
A large radiopaque lesion in the posterior mandible: a clinical case
Authors: G. Lodi, A. Pispero, E.M. Varoni, S. Decani, D. Costa
Giovanni Lodi
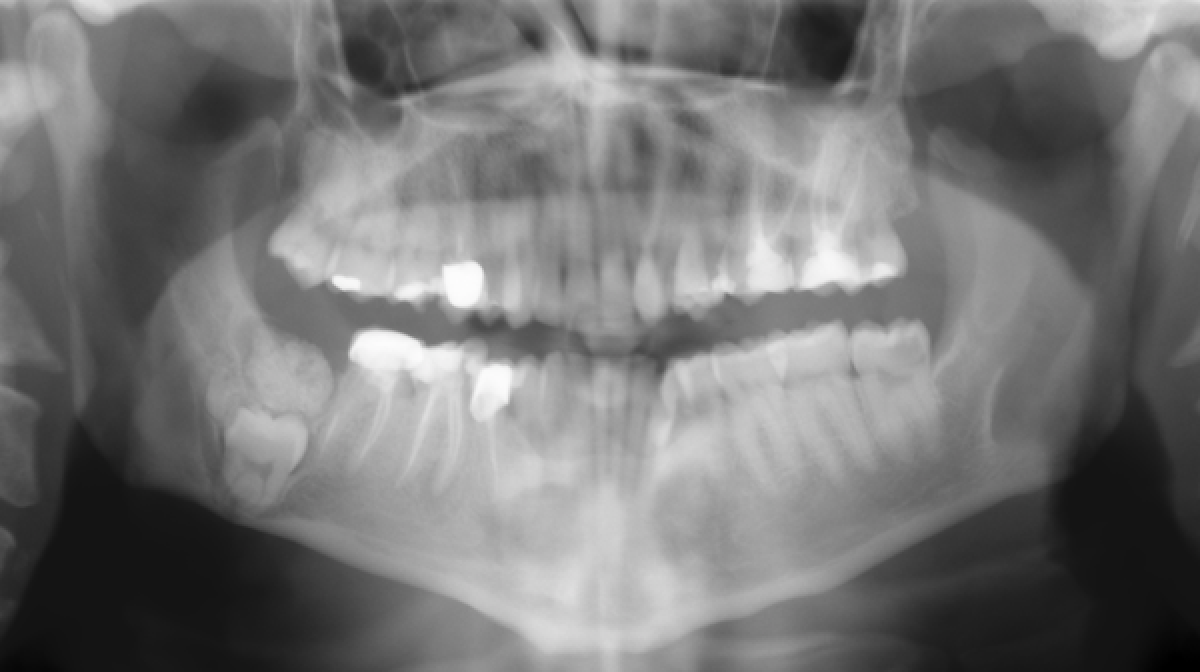
A 32-year-old male patient is sent, for a right mandibular injury, by his own doctor to the Oral Pathology and Surgery Service of the Operative Unit of Odontostomatology II of ASST Santi Paolo e Carlo of Milan. The medical history is negative for any type of pathology, facial deformations are not appreciated, no symptoms are reported and mucosal lesions are not appreciated intraorally. The panoramic radiography (fig. 1) and computed tomography (fig. 2), held by the patient at the time of the first visit, show a large irregular radiopacity that dominates the element 4.8. The lower right third molar is in total bone inclusion with the middle and apical third of the roots in close contact with the lower vascular-nerve bundle. The mandibular canal is strongly compressed and deviated apically in correspondence with the retained element, passing between the two mesial roots. The radiopaque mass, which dominates the crown, extends superiorly for about 1 cm up to the coronal margin of the bone cortex and distally occupies the space between the crown of the third molar and the cortex of the mandibular canal. Around the lesion there is a thin radiolucent area that creates a clear separation from the surrounding bone tissue. The patient has no other radiographic examinations prior to the visit that can allow to appreciate over time the degree of growth of the lesion.
In the case described, the clinical and radiographic signs suggest a diagnosis of a complex odontoma. The mass of the lesion prevented the normal eruption of the third molar. Although the clinical suspicion is strong, it is necessary to consider the possibility of comparing with other pathologies such as osteomyelitis sclerosing, periapical dysplasia of the cement, ossifying fibroid and cementusblastoma. In agreement with the patient, it was decided to carry out an incisional biopsy (fig. 3).
An envelope flap with a disto-vestibular discharge incision to the crown of the element 4.7 is performed and following the detachment of a mucoperiosteal flap, a lesion is taken to send the necessary material to the anatomical pathologist .
The consistency of the lesion is hard, comparable to that of the dentine of a healthy dental element. The histological examination confirms the clinical diagnosis of a complex odontoma. This type of lesion is classified as a benign tumor of odontogenic origin. It is considered to be a dental hamartoma made up of mineralized tissues that derive from odontogenic epithelium and ectomesenchima; enamel, dentin and cement are present and well developed but follow a macroscopically disordered pattern without leading to the formation of defined dental elements.
The lesion has characteristics of benignity and has no tendency to recurrence. In the case described there are no absolute indications for the treatment of the lesion but considering the size and the relationship with the distal root surface of the element 4.7 it is decided to remove the lesion leaving the third molar in place. The extraction of wisdom tooth is not a justified intervention, the invasiveness and the risks of alteration of the nerve conduction are propensity for a conservative attitude. The prediction is that the closure by primary intention and the amount of vestibular and lingual bone cortex will allow a good wound healing and, before the completion of the remineralization phase, a natural extrusion of the tooth.
The treatment plan is discussed with the patient, who gives consent for the intervention. The flap for the removal of the lesion is similar to that performed during the incisional biopsy. With the elevation of a mucoperiosteal flap and a modest vestibular ostectomy it is possible to access the entire lesion. In consideration of the hard consistency of the lesion, separation lines are made by means of slot cutters; the fragments obtained are thus removed without having to sacrifice additional bone tissue. The sizing is carried out by means of 4/0 resorbable polyfilament. The new histological examination performed on all the lesion confirms the first diagnosis. After 6 months it is possible to appreciate in the intraoral radiography (fig. 4) how, in accordance with the forecasts formulated, the cortex has completely reformed above the included element and how it appears in position more coronal than before surgery.
 Related articles
Related articles
Oral pathology 26 September 2023
The habit of smoking cigarettes has been associated with health problems for some time now, especially with regards to the link with diseases related to the...
Author: M. Berardini
A male patient, aged 60, underwent a visit complaining about the presence of a whitish and detected neoformation located in the right anterior abdomen of the tongue...
Oral pathology 06 August 2022
Co-authors: F. Scotti, M. Mandaglio, S. Decani, E. Baruzzi, L. Moneghini
An 85-year-old patient comes to our attention complaining of the presence of swelling of the right half-left, present for some time unspecified and gradually increased. The patient's medical history...
Oral pathology 01 August 2022
Author: Riccardo Mauro Bonacina
Patient AB, a 46-year-old male, comes to our observation complaining of an increase in volume at the palatal level for about a month. The systemic anamnesis...
Oral pathology 13 June 2022
The correlation between the quality of oral hygiene and oral HPV infection in adults
Aim of the study was to detect a possible association between the objectively determined quality of oral hygiene and the presence of oral HPV. MATERIALS AND METHODS In this perspective...
 Read more
Read more
Digital Dentistry 18 April 2024
The Columbia University College of Dental Medicine (CDM) and the Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science have received approval from the New York State Department of Education to...
Dr. Richard Eidelson, DDS, MAGD, a nationally recognized leader in cosmetic dentistry, is thrilled to announce the opening of his second dental practice, Premier Dentist Philadelphia, located in the...
DDS Lab (DDS), one of the largest full-service dental laboratories in the world, today announced the commencement of operations out of its new state-of-the-art, full-service dental laboratory based...
The global electric toothbrush market size is estimated to grow by USD 2780 million from 2023 to 2027, according to Technavio. The market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of over 8.24% during the...












d5.jpg)


