Is intraoral scanning accurate to evaluate dental implant position?
Purpose
The position of dental implants is generally verified through imaging exams, even though its use exposes patients to radiation. Intraoral scanning (IOS) may be a suitable alternative to using radiographic imaging to verify implant position. Using polyurethane jaw models, the purpose of this in-vitro study was to measure and compare implant positions determined by IOS and cone-bean computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods
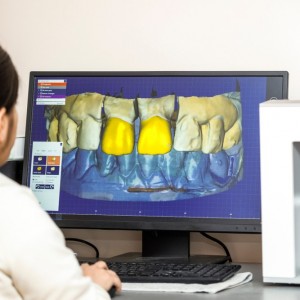
The research team installed 120 implants in 30 edentulous polyurethane jaws, four dental implants in each prototype. Four scanbodies were attached to the implants, and a scanning of each mandible was acquired using an intraoral scanner (CS 3600). All prototypes were also submitted to CBCT. Then, the 3D scan files in STL (Standard Tessellation Language) format were superimposed on the DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) images of the tomographic mandibles.
Researchers evaluated the accuracy of IOS by the metric analyses of deviations between the position of the implants projected by the IOS versus the detected tomographically, in which CBCT served as the gold standard, using a free software for digital planning (Bluesky 4 - Grayslake, IL, USA). The following measures were analyzed: radial deviations at the shoulder (Xc) and at the apex of the implants (Xa), height deviation (Xh) and axial deviation.
Bland-Altman and a paired t-test were applied to verify the reproducibility between measurements and a t-test for a mean was applied to compare the measurements with zero value.
Results
The results showed Xc and Xa deviation means of 0.14 ± 0.09 mm and 0.12 ± 0.12 mm, respectively. The Xh mean was 0.2 ± 0.12 mm and the axial deviation mean was 0.71° ± 0.66°. T-test showed a statistically significant difference when the 4 means were compared to zero value, represented by the CBCT (P < .0001).
Conclusions
There was a statistically significant difference in the scanned measures compared to CBCT as the standard, but the differences may not be clinically significant. The IOS utilization to evaluate the position of dental implants is a radiation-free and reproducible method, with the advantage of not generating metal artifacts. Further clinical studies are needed to validate this new method of postoperative evaluation.
Isabela Polesi Bergamaschi, Karine Laura Cortellazzi, Alexander Tadeu Sverzut. "Is Intraoral Scanning Accurate to Evaluate Dental Implant Position? An In-Vitro Study." 2 December 2022. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2022.11.018
 Related articles
Related articles
News 23 October 2025
The global dental implants market is projected to grow from USD 5.45 billion in 2024 to USD 15.41 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 9.95% from.
Editorials 07 August 2025
Researchers are developing ‘smart’ implants that would provide a more natural feel while chewing or talking
Implantology 25 July 2025
Background: Cytokine–microbiology–virology monitoring after implant placement may help to develop profiles of variables that can help to explain interaction between the immune system and alveolar...
Prosthodontics 30 June 2025
Prosthodontic rehabilitation in the maxillary area using zirconia dental implants: a case report.
Purpose: Zirconia (ZrO2) is a ceramic material with adequate mechanical properties for manufacturing of medical devices. Zirconia stabilized with Y2O3 has the best properties for these applications.
Digital Dentistry 02 June 2025
A novel workflow for computer guided implant surgery matching digital dental casts and CBCT scan
Nowadays computer-guided “flap-less” surgery for implant placement using stereolithographic tem-plates is gaining popularity among clinicians and patients.
 Read more
Read more
Much like EMTs rushing to the scene after an accident, stem cells hurry to the site of a skull fracture to start mending the damage. A new finding has uncovered the signaling mechanism that triggers...
Products 05 November 2025
SimplyTest has launched a groundbreaking saliva-based test to detect high-risk strains of oral human papillomavirus (HPV), a major cause of oropharyngeal cancers.
News 05 November 2025
Perimetrics, Inc., a dental technology company pioneering quantitative diagnostics, announced today that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted clearance for the InnerView...
News 05 November 2025
On October 15, open enrollment for Medicare began nationwide. Hundreds of thousands of seniors in New Jersey will once again face the challenge of finding the right Medicare coverage, including the...
Digital Dentistry 04 November 2025
Digitalisation is an expanding field in dentistry and implementation of digital teaching methods in dental education is an essential part of modern education.