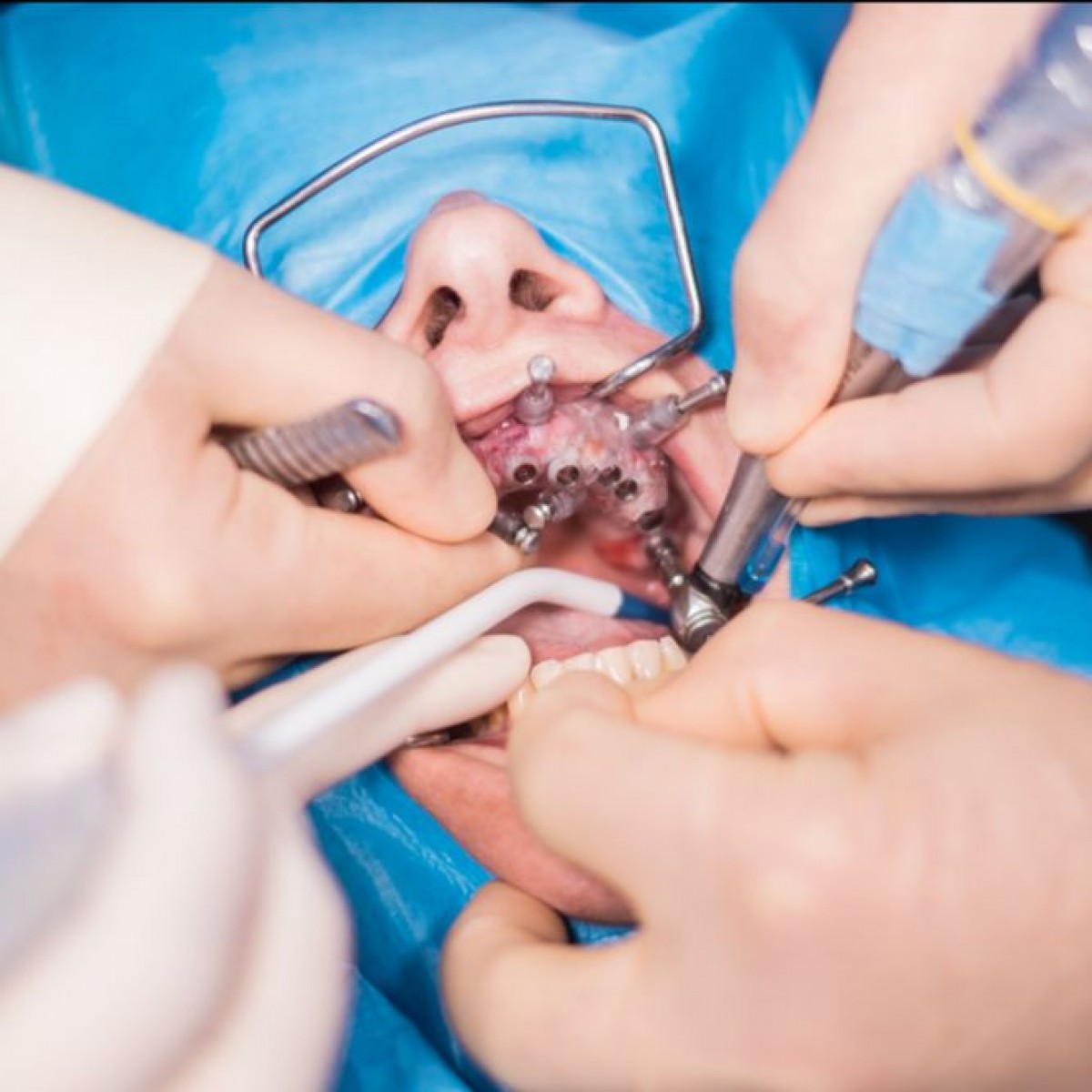
A systematic review on the accuracy and the clinical outcome of computer-guided template-based implant dentistry
Introduction: The aim of this systematic review was to analyze the dental literature regarding accuracy and clinical application in computer-guided template-based implant dentistry.
Materials and methods: An electronic literature search complemented by manual searching was performed to gather data on accuracy and surgical, biological and prosthetic complications in connection with computer-guided implant treatment. For the assessment of accuracy meta-regression analysis was performed. Complication rates are descriptively summarized.
Results: From 3120 titles after the literature search, eight articles met the inclusion criteria regarding accuracy and 10 regarding the clinical performance. Meta-regression analysis revealed a mean deviation at the entry point of 1.07 mm (95% CI: 0.76–1.22 mm) and at the apex of 1.63 mm (95% CI: 1.26–2 mm). No significant differences between the studies were found regarding method of template production or template support and stabilization. Early surgical complications occurred in 9.1%, early prosthetic complications in 18.8% and late prosthetic complications in 12% of the cases. Implant survival rates of 91–100% after an observation time of 12–60 months are reported in six clinical studies with 537 implants mainly restored immediately after flapless implantation procedures.
Conclusion: Computer-guided template-based implant placement showed high implant survival rates ranging from 91% to 100%. However, a considerable number of technique-related perioperative complications were observed. Preclinical and clinical studies indicated a reasonable mean accuracy with relatively high maximum deviations. Future research should be directed to increase the number of clinical studies with longer observation periods and to improve the systems in terms of perioperative handling, accuracy and prosthetic complications.
Authors: David Schneider, Pascal Marquardt, Marcel Zwahlen, Ronald E. Jung
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com
 Related articles
Related articles
Orthodontics 12 November 2025
Effectiveness of dental monitoring system in orthodontics: A systematic review
Dental monitoring (DM) constitutes a recent technological advance for the remote monitoring of patients undergoing an orthodontic therapy.
A systematic review was conducted to examine the evidence for the effectiveness and safety of corticotomy-facilitated orthodontics.
Periodontology 10 September 2025
To update the findings of a systematic review from the year 2016 on the evidence for the accuracy and potential benefits of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) in periodontal diagnostics.
Orthodontics 08 September 2025
Records needed for orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning: a systematic review
Traditionally, dental models, facial and intra-oral photographs and a set of two-dimensional radiographs are used for orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning.
Oral Hygiene & Prevention 20 August 2025
Personal oral hygiene and dental caries: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials
To conduct a systematic review of randomised trials assessing the association between personal oral hygiene and dental caries in the absence of the confounding effects of fluoride.
 Read more
Read more
Digital Dentistry 19 November 2025
Increasing awareness of tooth fracture, both complete and incomplete, as a significant disease entity has led to improved diagnostic techniques.
Editorials 19 November 2025
As Ellen Simmons-Shamrell of the Class of 1977 wrote her annual check for the Michael D. Scotti, DMD Endowed Scholarship—established in memory of her late classmate—she reflected on how different...
Products 19 November 2025
Smartee Denti-Technology has unveiled the Smartee Digital Orthodontic Technology Exhibition Hall, a 1,200-square-meter space dedicated to showcasing the company’s innovations in clear aligner...
News 19 November 2025
Coupa, the global leader in AI-powered spend management, today announced a new collaboration with Specialized Dental Partners, a premier dental support organization (DSO) dedicated to enabling its...
News 19 November 2025
Breakthrough T1D has been selected as a 2025 Health Access Hero Award grant recipient by Sun Life U.S. and DentaQuest.