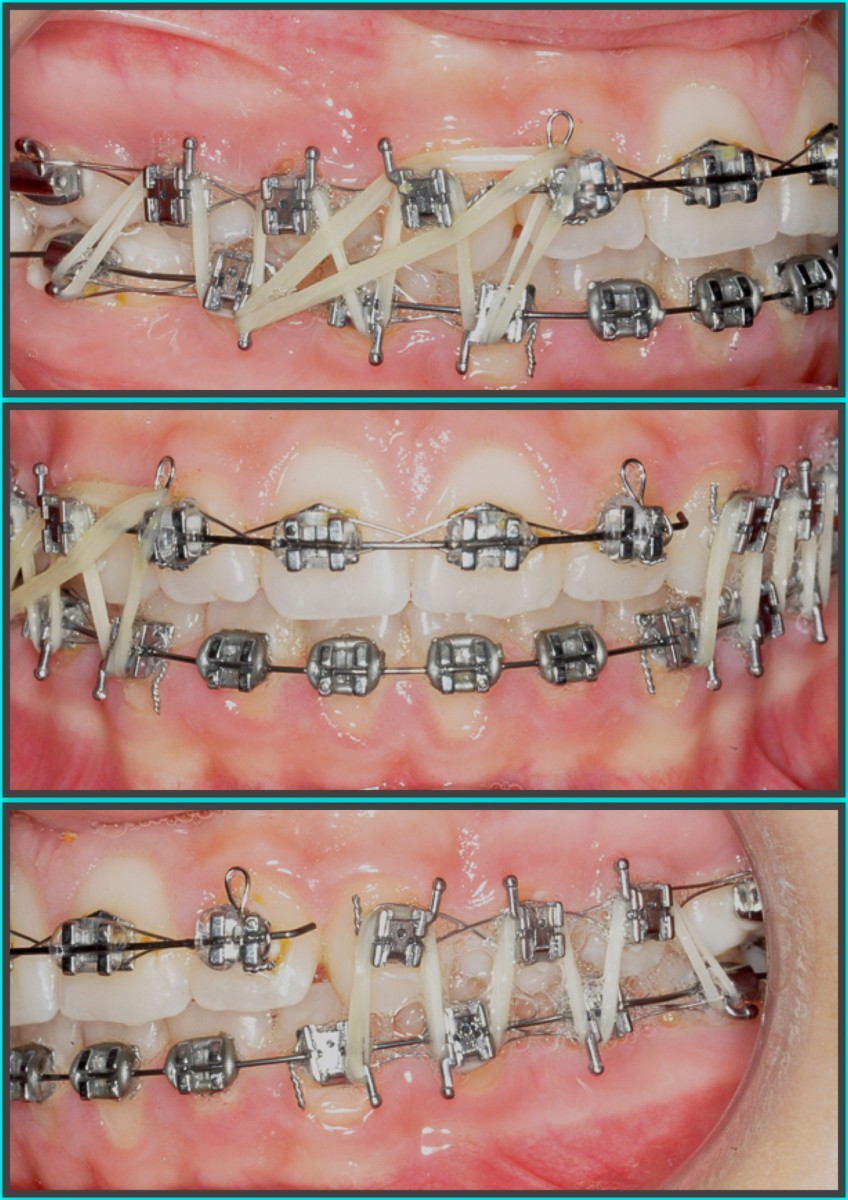
Finishing phase (6 weeks) according to the MBT technique (section from 0.018 '' Aus from 1.2 to 2.2 in the upper arch and continuous thread 0.014 '' NiTi in the lower arch). (Figures 8-12)
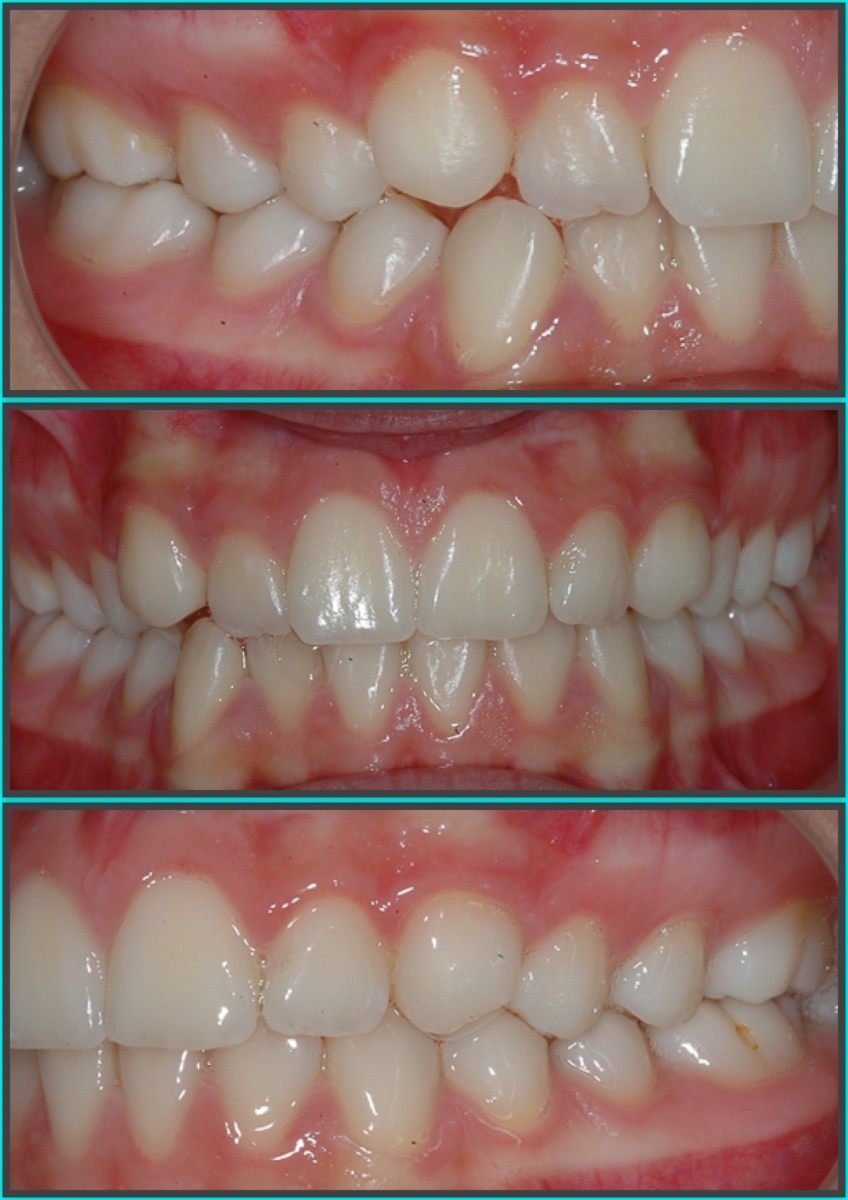
After 14 months of treatment the patient maintains his harmonic profile; we reach a class I molar and canine with ideal overbite and overjet. The arches appear with good shape without open spaces and rotations. Periodontal health has been maintained. (Figures 13-16)
CONCLUSIONS
Our equipment is strongly inspired by the versatility of the two-dimensional technique of A. Gianelly, to the sliding efficiency of the MBT mechanics that we recognize as S.W. mother, to the variable friction philosophies that from D. Damon have influenced multitudes of orthodontists and patients and to the Tweedian principles of 3D teeth control when this is required and indispensable. We ultimately sought a '' selection of the best '' available in science and orthodontic practice.
The results of years of clinical experience with our dual slot hybrid system confirm:
- the achievement of excellent 3D control, easily obtainable with the use of traditional ligatures;
- ability to control the clutch by the differentiated use of different progressively increasing binding systems;
- possibility to make folds on the wire if necessary, thanks to the use of conventional front connections, although the use of a reduced slot of height at .020 and work threads .019x.025 S.S. they reduce the request;
- excellent sliding mechanics thanks to the rigidity of the work threads .019x.025 S.S.
- excellent incisal torque control thanks to the combination of reduced height slots and .19x.025 S.S.
 Related articles
Related articles
Orthodontics 12 November 2025
Effectiveness of dental monitoring system in orthodontics: A systematic review
Dental monitoring (DM) constitutes a recent technological advance for the remote monitoring of patients undergoing an orthodontic therapy.
Orthodontics 08 October 2025
The field of orthodontics in its new era is venturing ahead to more up-to-date technological point of view.
Orthodontics 25 August 2025
Orthodontics 25 June 2025
Clinical application of magnets in orthodontics and biological implications: a review
Over the last decade magnets have been used in orthodontic and dentofacial orthopaedics and attempts have been made to evaluate the biological implications of magnets and magnetic fields during...
Orthodontics 10 June 2025
It has long been claimed that presurgical orthodontics is crucial to the outcome of surgical-orthodontic treatment for dentofacial deformity
 Read more
Read more
Periodontology 14 November 2025
This study was carried out to assess the oral hygiene awareness and practices amongst patients visiting the Department of Periodontology at Gian Sagar Dental College and Hospital, Ramnagar (Patiala).
Editorials 14 November 2025
Penn Dental Medicine shared its expertise in caring for persons with disabilities with dental care providers from throughout Jamaica at a 1 ½ -day hands-on continuing education program, held October...
News 14 November 2025
Dr. Thomas M. Paumier, a dentist in Canton, Ohio, is the new President-Elect of the American Dental Association (ADA). Dr. Paumier was elected at the ADA House of Delegates meeting in Washington,...
News 14 November 2025
Premier Dental Implants & Prosthodontics is proud to announce the opening of its newly renovated dental office and the launch of its new website
News 14 November 2025
Henry Schein One and AWS Collaborate to Transform Global Dentistry with Generative AI
Industry leaders join forces to bring advanced AI capabilities to dental technology platforms — redefining patient care, clinical efficiency, and practice performance worldwide