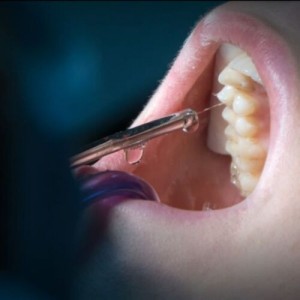
Bonding to hypomineralized enamel
Co-authors: A. Comba, F. Florenzano
Lorenzo Breschi
Molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH) is a developmental dental defect which affect first permanent molars (FPMs) and sometimes permanent incisors. The effects on teeth enamel are presence of opacities, modified translucency and cuspidal breakdown even at very early stage of eruption. MIH has a high prevalence worldwide, affecting one in seven children.
Hypomineralised enamel (HE) is considered a weak substrate as the decreased mineral density and the higher protein content arise in hypersensitivity, cuspidal breakdown, and secondary caries. Consequently, conservative treatments become necessary already immediately after the onset of tooth eruption. Due to the altered enamel tissue characteristics, the mechanisms of adhesion to HE is challenging.
Very recently, Yu-Lynn et al. aimed at investigating the effects of surface pre-treatment protocols with Papacarie Duo gel and Scotchbond Universal (SU) on the micro-shear bond strength (µSBS) of resin composite (RC) to HE.
Materials and Methods:
HE or mineralized enamel (NE) obtained from extracted hypomineralized FPMs were used for the study. According to the colour of the opacities, the HE specimens were classified as creamy/white (CW) or yellow/brown (YB). Eight groups were formed according to the enamel surface pre-treatments (n = 20): Papacarie Duo gel or no pretreatment, and SU applied in etch-and-rinse (E&R) or self-etch (SE) mode. After RC build-up (Filtek supreme XTE Universal restorative) the specimens were submitted to the µSBS test. Failure modes were analyzed using an optical microscope and scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Results:
Statistical analysis revealed that the type of enamel substrate (NE vs HE), and the etching mode significantly influenced the bond strength (p < 0.001). Comparing CW/HE with YB/HE, a significant interaction between “deproteinising pre-treatment” and “etching mode” was observed (p = 0.028). When Papacarie Duo gel and ortophosphoric acid were used concurrently, increased SBS values were recorded for HE (p < 0.001).
Conclusion:
Deproteinising surface pre- with Papacarie Duo gel followed by the application of SU in ER mode increased the µSBS of resin composite to hypomineralized enamel.
For more information: Bonding Universal Dental Adhesive to Developmentally Hypomineralised Enamel.
 Tag
Tag
 Related articles
Related articles
By Arianna Bianchi
Molar and incisor hypomineralization is a well-recognized enamel quality defect, which can involve one to four permanent first molars, often the permanent incisors.
Dental materials 21 February 2023
Remineralization of molar incisor hypomineralization with a hydroxyapatite toothpaste
Molar incisor hypomineralization is a qualitative enamel defect affecting at least one first permanent molar, with a frequently associated affection of the permanent maxillary incisors or the...
 Read more
Read more
Editorials 10 October 2025
With proud smiles and crisp white coats, ninety-three learners from the DDS Class of 2029 and the International Dentist Pathway Class of 2028 marked the start of their dental careers at the UCSF...
Periodontology 10 October 2025
Continuous professional development (CPD) in Periodontology refers to the overall framework of opportunities that facilitate a life-long learning practice, driven by the learner-practitioner and...
TheraBreath, the #1 alcohol-free mouthwash brand in the U.S.*, has introduced a new line of dentist-formulated, clinically tested toothpastes designed to support professional oral care...
News 10 October 2025
New officers and trustees were installed at the Minnesota Dental Association’s Leadership Conference on September 19 in Minneapolis.
News 10 October 2025
Smartee Denti-Technology today announced that Professor Gang Shen, its Chief Scientist and Executive President of TaiKang ByBo Dental, has once again been named to the World’s Top 2% Scientists...