Comparison between two surgical approaches
Authors:Magda Mensi, Elisabetta Audino, Eleonora Scotti, Emanuele Zanola, Elisa Bettinsoli, Stefano Negrini, Luca Visconti, Stefano Alessandro Salgarello
INTRODUCTION
The aim of this retrospective observational study is the comparison between two different surgical approaches for the ONJ treatment in terms of healing and absence of recurrences. These different surgical techniques are divided into conservatives (group A) and radical (group B).
MRONJ means “exposed bone or bone that can be probed through an intraoral or extraoral fistula in the maxillofacial region that has persisted for longer than 8 weeks in patients who have or are taking ONJ-related drugs and in the absence of radiation therapy”.
Drugs associated with ONJ development risk are used to treat bone metastases from solid cancers, osteolytic lesions from multiple myeloma, malignant hypercalcaemia or osteometabolic diseases. These drugs belong to bisphosphonates, antiresorptive and antiangiogenetics class.
In recent years, the efficacy of primary prevention of MRONJ has been noted. The primary prevention consists in the elimination of local risk factors and by carrying out dental treatments before starting therapy.
METHODS
The study analyses reports on 77 oncology and hematology patients. The data were collected from the Stomatology and Maxillo-facial surgery departments of ASST Spedali Civili of Brescia, from November 2016 to February 2018. The patients had taken or are taking bisphosphonate therapy or denosumab therapy. The patients included in the study have a minimum follow-up of one year.
The patients were divided into two groups according to the type of surgical approaches: the group A if the surgical technique is more conservative, group B if the surgical approaches is more radical. The type of surgical approaches is decided according with the MRONJ staging, proposed by American Association of Maxillofacial Surgeons.
The groups are homogeneous for the pre and post-surgical protocols and for the follow-up program. The outcome was defined with the recurrence.
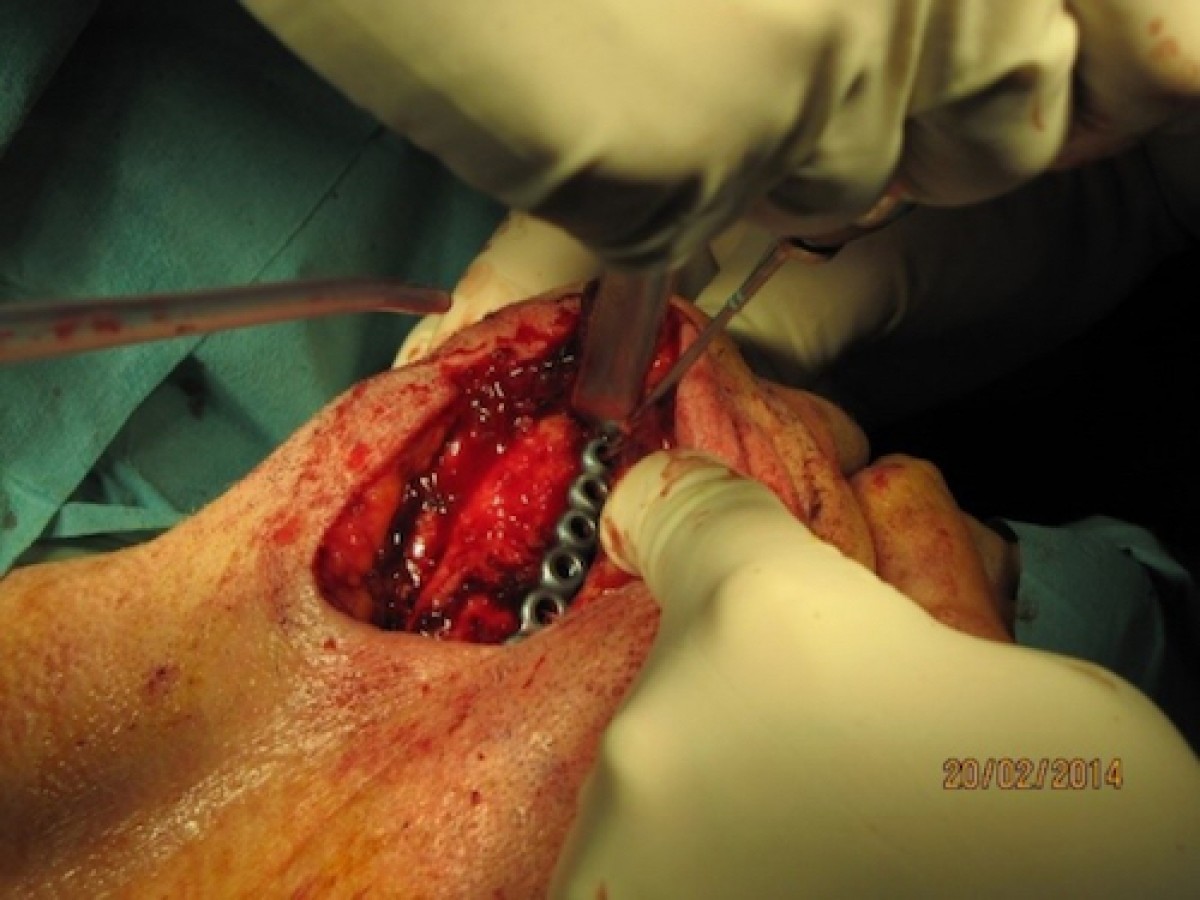
The conservative surgical approaches were limited to bone curettage or sequestrectomies under local anesthesia; the radical surgical approaches included marginal or segmental resective surgery under general anesthesia.
RESULTS
The statistical analysis was conducted on a group of 52 patients, since 25 of the 77 initial patients could not be traced back to the underlying pathology or type of surgical technique performed.
Analysis of recurrence rates in surgical procedures show that are not statistically significant difference (p value=1; odd ratio=1,09).
The percentage of recurrences in conservative surgical approaches (bone curettage, sequestrectomies) was analyzed compared to the percentage of recurrences in radical surgical procedures (marginal or segmental resective surgery). The number of recurrences in group A (conservative surgical approaches) was 4 out of 24 cases, while in group B (radical surgical approaches) it was 5 out of 28 cases.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of the study show that there is no statistically significant difference between minimally invasive and invasive surgery technique. The results could be influenced by the small sample size, so further studies are needed, in particular RCT.
CLINICAL MEANING
The results of the study show that there is no statistically significant difference between minimally invasive and invasive surgery technique.
 Read more
Read more
Pediatric dentistry 10 February 2026
Pediatric Dentists' Approaches to Dental Treatment of Children with Dental Fear and Anxiety
Dental fear and anxiety (DFA) are important facets of pediatric dental treatment and may cause oral health neglect and dental treatment evasion.
Editorials 10 February 2026
AI-Powered Data-Mining Study Illuminates Clinical Complexity of Tooth Decay
An artificial intelligence-powered “data cleaning-and-analysis” process fixed data quality problems in a large health dataset and evaluated the data to identify previously unrecognized clinical...
Master Dental Technician Roberto Rossi showcased some of the burs and polishers in action with his hands-on presentations.
News 10 February 2026
Vatech, a global leader in dental medical imaging, has announced the achievement of 100,000 systems in cumulative production of dental digital X-ray devices, further solidifying its unrivaled...
News 10 February 2026
Spear Education, the leading provider of advanced dental education and team training, today announces a partnership with Overjet, a top provider of dental diagnostic software.