Dental Prosthodontics retained devices for increasing the stability in the overdenture rehabilitation of the atrophic mandible - an original study
Authors: M. Cicciù, G. Risitano, G. Cervino
The dental removable prosthesis is today a good therapeutic option for edentulous patients offering function and aesthetics with low biological low cost. However, even if in the upper maxilla the stability of the prosthesis can be achieved by the large contact basis surface, in the mandible the presence of the tongue reduces the contact surface of the removable prosthesis increasing the instability of the device [1-2]. Thankfully, several clinical studies demonstrated how the rehabilitation of the mandibular atrophic ridge by positioning dental implants can be considered a predictable and a safe procedure today.
Recently, the opportunity of placing two or more dental implants in the anterior mandible gives the practitioners the possibility of incrementing the removable prosthesis stability or to retain partial or complete lower dentures [1-4]. Dental implants and related prosthodontics treatment offer the opportunity of high levels of oral health related quality of life and is particularly important in times of population aging as edentulousness percentage continue to be relevantly high.
After the dental implants placing the next step is to choice the prosthodontics rehabilitation related to the patients request and expectations. The challenge is to select an ideal solution guaranteeing aesthetics, functions, low cost, stability and to easily perform oral hygiene maneuvers by the patients. Accordingly with a recent systematic review, there is no sufficient evidence to determine the true effectiveness of different attachment systems for mandibular overdenture on patient’s needs and satisfactions, prosthodontics success, needs and costs [4]. The last steps in the research fields found several papers that recently recreated the masticatory system by engineering tools for simulating long term stress over dental, bone of the jaws and prosthodontics components. Finite Element Method (FEM) is a computer method for the stress analysis.
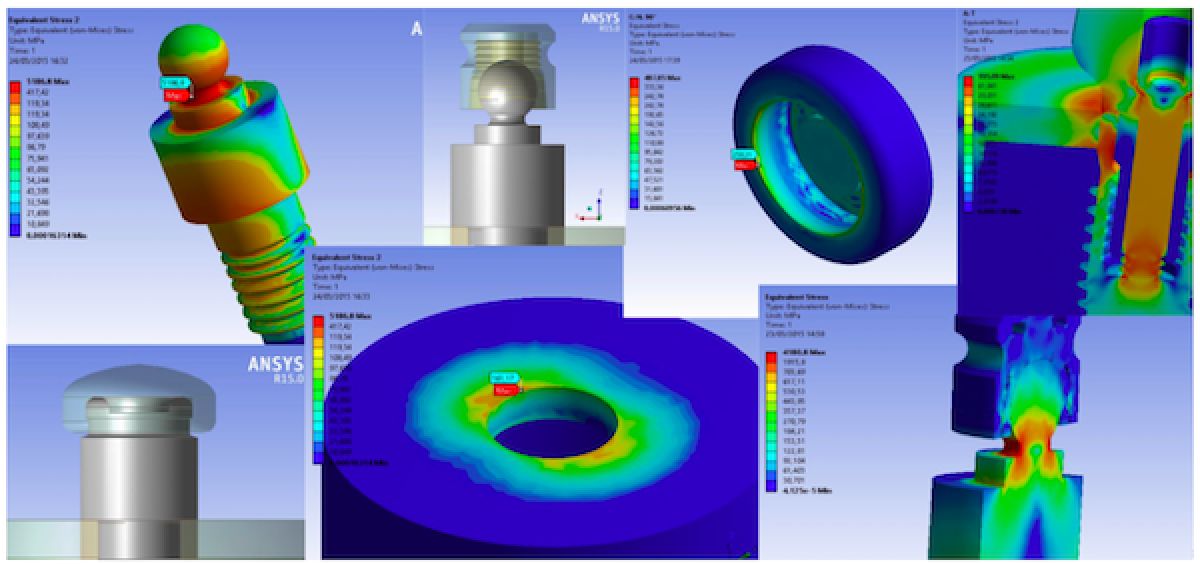
The effect of loading strengths over dental implant elements and periimplant bone can be recorded by applying the equivalent Von Mises stress, expressed in MPa. The difference of tension distribution is usually presented by different colors and red is the maximum stress [5, 6]. Aim of this report is to analyze the mechanical features of two different prosthetic retention systems for mandibular overdenture. By applying engineering tools like FEM and Von Mises analyses, it has been investigated how the dental implant devices hold out against the masticatory strength during the chewing cycles at different angle of loads. Two common dental implant overdenture retention systems have been investigated and then compared with a universal – common dental abutment. The Equator® attachment system and the Locator® arrangement have been processed by FEM Ansys® Workbench. The elastic features of the materials used in the study have been taken from recent literature data.
Specifically, for performing the analysis it was created the CAD model of the human skull and specifically of the jaw which reproduced the perfect human mandible anatomy, the cortical and marrow bone, using SolidWorks®. A standard dental implant (Osstem TSIII ®) virtual model CAD Ø 4.0/4.5 mm 10.0 mm on length and characterized by titanium alloy 4th grade was created using engineering draws of the implant by SolidWorks®. The model of the force distribution was achieved by Matlab® (influenced by dental implant positions) over dental implants during a generic chewing cycle. Afterwards, Ansys Worchbench® performed FEA mandible-fixture and showed the stresses and deformation between bone and implant. A 3D linear static structural simulation was performed showing the relation (stress and strain) between the bone and the implant prosthodontics elements: fixture, Equator®, and Locator® systems.
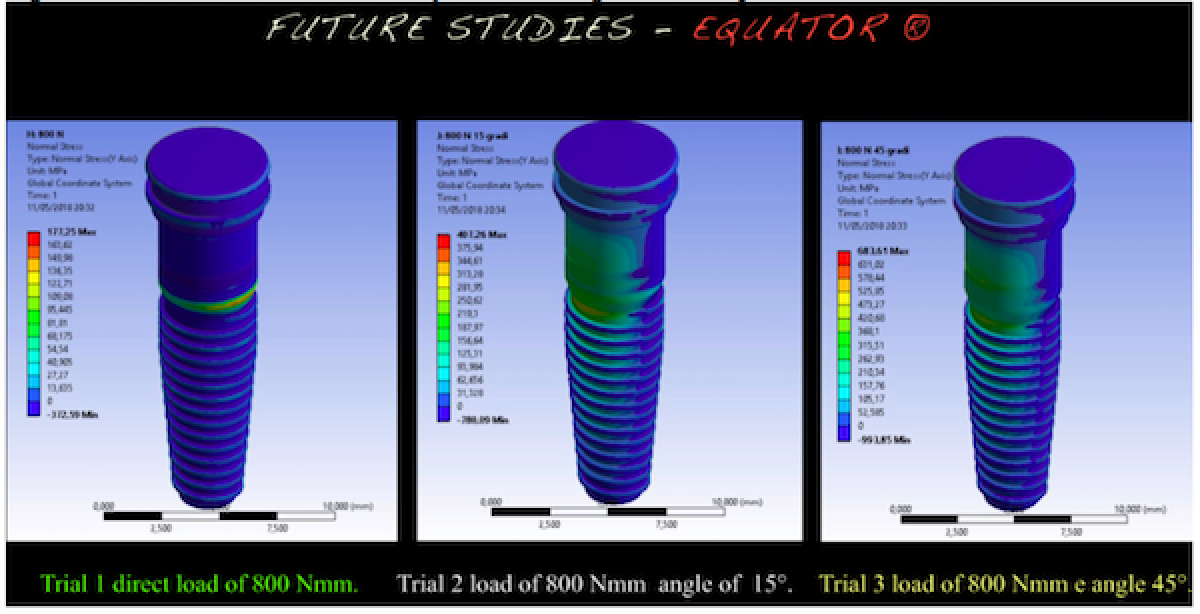
The components of the dental implants were tested using a compression load of 800 N. All the loads were distributed on the prosthodontics components surface in contact (screwed) with the dental implant. Prior to study the mechanical forces applied to the model, it’s important to keep in mind that bone characteristic are connected with individual physical features and so there is a high variability, consequently the bone values and parameters were chosen by literary references.
Results revealed different response for both type of device. From an initial recording of the data, the whole system was not prejudiced. As observed, no system reached fracture or failure due to static rupture. In general, from the extension of the stressed areas, the following results were registered, that is, the system that stressed the bone less was the universal prosthesis, the system that most stressed the bone was the locator prosthesis, and the system that had the highest peak stress value was the equator prosthesis.
Both systems guarantee perfect fit over axial load; however, the different design and shape should customize the use of each one for typical clinical condition of applying overdenture systems over dental implants. The data of this virtual model highlighted different characteristics and mechanical behaviors of overdenture prosthodontics attachments. This paper is a spot for clinicians aiming to show the three-dimensional system involved fixtures, abutment and passant screws of two different dental implants retained system and offer the view of the stress distributions under the masticatory load (Figg. 1-4)
Within the limitation of the present study, the Von Mises analysis underlined how even both two prosthodontics overdenture retainer systems can well tolerate the masticatory stress; the equator ® system less involve the bone perimplant tissues.
Specifically the results could be interpreted as follows: Both, Equator ® and Locator ® retention systems offer adequate retention system and overdenture prosthesis support.
• This in vitro study underlined how the shape of the Locator ® distributes the stress over the dental implant and the gum retainer could be well tolerated. The limit before having fracture of the components results 476,92 MPa.
• The shape of the Equator ® retained system seems to collect the strength over the head of the retainer. These conditions favor the higher stress on the retainer gum. The advantage is related to the minor stress located around the perimplant bone tissue and fixture.
Clinicians should find the better prosthetic balance in order to better distribute the stress over the component and to guarantee the patients clinical long-term results.
Future outcomes: Time is running and the progresses in the field of dentistry, materials and engineering can give the practitioners new different solutions that can be applied in the daily practice. The next step will be offered by a more close relationship between the” ideal” 3D reproduction of devices with a perfect fit within the clinical evidence.
References
1. Priorov, N.N. Amputation of the Extremities and Prosthesis. Br Med J. 1945; 1(4388), 178–179. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.4388.178
2. GILLIS, L. Recent advances in the treatment of arm amputations, kineplastic surgery and arm prostheses. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1948; 3(5), 227–247.
3. MOWLEM, R. Surgery and prostheses. Proc R Soc Med. 1950; 43(9), 711–716. Wang, T.; Liu, N.; Su, Z.; Li, C. A New Time–Frequency Feature Extraction Method for Action Detection on Artificial Knee by Fractional Fourier Transform. Micromachines 2019, 10, 333
4. Payne AG, Alsabeeha NH, Atieh MA, Esposito M, Ma S, Anas El-Wegoud M. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: attachment systems for implant overdentures in edentulous jaws. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;10(10):CD008001. Published 2018 Oct 11. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008001.pub2
5. Cicciù, M.; Cervino, G.; Milone, D.; Risitano, G. FEM Investigation of the Stress Distribution over Mandibular Bone Due to Screwed Overdenture Positioned on Dental Implants. Materials 2018, 11, 1512
6. Cenkoglu, B.G.; Balcioglu, N.B.; Ozdemir, T.; Mijiritsky, E. The Effect of the Length and Distribution of Implants for Fixed Prosthetic Reconstructions in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla: A Finite Element Analysis. Materials 2019, 12, 2556
 Tag
Tag
 Read more
Read more
Editorials 16 April 2024
Dr. Kyle Vining Earns Hartwell Foundation Award to Study Childhood Leukemia
Every year, thousands of American children are diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the most common form of childhood cancer. The disease begins in bone marrow, when immature cells...
News 16 April 2024
The UF College of Dentistry notched a record turnout for its annual celebration of research – Spring Synergy – on Friday, March 29 at the HPNP Auditorium
Products 16 April 2024
Glidewell recently announced a rebrand of its flagship Hahn Tapered Implant System, now known as the Glidewell HT Implant System.
Market 16 April 2024
Zentist Launches Cavi AR, an RCM Software for Dental Insurance AR & Claims Management
Zentist, the leading cloud-based insurance Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) software for U.S. dental groups, proudly announces the introduction of Cavi AR, an additional innovative solution that is...
News 16 April 2024
Standard Dental Labs Sets Sights on Expansion Following Strong FYE 2023 Performance
Costas, Inc., operating as Standard Dental Labs Inc., a renowned name in the dental industry, is pleased to announce the filing of its annual report for the fiscal year ending 2023 on April 10th,...