Direct composite restoration of 1.1 and 2.1
Allegra Comba
Young male patient came to my attention after trauma involving the elements of the upper frontal sector. The patient reported not having collected the fragments thus, IV class reconstruction of the involved dental elements was necessary.
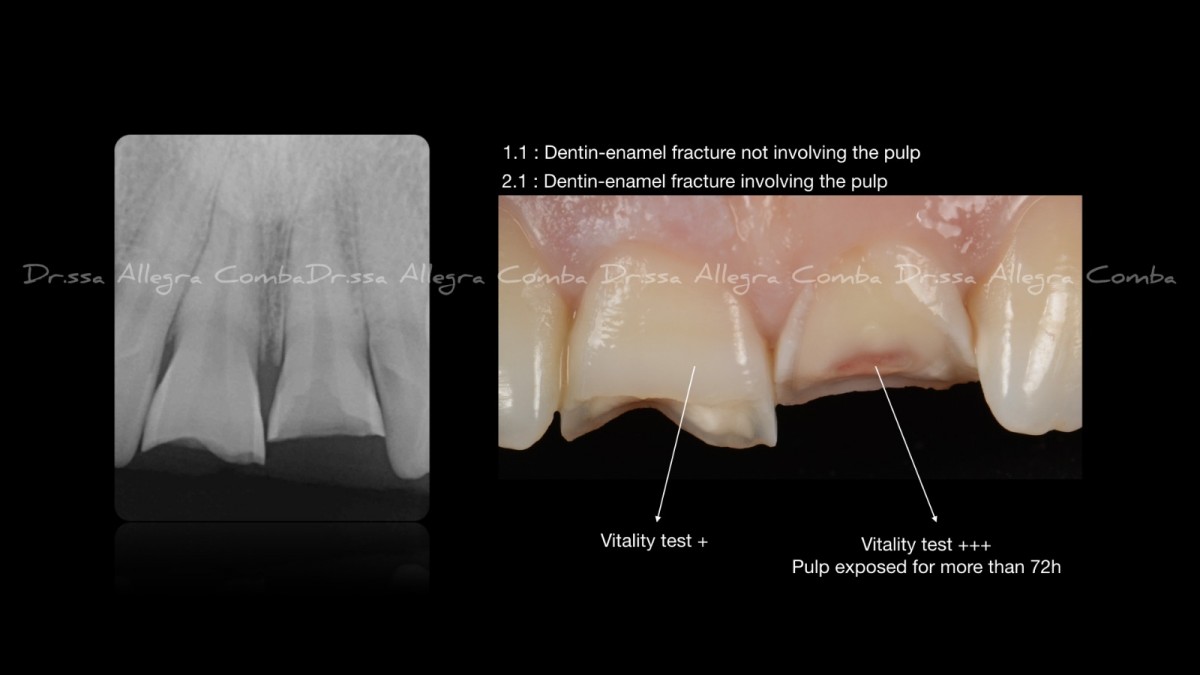
The general medical history was negative. The oral examination detected a coronal fracture without pulp involvement of 1.1 and a complicated fracture with pulp exposure for more than 72h on 2.1. The radiographic examination highlighted the absence of root fractures of the elements involved in the trauma and did not detect the presence of carious lesions on the other dental elements.
A pulp viability test was performed on the elements involved which resulted to be positive on 1.1 and showed sign of irreversible pulpitis on 2.1. After explaining the patient the complications that may arise after a dental trauma, the decision was to continue with the initial photographs, the endodontic treatment of 2.1 and the direct restorative therapy of the fractured elements. (Fig. 1)
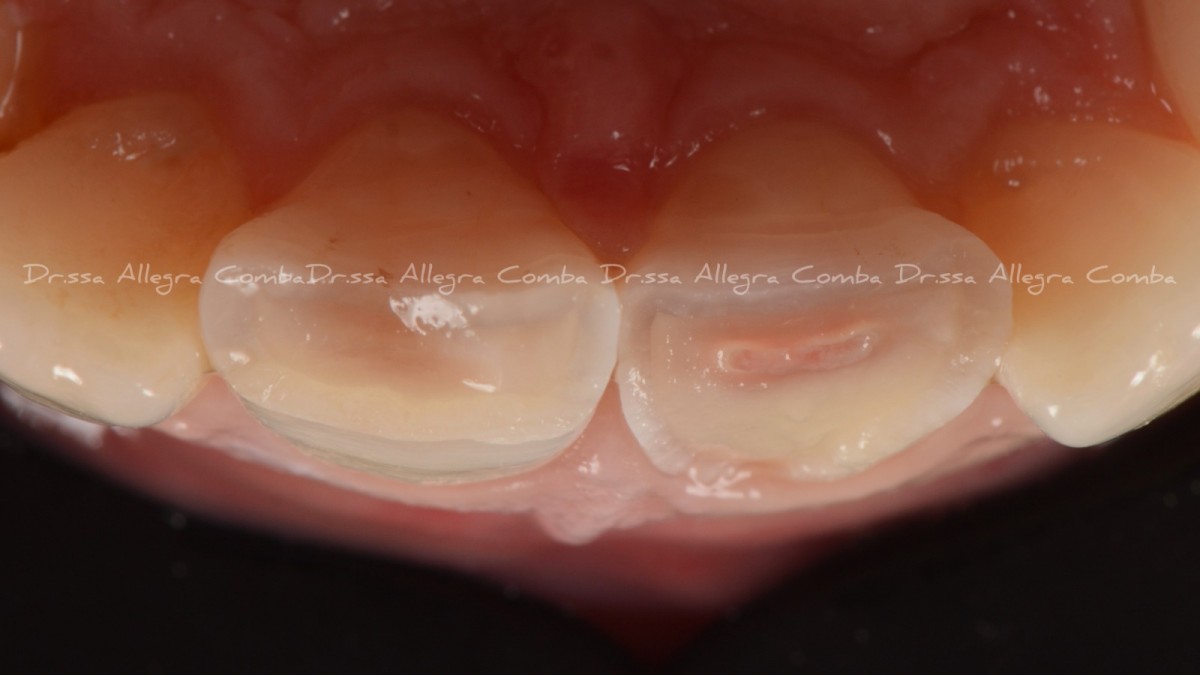
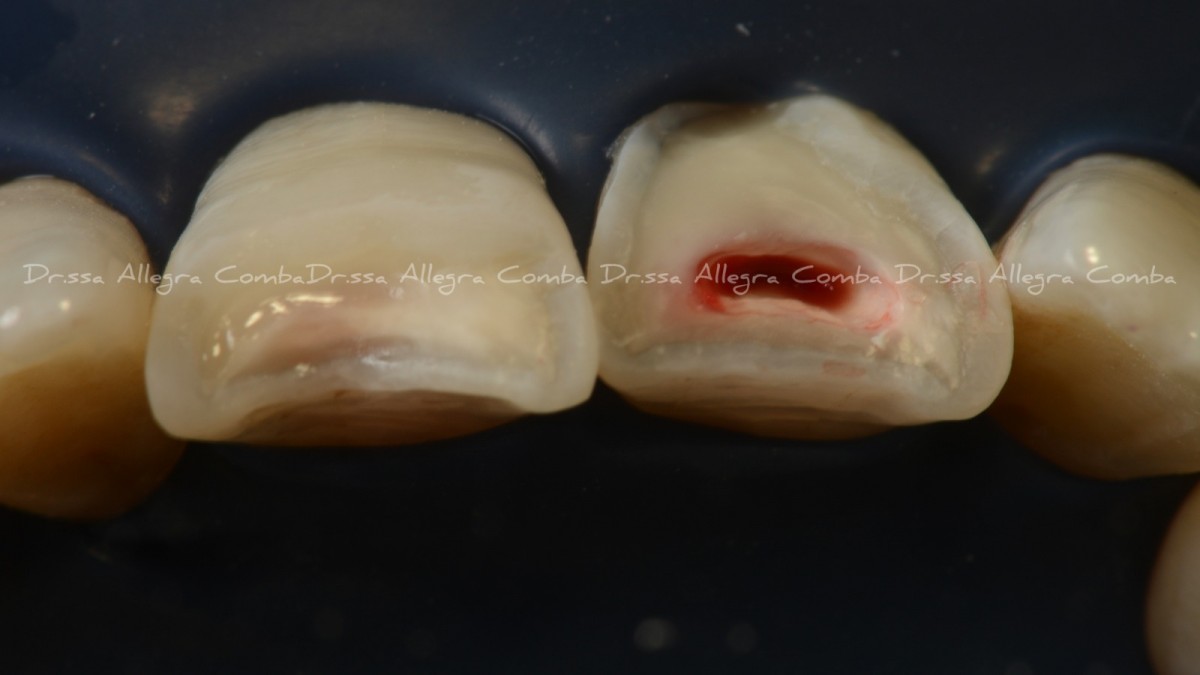
Palatal view of fractured elements showing pulp exposure of 2.1. (Fig. 2)
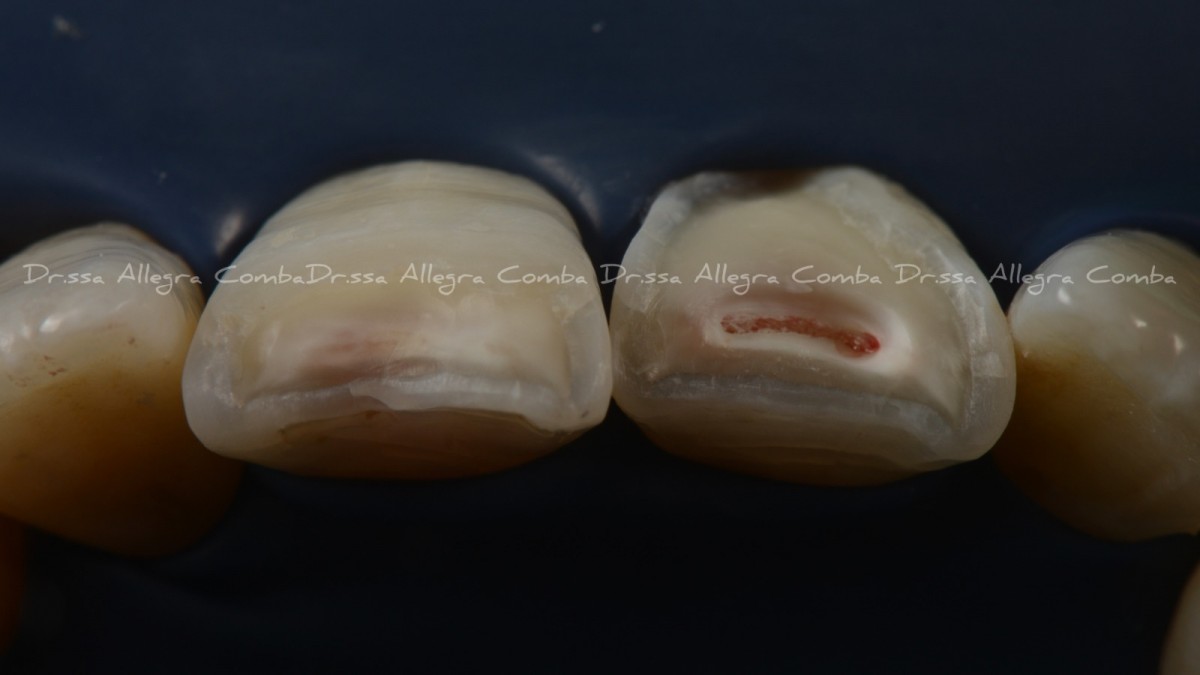
Isolation of the operating field. (Fig 3)
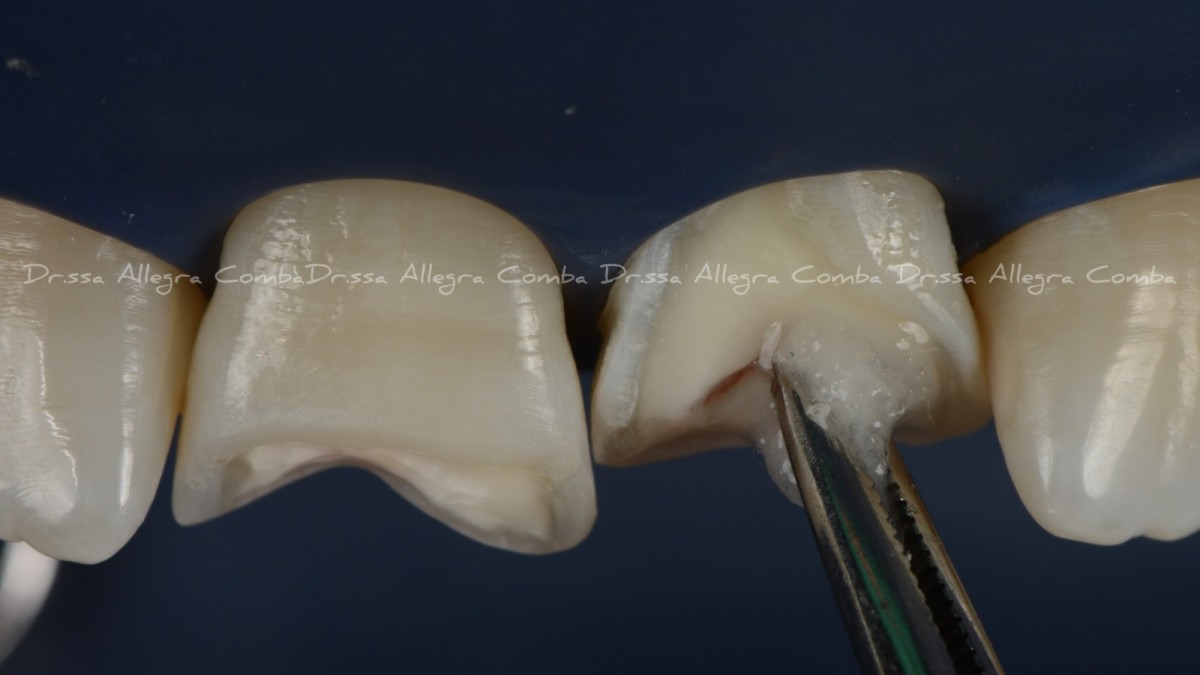
Cavity preparation of 1.1 and initial endodontic treatment on 2.1 (Fig. 4)
Endodontic treatment of 2.1 (Fig. 5)
Adhesive procedures on 1.1 and 2.1 (Fig. 6)
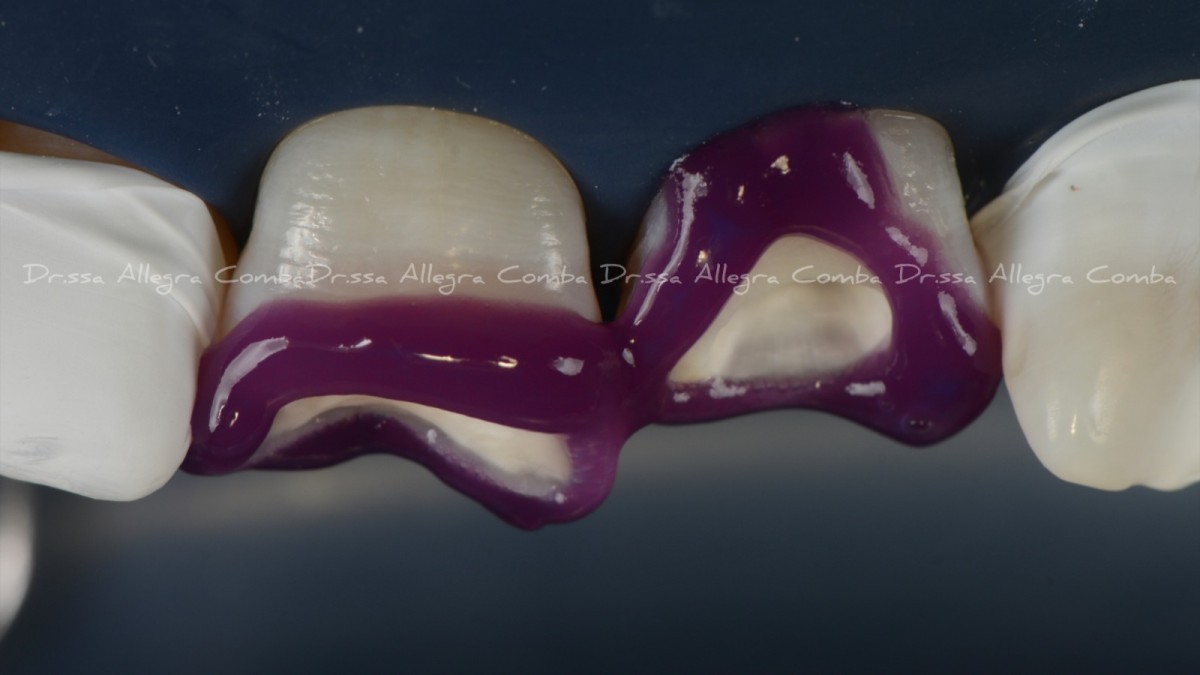
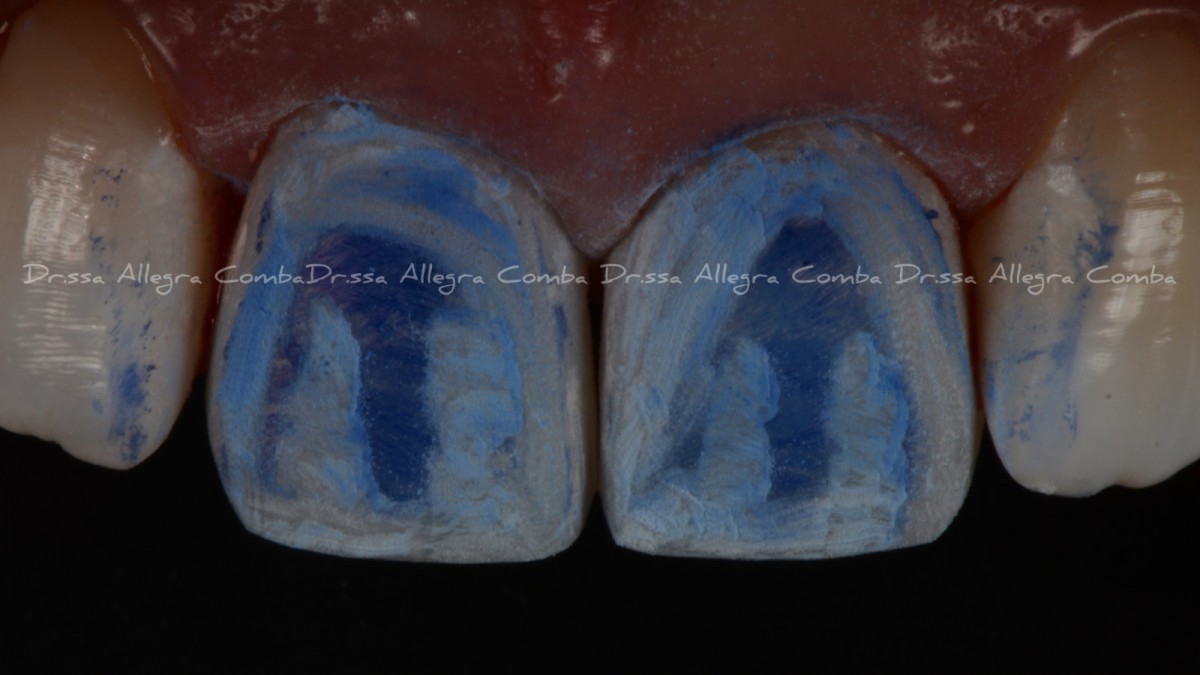
Reconstruction of the palatal wall of 1.1 and 2.1 with the help of a silicone index. (Fig. 7)
Layering of the composite material. (Fig. 8)
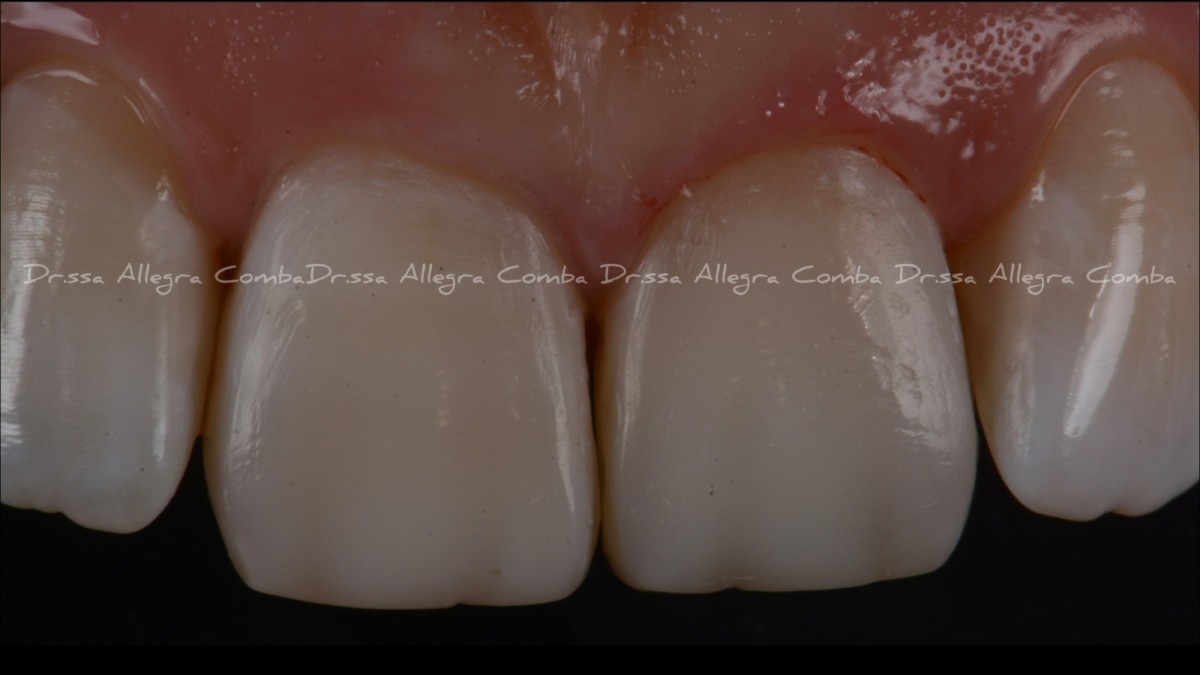
Restorations completed under dental dam isolation during finishing procedures (Fig. 9)
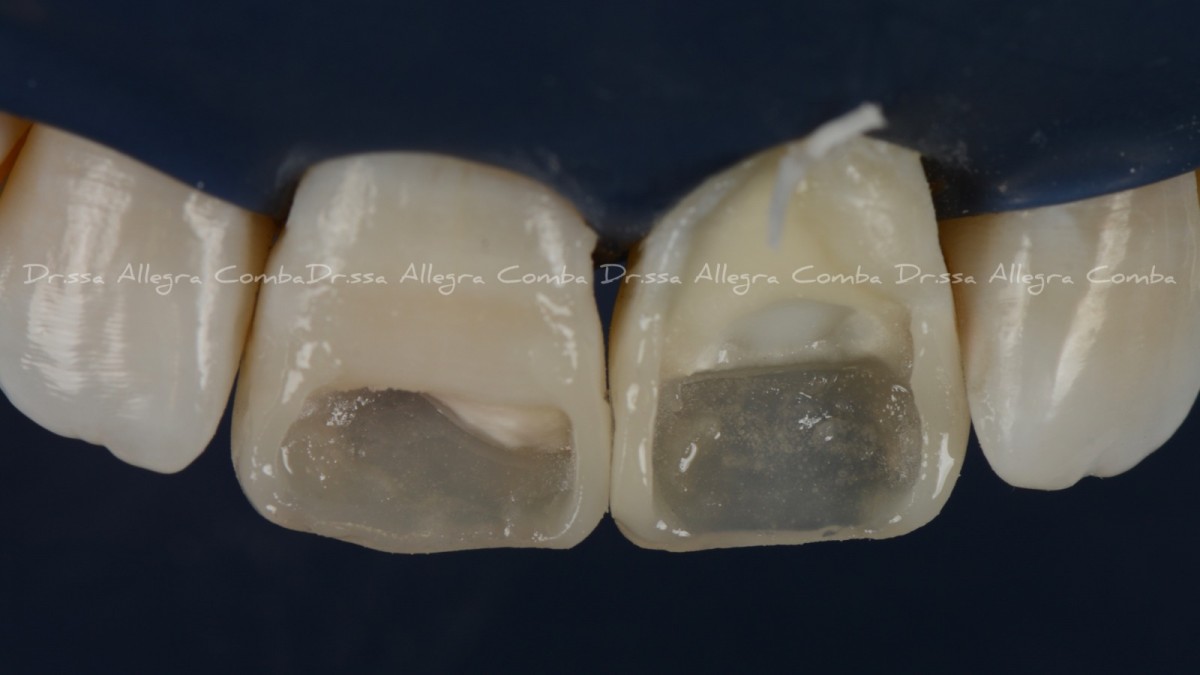
Color check after 2 months from the execution of the restorations (Fig. 10)
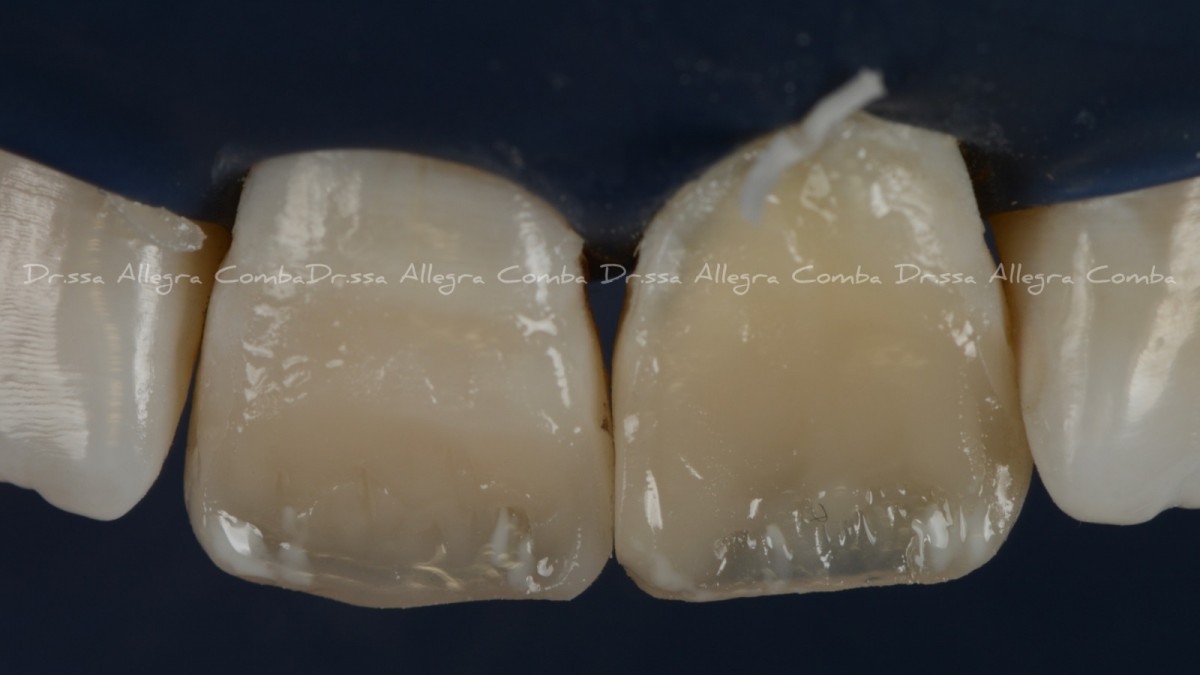
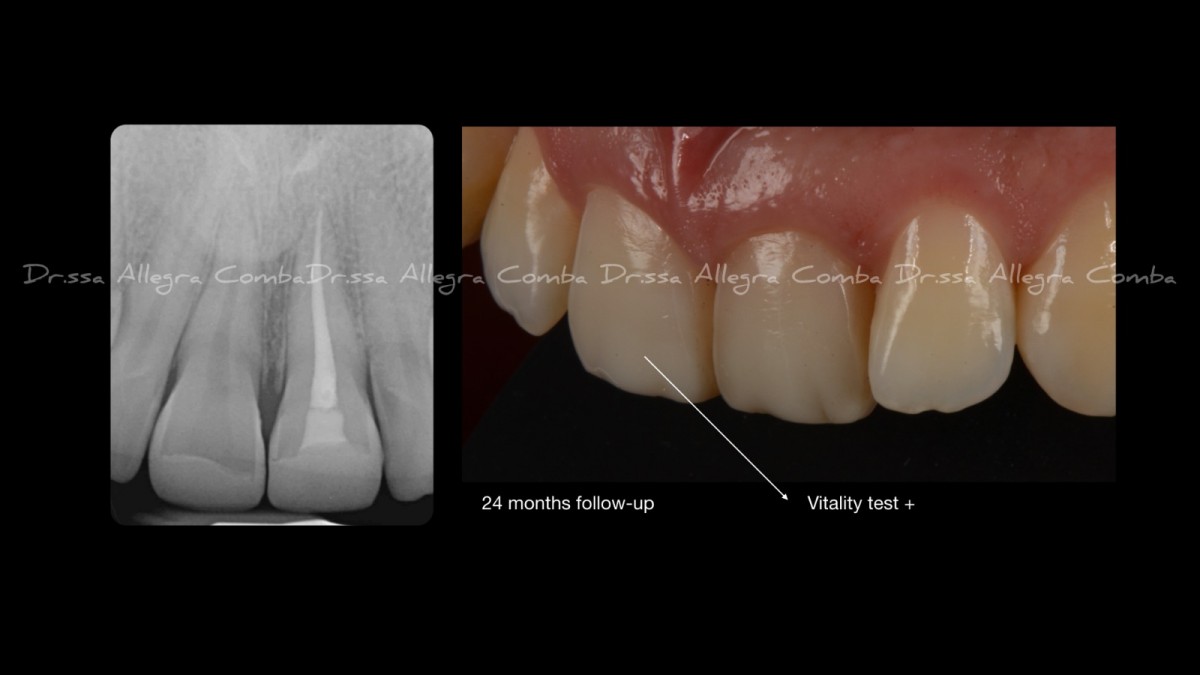
Two Year follow-up (Fig. 11)
 Related articles
Related articles
Restorative dentistry 03 November 2025
The worldwide interest of both dentists and patients in esthetic dentistry has affected decision-making in dental practice.
Restorative dentistry 12 September 2025
Traumatic tooth injuries involve function and aesthetics and cause damage that range from minimal enamel loss to complex fractures involving the pulp tissue and even loss of the tooth crown.
The purpose of restorative dentistry is to restore and maintain health and functional comfort of the natural dentition combined with satisfactory aesthetic appearance.
Oral surgery 15 July 2025
The influence of patients' decisions on treatment planning in restorative dentistry
As part of treatment planning, options are presented to patients by dentists. An informal discussion takes place involving a cost-benefit analysis and a treatment plan is agreed.
Restorative dentistry 01 July 2025
Advances in CAD/CAM Technology for Chairside Restorative Dentistry: A Workflow Analysis
Chairside CAD/CAM technology has revolutionized restorative dentistry, offering streamlined workflows and improved patient outcomes.
 Read more
Read more
Much like EMTs rushing to the scene after an accident, stem cells hurry to the site of a skull fracture to start mending the damage. A new finding has uncovered the signaling mechanism that triggers...
Products 05 November 2025
SimplyTest has launched a groundbreaking saliva-based test to detect high-risk strains of oral human papillomavirus (HPV), a major cause of oropharyngeal cancers.
News 05 November 2025
Perimetrics, Inc., a dental technology company pioneering quantitative diagnostics, announced today that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted clearance for the InnerView...
News 05 November 2025
On October 15, open enrollment for Medicare began nationwide. Hundreds of thousands of seniors in New Jersey will once again face the challenge of finding the right Medicare coverage, including the...
Digital Dentistry 04 November 2025
Digitalisation is an expanding field in dentistry and implementation of digital teaching methods in dental education is an essential part of modern education.